Andromedasbitch-blog - Spacey

More Posts from Andromedasbitch-blog and Others

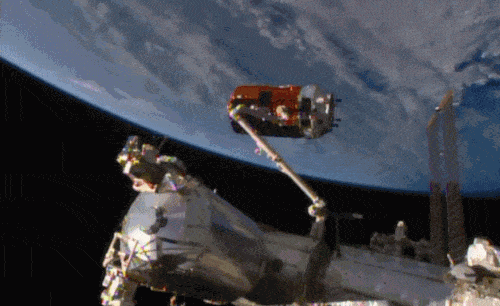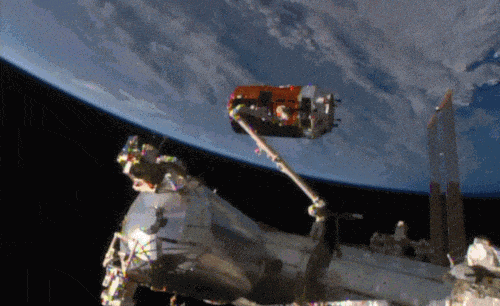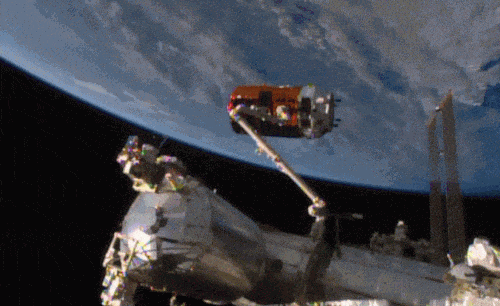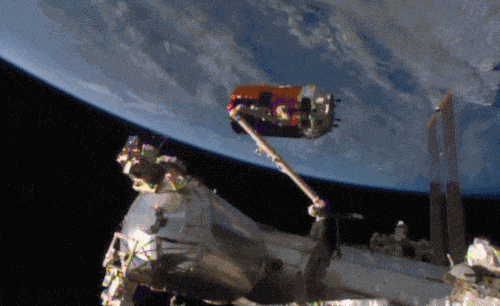
Aboard the International Space Station this morning, Astronaut Kimiya Yui of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) successfully captured JAXA’s Kounotori 5 H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV-5) at 6:28 a.m. EDT.
Yui commanded the station’s robotic arm, Canadarm2, to reach out and grapple the HTV-5, while NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren provided assistance and Scott Kelly monitored HTV-5 systems. The HTV-5 launched aboard an H-IIB rocket at 7:50 a.m. Wednesday, Aug. 19, from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan. Since then, the spacecraft has performed a series of engine burns to fine-tune its course for arrival at the station.
The HTV-5 is delivering more than 8,000 pounds of equipment, supplies and experiments in a pressurized cargo compartment. The unpressurized compartment will deliver the 1,400-pound CALorimetric Electron Telescope (CALET) investigation, an astrophysics mission that will search for signatures of dark matter and provide the highest energy direct measurements of the cosmic ray electron spectrum.
Below is a breathtaking image shared by Astronaut Scott Kelly of the HTV-5 and Canadarm2, which reached out and grappled the cargo spacecraft.


631 Exposures Blended - Cloverdale, CA
js

Here’s something for you to start the week off with a bang. This is a computer simulation of a supernova event, the moments when a massive star collapses in on itself to evolve into a neutron star. The violent and knobbly shock wave from the collapse expands out in a fraction of a second, with the coldest gas in the model colored blue and the hottest colored red. Ejected stellar material moves away from the core at speeds that can reach almost 19,000 miles per second.
The simulation was created in 2012 by the Simulating eXtreme Spacetimes (SXS) Project. Now, direct observations of a supernova called 1987A using NASA’s Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array has confirmed a detail found in the model–that the collapse leads to a lopsided ejection of debris in one direction and the stellar core into another.
Read more from Caltech about how models predicted that perfectly spherical star cores evolve into asymmetric blobs with plumes of broiling hot gasses powered by neutrino emissions.

(Hubble Space Telescope captured supernova 1987A with a bright ring of material ejected from the dying star before it detonated. The ring is being lit up by the explosion’s shock wave.Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA.)
Keep reading













Steampunk Art
-
 javatunes liked this · 6 months ago
javatunes liked this · 6 months ago -
 esmeraldacasablanca liked this · 4 years ago
esmeraldacasablanca liked this · 4 years ago -
 modern-serendipity liked this · 6 years ago
modern-serendipity liked this · 6 years ago -
 fillehefker reblogged this · 6 years ago
fillehefker reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 fillehefker liked this · 6 years ago
fillehefker liked this · 6 years ago -
 luzdeluna76 liked this · 6 years ago
luzdeluna76 liked this · 6 years ago -
 fvckingfvnkydjentleman6667789 reblogged this · 6 years ago
fvckingfvnkydjentleman6667789 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 killernun liked this · 6 years ago
killernun liked this · 6 years ago -
 deathonthecheap reblogged this · 6 years ago
deathonthecheap reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 deathonthecheap reblogged this · 6 years ago
deathonthecheap reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 tulaytorun reblogged this · 6 years ago
tulaytorun reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 suckitttbitch liked this · 6 years ago
suckitttbitch liked this · 6 years ago -
 vintagecarmen liked this · 6 years ago
vintagecarmen liked this · 6 years ago -
 macellaninpusulasi reblogged this · 6 years ago
macellaninpusulasi reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 macellaninpusulasi liked this · 6 years ago
macellaninpusulasi liked this · 6 years ago -
 christine-destler-222 liked this · 6 years ago
christine-destler-222 liked this · 6 years ago -
 iamlancevance reblogged this · 6 years ago
iamlancevance reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 iamlancevance liked this · 6 years ago
iamlancevance liked this · 6 years ago -
 someone-that-you-dont-know-blog1 liked this · 6 years ago
someone-that-you-dont-know-blog1 liked this · 6 years ago -
 metamorphosed-girl reblogged this · 6 years ago
metamorphosed-girl reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 jossrandalluniverse liked this · 7 years ago
jossrandalluniverse liked this · 7 years ago -
 doneboy liked this · 7 years ago
doneboy liked this · 7 years ago -
 redesigningjewel reblogged this · 7 years ago
redesigningjewel reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 dearyouthisisme liked this · 7 years ago
dearyouthisisme liked this · 7 years ago -
 allaboutfashionnn reblogged this · 7 years ago
allaboutfashionnn reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 tresfoufou liked this · 7 years ago
tresfoufou liked this · 7 years ago -
 sitwithmeinsilence liked this · 7 years ago
sitwithmeinsilence liked this · 7 years ago -
 little-so-littlest reblogged this · 7 years ago
little-so-littlest reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 dxnxc liked this · 7 years ago
dxnxc liked this · 7 years ago -
 sleaze-cheese-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
sleaze-cheese-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 eyelahda liked this · 7 years ago
eyelahda liked this · 7 years ago -
 manifestdestinyyyy3 liked this · 7 years ago
manifestdestinyyyy3 liked this · 7 years ago
