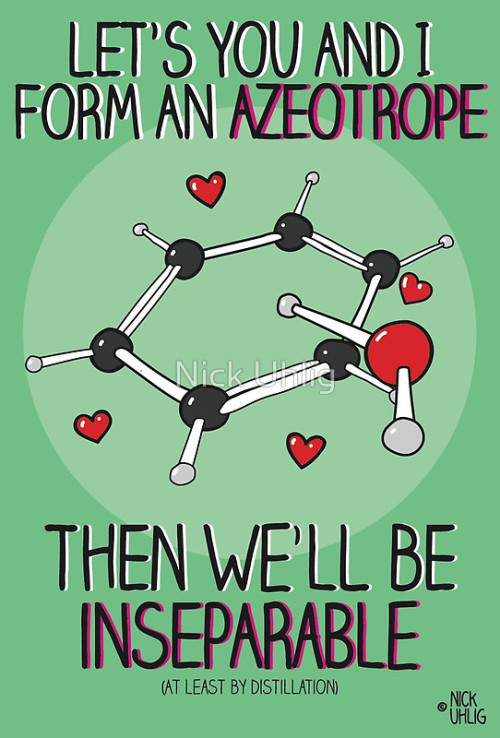
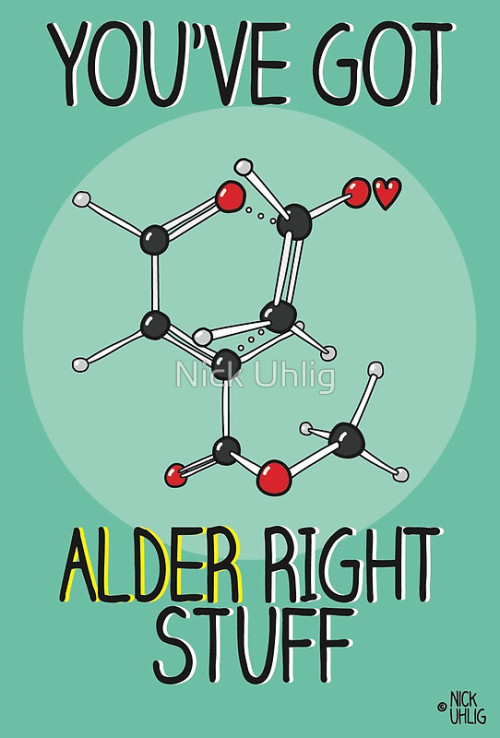
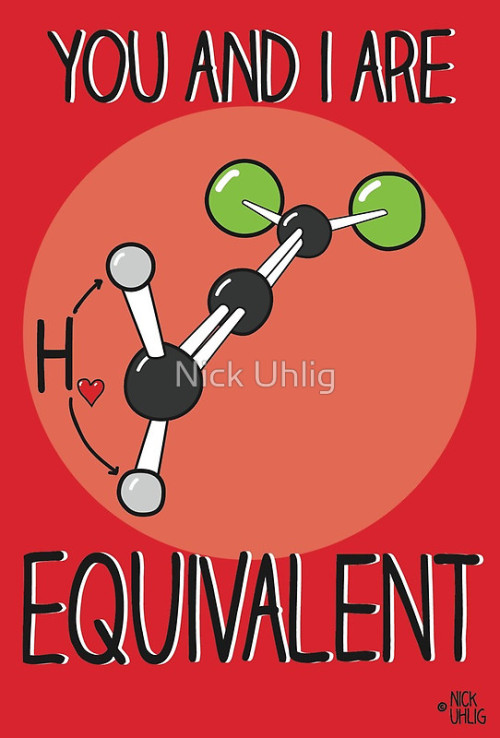
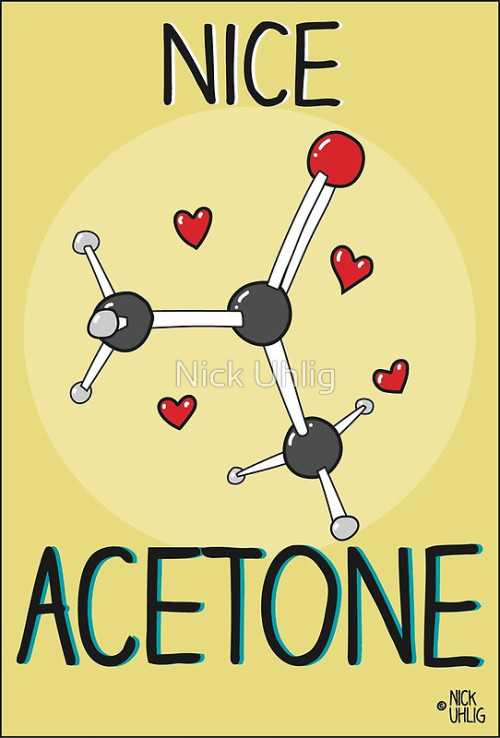
I Want To Play An Rpg Where These Are My Four Stats

i want to play an rpg where these are my four stats
More Posts from In-pursuit-of-knowledge-blog and Others
What we all need to understand about AI in a nutshell:
There’s an algorithm that can reliably predict, from aggregate facebook posts, the onset of a manic episode in a person suffering from bipolar disorder – more reliably even, than a trained psychotherapist, who only has access to the information a patient provides them in therapy sessions.
“Won’t technology like that help people with bipolar disorder?”
Theoretically, it could. But this algorithm wasn’t designed to help people with bipolar disorder.
This algorithm was designed to sell plane tickets to Las Vegas.
[source]
Other dragons, mostly! Side-facing eyes offer a wider range of vision with which to watch the skies. Being caught off guard would most certainly not be good. Though in more recent times I’m sure it’s helped many a chromatic spot smaller would-be hunters. Metallics are less aggressive, but still need to defend themselves from territorial chromatics and the occaisional roc (though a wary dragon typically avoids nesting grounds). Besides, it’s fairly likely the side-facing eyes emerged in all dragons’ common ancestor before they diverged into color-categories.
A sudden, terrifying thought
When you see an animal with its eyes set to the front, like wolves, or humans, that’s usually a predator animal.

If you see an animal with its eyes set farther back, though—to the side—that animal is prey.
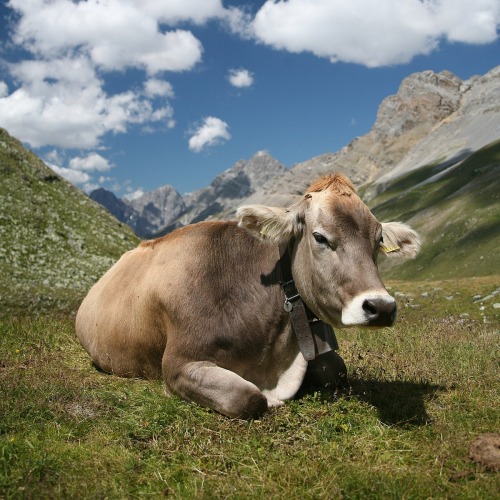

Now look at this dragon.

See those eyes?

They’re to the SIDE.

This raises an interesting—and terrifying—question.

What in the name of Lovecraft led evolution to consider DRAGONS…
As PREY?
I remembering being at the Monterey aquarium a few times and I recall it's repurposed from a cannery. Does the aquarium have a book of the building's history? I'd love to buy it and read up on the local history.
It’s true! The Aquarium stands on the site of the former Hovden and Sea Pride canneries. Here’s a brief history of the Aquarium. For a longer read, this book delves into the history of Monterey Bay, including the Aquarium!
The canneries are an important part of Monterey Bay history and you can find tributes to them throughout the Aquarium, including the smokestacks on the roof and the boiler exhibit in the atrium.

The smokestacks! They’re now sealed and primarily used as a perch by peregrine falcons searching for prey.

Restored boilers—fish would be cooked in these as part of the canning process.

Old Hovden Cannery building as seen from Hopkins Beach in the late 60′s. (📷: Mark Silberstein)

Same spot today! The Aquarium building incorporates some of the original structures and style of the canneries. You can read more about the architectural design of the Aquarium here.
“There have been too great a tendency to call anyone ‘impractical’ who dare to look too far in advance of the well beaten path. What is being ‘practical’? One must have imagination in order to be truly practical.
"I know scientific men who have spent years in attempts to do some obviously impossible thing and who yet have been called 'practical’ because if they succeeded in accomplishing that for which they were striving they would make much money.
"The same man would have jeered not long ago at the suggestion that we on the earth might receive signals from Mars. Big things are not 'practical’. They are wonderful. Many scientific minds, like many minds which are not scientific, shy at anything which is wonderful. Yet the simplest things in nature are wonderful almost beyond the limits of the human imagination.
"Men ignorant of the way in which plants grow would jeer at a farmer if suddenly they should be so placed that they saw him planting seeds. They would declare him an impractical creature because the fruition of his efforts if at all possible of realization is so remote. They want immediate results.
"The sending to and reception from Mars of signals would be an achievement by no means as wonderful as Nature’s simple process of making seeds grow in the ground.”
–Nikola Tesla
“Marconi Credits Mystery Flash To Far Planet”New York Sun, January 25, 1920.

Two Steps Forward in the Search for Life on Mars
We haven’t found aliens but we are a little further along in our search for life on Mars thanks to two recent discoveries from our Curiosity Rover.

We detected organic molecules at the harsh surface of Mars! And what’s important about this is we now have a lot more certainty that there’s organic molecules preserved at the surface of Mars. We didn’t know that before.
One of the discoveries is we found organic molecules just beneath the surface of Mars in 3 billion-year-old sedimentary rocks.

Second, we’ve found seasonal variations in methane levels in the atmosphere over 3 Mars years (nearly 6 Earth years). These two discoveries increase the chances that the record of habitability and potential life has been preserved on the Red Planet despite extremely harsh conditions on the surface.

Both discoveries were made by our chem lab that rides aboard the Curiosity rover on Mars.

Here’s an image from when we installed the SAM lab on the rover. SAM stands for “Sample Analysis at Mars” and SAM did two things on Mars for this discovery.
One - it tested Martian rocks. After the arm selects a sample of pulverized rock, it heats up that sample and sends that gas into the chamber, where the electron stream breaks up the chemicals so they can be analyzed.
What SAM found are fragments of large organic molecules preserved in ancient rocks which we think come from the bottom of an ancient Martian lake. These organic molecules are made up of carbon and hydrogen, and can include other elements like nitrogen and oxygen. That’s a possible indicator of ancient life…although non-biological processes can make organic molecules, too.
The other action SAM did was ‘sniff’ the air.

When it did that, it detected methane in the air. And for the first time, we saw a repeatable pattern of methane in the Martian atmosphere. The methane peaked in the warm, summer months, and then dropped in the cooler, winter months.

On Earth, 90 percent of methane is produced by biology, so we have to consider the possibility that Martian methane could be produced by life under the surface. But it also could be produced by non-biological sources. Right now, we don’t know, so we need to keep studying the Mars!

One of our upcoming Martian missions is the InSight lander. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is a Mars lander designed to give the Red Planet its first thorough checkup since it formed 4.5 billion years ago. It is the first outer space robotic explorer to study in-depth the “inner space” of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core.
Finding methane in the atmosphere and ancient carbon preserved on the surface gives scientists confidence that our Mars 2020 rover and ESA’s (European Space Agency’s) ExoMars rover will find even more organics, both on the surface and in the shallow subsurface.
Read the full release on today’s announcement HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.


Hide the cheese and crackers guys, this raccoon skull is W H I T E!
Seems like heating peroxide to a comfortably warm temperature makes it work twice as fast. This skull now looks like a plastic replica rather than a real skull. Its also 100% complete! My first complete raccoon skull. No cracks, no missing teeth, nothing. Just absolutely perfect.
9 Ocean Facts You Likely Don’t Know, but Should
Earth is a place dominated by water, mainly oceans. It’s also a place our researchers study to understand life. Trillions of gallons of water flow freely across the surface of our blue-green planet. Ocean’s vibrant ecosystems impact our lives in many ways.
In celebration of World Oceans Day, here are a few things you might not know about these complex waterways.
1. Why is the ocean blue?

The way light is absorbed and scattered throughout the ocean determines which colors it takes on. Red, orange, yellow,and green light are absorbed quickly beneath the surface, leaving blue light to be scattered and reflected back. This causes us to see various blue and violet hues.
2. Want a good fishing spot?

Follow the phytoplankton! These small plant-like organisms are the beginning of the food web for most of the ocean. As phytoplankton grow and multiply, they are eaten by zooplankton, small fish and other animals. Larger animals then eat the smaller ones. The fishing industry identifies good spots by using ocean color images to locate areas rich in phytoplankton. Phytoplankton, as revealed by ocean color, frequently show scientists where ocean currents provide nutrients for plant growth.
3. The ocean is many colors.

When we look at the ocean from space, we see many different shades of blue. Using instruments that are more sensitive than the human eye, we can measure carefully the fantastic array of colors of the ocean. Different colors may reveal the presence and amount of phytoplankton, sediments and dissolved organic matter.
4. The ocean can be a dark place.
About 70 percent of the planet is ocean, with an average depth of more than 12,400 feet. Given that light doesn’t penetrate much deeper than 330 feet below the water’s surface (in the clearest water), most of our planet is in a perpetual state of darkness. Although dark, this part of the ocean still supports many forms of life, some of which are fed by sinking phytoplankton.
5. We study all aspects of ocean life.

Instruments on satellites in space, hundreds of kilometers above us, can measure many things about the sea: surface winds, sea surface temperature, water color, wave height, and height of the ocean surface.
6. In a gallon of average sea water, there is about ½ cup of salt.

The amount of salt varies depending on location. The Atlantic Ocean is saltier than the Pacific Ocean, for instance. Most of the salt in the ocean is the same kind of salt we put on our food: sodium chloride.
7. A single drop of sea water is teeming with life.

It will most likely have millions (yes, millions!) of bacteria and viruses, thousands of phytoplankton cells, and even some fish eggs, baby crabs, and small worms.
8. Where does Earth store freshwater?

Just 3.5 percent of Earth’s water is fresh—that is, with few salts in it. You can find Earth’s freshwater in our lakes, rivers, and streams, but don’t forget groundwater and glaciers. Over 68 percent of Earth’s freshwater is locked up in ice and glaciers. And another 30 percent is in groundwater.
9. Phytoplankton are the “lungs of the ocean”.

Just like forests are considered the “lungs of the earth”, phytoplankton is known for providing the same service in the ocean! They consume carbon dioxide, dissolved in the sunlit portion of the ocean, and produce about half of the world’s oxygen.
Want to learn more about how we study the ocean? Follow @NASAEarth on twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

LiDAR continues to aid archaeologists by mapping ancient settlements in the Americas from the sky. Check out Dr. Fishers recent LiDAR research:
-
 cloudhillshaze liked this · 7 months ago
cloudhillshaze liked this · 7 months ago -
 lilydh liked this · 11 months ago
lilydh liked this · 11 months ago -
 d1rpg liked this · 1 year ago
d1rpg liked this · 1 year ago -
 calvinquigley liked this · 1 year ago
calvinquigley liked this · 1 year ago -
 ittakesrain reblogged this · 1 year ago
ittakesrain reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 habakarukotonaku reblogged this · 1 year ago
habakarukotonaku reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 vicaridoo liked this · 1 year ago
vicaridoo liked this · 1 year ago -
 mirnr liked this · 1 year ago
mirnr liked this · 1 year ago -
 heidivanderlee liked this · 1 year ago
heidivanderlee liked this · 1 year ago -
 ipresryoperspen liked this · 1 year ago
ipresryoperspen liked this · 1 year ago -
 bluesfunnysreblogs reblogged this · 1 year ago
bluesfunnysreblogs reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 thereisagirlwhonevergoesoutpt2 reblogged this · 1 year ago
thereisagirlwhonevergoesoutpt2 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 totally-not-an-awkward-okapi liked this · 2 years ago
totally-not-an-awkward-okapi liked this · 2 years ago -
 nocticola liked this · 2 years ago
nocticola liked this · 2 years ago -
 technicolorrelays reblogged this · 2 years ago
technicolorrelays reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 cripple-cat reblogged this · 2 years ago
cripple-cat reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 cripple-cat liked this · 2 years ago
cripple-cat liked this · 2 years ago -
 xdramarenamed liked this · 2 years ago
xdramarenamed liked this · 2 years ago -
 blatantcontradiction reblogged this · 2 years ago
blatantcontradiction reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 foodb4dudez liked this · 2 years ago
foodb4dudez liked this · 2 years ago -
 stairwell-flowers reblogged this · 2 years ago
stairwell-flowers reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 freedomreversalrebel liked this · 3 years ago
freedomreversalrebel liked this · 3 years ago -
 grosse-lisse liked this · 3 years ago
grosse-lisse liked this · 3 years ago -
 argentconflagration liked this · 3 years ago
argentconflagration liked this · 3 years ago -
 mrdarcyaceicon liked this · 3 years ago
mrdarcyaceicon liked this · 3 years ago -
 somehow-still-sane reblogged this · 3 years ago
somehow-still-sane reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ori-stole-the-cheese-again liked this · 3 years ago
ori-stole-the-cheese-again liked this · 3 years ago -
 angelcatsiel reblogged this · 3 years ago
angelcatsiel reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 glurk-world liked this · 3 years ago
glurk-world liked this · 3 years ago -
 crowleys-angels reblogged this · 3 years ago
crowleys-angels reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 crowleys-angels liked this · 3 years ago
crowleys-angels liked this · 3 years ago -
 dontbreakthechain reblogged this · 3 years ago
dontbreakthechain reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 dontbreakthechain liked this · 3 years ago
dontbreakthechain liked this · 3 years ago
Once I was made of stardust. Now I am made of flesh and I can experience our agreed-upon reality and said reality is exciting and beautiful and terrifying and full of interesting things to compile on a blog! / 27 / ENTP / they-them / Divination Wizard / B.E.y.O.N.D. department of Research and Development / scientist / science enthusiast / [fantasyd20 character]
162 posts