From A 9th Century Irish Manuscript, The Phrase ‘massive Hangover’ (Latheirt) written In The Ancient

From a 9th century Irish manuscript, the phrase ‘massive hangover’ (Latheirt) written in the ancient Irish text Ogham. The monk must have been having a very rough day…..
Source
More Posts from In-pursuit-of-knowledge-blog and Others
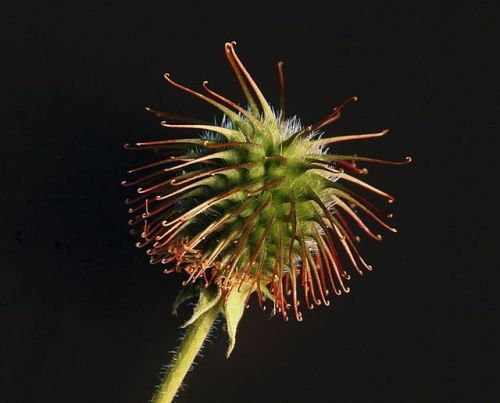

In 1941, Swiss engineer George de Mestral noticed after a hunting trip that burrs from burdock plants stuck to his pants and his dog’s fur.
He took the seed and looked at them through a microscope to find that this seed attaches to animal fur via the hooks on its surface to improve distribution.

Source: All of Nature on Blogspot
These hooks would latch onto anything loop-shaped, such as the fibers in his pants and his dog’s tangled fur. This inspired him to come up with the ‘Velcro’.
Velcro is a bio-mimicry of this burrs with small flexible hooks attached on its surface to attach to fluffy surfaces.


Although it goes by the name Velcro the generic name is a hook-and-loop fastener)

And depending on the load that needs to be held there are different types of hooks that are available:

The sound that the velcro makes when you rip it apart is oddly satisfying. It is made when the loops are ripped apart from the hooks.
It was always in my head that the hooks or the loops would break whenever you would rip it apart. But turns out, they are extremely flexible.

Source
For a long time I believed that this was the end of the story and that’s how far we had gone. But recently when I was trying to mount a board to the wall, I came across the 3M dual lock fasteners.
These use a mushroom shaped hook on both the sides to snap together in place.


Source
And evidently it turns out the mushroom fastener design were inspired from dragonflies who used it for stability during mating (check source video above for more).
This is great, but since this is made of plastic this surely would fail at higher temperatures. You need something robust to handle higher temperatures, and this is where the Metaklett comes into the picture:

A square metre of this fastener, called Metaklett (made of steel), is capable of supporting 35 tonnes at temperatures up to 800 ºC, (Video)
There is something exotic in the blend of nature and technology that is manifested in the Velcro, I just cannot put my hand on what it is.
Have a great day!
9 Ocean Facts You Likely Don’t Know, but Should
Earth is a place dominated by water, mainly oceans. It’s also a place our researchers study to understand life. Trillions of gallons of water flow freely across the surface of our blue-green planet. Ocean’s vibrant ecosystems impact our lives in many ways.
In celebration of World Oceans Day, here are a few things you might not know about these complex waterways.
1. Why is the ocean blue?

The way light is absorbed and scattered throughout the ocean determines which colors it takes on. Red, orange, yellow,and green light are absorbed quickly beneath the surface, leaving blue light to be scattered and reflected back. This causes us to see various blue and violet hues.
2. Want a good fishing spot?

Follow the phytoplankton! These small plant-like organisms are the beginning of the food web for most of the ocean. As phytoplankton grow and multiply, they are eaten by zooplankton, small fish and other animals. Larger animals then eat the smaller ones. The fishing industry identifies good spots by using ocean color images to locate areas rich in phytoplankton. Phytoplankton, as revealed by ocean color, frequently show scientists where ocean currents provide nutrients for plant growth.
3. The ocean is many colors.

When we look at the ocean from space, we see many different shades of blue. Using instruments that are more sensitive than the human eye, we can measure carefully the fantastic array of colors of the ocean. Different colors may reveal the presence and amount of phytoplankton, sediments and dissolved organic matter.
4. The ocean can be a dark place.
About 70 percent of the planet is ocean, with an average depth of more than 12,400 feet. Given that light doesn’t penetrate much deeper than 330 feet below the water’s surface (in the clearest water), most of our planet is in a perpetual state of darkness. Although dark, this part of the ocean still supports many forms of life, some of which are fed by sinking phytoplankton.
5. We study all aspects of ocean life.

Instruments on satellites in space, hundreds of kilometers above us, can measure many things about the sea: surface winds, sea surface temperature, water color, wave height, and height of the ocean surface.
6. In a gallon of average sea water, there is about ½ cup of salt.

The amount of salt varies depending on location. The Atlantic Ocean is saltier than the Pacific Ocean, for instance. Most of the salt in the ocean is the same kind of salt we put on our food: sodium chloride.
7. A single drop of sea water is teeming with life.

It will most likely have millions (yes, millions!) of bacteria and viruses, thousands of phytoplankton cells, and even some fish eggs, baby crabs, and small worms.
8. Where does Earth store freshwater?

Just 3.5 percent of Earth’s water is fresh—that is, with few salts in it. You can find Earth’s freshwater in our lakes, rivers, and streams, but don’t forget groundwater and glaciers. Over 68 percent of Earth’s freshwater is locked up in ice and glaciers. And another 30 percent is in groundwater.
9. Phytoplankton are the “lungs of the ocean”.

Just like forests are considered the “lungs of the earth”, phytoplankton is known for providing the same service in the ocean! They consume carbon dioxide, dissolved in the sunlit portion of the ocean, and produce about half of the world’s oxygen.
Want to learn more about how we study the ocean? Follow @NASAEarth on twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.


A couple of springboard notched stumps spotted in the field yesterday. Evidence of early 20th century logging activity.
People horrifically fucking up facts about evolution and genetics too support their stupid beliefs or to seem smart and “rational” is probably one of my big pet peeves

The Hunt for New Worlds Continues with TESS
We’re getting ready to start our next mission to find new worlds! The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will find thousands of planets beyond our solar system for us to study in more detail. It’s preparing to launch from our Kennedy Space Center at Cape Canaveral in Florida.

Once it launches, TESS will look for new planets that orbit bright stars relatively close to Earth. We’re expecting to find giant planets, like Jupiter, but we’re also predicting we’ll find Earth-sized planets. Most of those planets will be within 300 light-years of Earth, which will make follow-up studies easier for other observatories.

TESS will find these new exoplanets by looking for their transits. A transit is a temporary dip in a star’s brightness that happens with predictable timing when a planet crosses between us and the star. The information we get from transits can tell us about the size of the planet relative to the size of its star. We’ve found nearly 3,000 planets using the transit method, many with our Kepler space telescope. That’s over 75% of all the exoplanets we’ve found so far!

TESS will look at nearly the entire sky (about 85%) over two years. The mission divides the sky into 26 sectors. TESS will look at 13 of them in the southern sky during its first year before scanning the northern sky the year after.

What makes TESS different from the other planet-hunting missions that have come before it? The Kepler mission (yellow) looked continually at one small patch of sky, spotting dim stars and their planets that are between 300 and 3,000 light-years away. TESS (blue) will look at almost the whole sky in sections, finding bright stars and their planets that are between 30 and 300 light-years away.

TESS will also have a brand new kind of orbit (visualized below). Once it reaches its final trajectory, TESS will finish one pass around Earth every 13.7 days (blue), which is half the time it takes for the Moon (gray) to orbit. This position maximizes the amount of time TESS can stare at each sector, and the satellite will transmit its data back to us each time its orbit takes it closest to Earth (orange).

Kepler’s goal was to figure out how common Earth-size planets might be. TESS’s mission is to find exoplanets around bright, nearby stars so future missions, like our James Webb Space Telescope, and ground-based observatories can learn what they’re made of and potentially even study their atmospheres. TESS will provide a catalog of thousands of new subjects for us to learn about and explore.

The TESS mission is led by MIT and came together with the help of many different partners. Learn more about TESS and how it will further our knowledge of exoplanets, or check out some more awesome images and videos of the spacecraft. And stay tuned for more exciting TESS news as the spacecraft launches!
Watch the Launch + More!

Sunday, April 15 11 a.m. EDT - NASA Social Mission Overview
Join mission experts to learn more about TESS, how it will search for worlds beyond our solar system and what scientists hope to find! Have questions? Use #askNASA to have them answered live during the broadcast.
Watch HERE.
1 p.m. EDT - Prelaunch News Conference
Get an update on the spacecraft, the rocket and the liftoff operations ahead of the April 16 launch! Have questions? Use #askNASA to have them answered live during the broadcast.
Watch HERE.
3 p.m. EDT - Science News Conference
Hear from mission scientists and experts about the science behind the TESS mission. Have questions? Use #askNASA to have them answered live during the broadcast.
Watch HERE.
4 p.m. EDT - TESS Facebook Live
This live show will dive into the science behind the TESS spacecraft, explain how we search for planets outside our solar system and will allow you to ask your questions to members of the TESS team.
Watch HERE.
Monday, April 16 10 a.m. EDT - NASA EDGE: TESS Facebook Live
This half-hour live show will discuss the TESS spacecraft, the science of searching for planets outside our solar system, and the launch from Cape Canaveral.
Watch HERE.
1 p.m. EDT - Reddit AMA
Join us live on Reddit for a Science AMA to discuss the hunt for exoplanets and the upcoming launch of TESS!
Join in HERE.
6 p.m. EDT - Launch Coverage!
TESS is slated to launch at 6:32 p.m. EDT on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from our Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Watch HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
you: lich
me, an intellectual: spelleton


oh, that is quite literally eating something alive. I’m sure it’s very fresh! and severed tentacles grow back remarkably well, as if they were never gone, in about six weeks. Which may or may nor be relevant, depending on their fishing practices.
just woke up from one hell of a nightmare i need a distraction…
-
 prince-leorio reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
prince-leorio reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 liedownquisition reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
liedownquisition reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
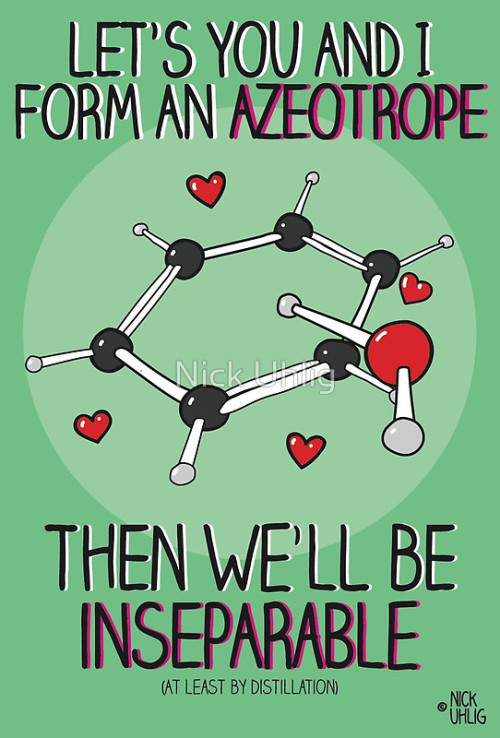
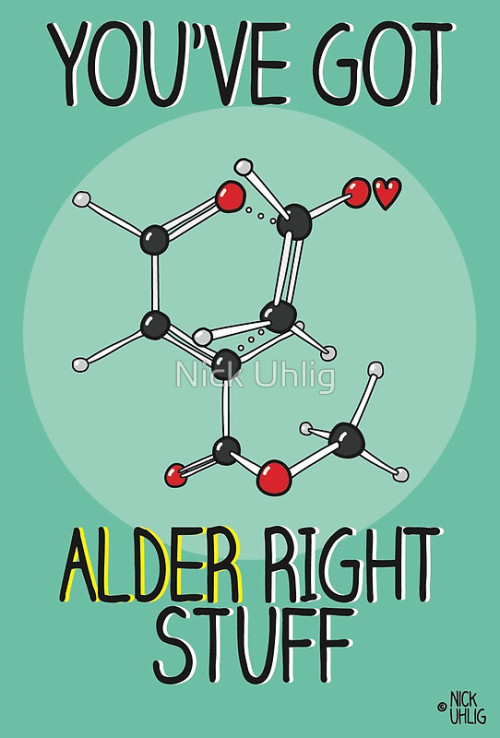
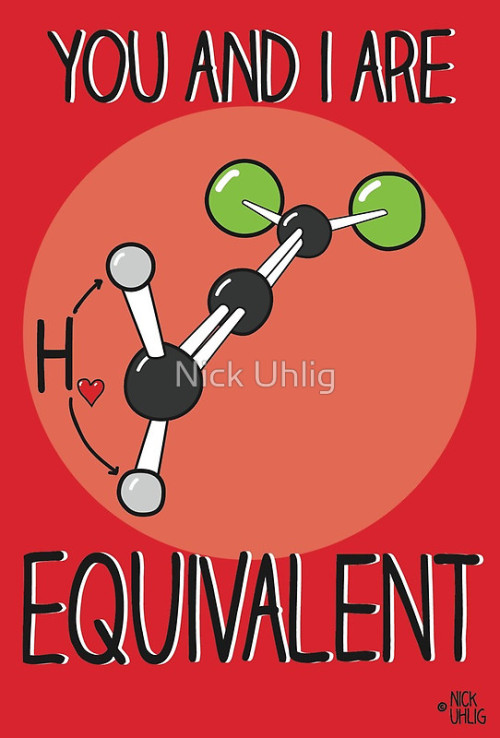
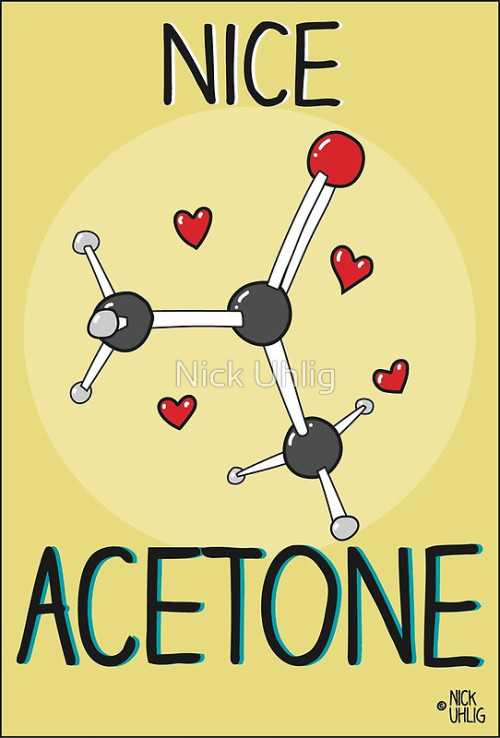
 epoxide reblogged this · 1 month ago
epoxide reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 perikaryon reblogged this · 1 month ago
perikaryon reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 vasilihound reblogged this · 1 month ago
vasilihound reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 corginzola liked this · 1 month ago
corginzola liked this · 1 month ago -
 jokepool liked this · 1 month ago
jokepool liked this · 1 month ago -
 absolutelyfibulas liked this · 1 month ago
absolutelyfibulas liked this · 1 month ago -
 hoarder-of-shinies liked this · 1 month ago
hoarder-of-shinies liked this · 1 month ago -
 scrawlinglines reblogged this · 1 month ago
scrawlinglines reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 rebel-reblogs reblogged this · 1 month ago
rebel-reblogs reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 the-rebel-spy-art liked this · 1 month ago
the-rebel-spy-art liked this · 1 month ago -
 ihadtologinforthis reblogged this · 1 month ago
ihadtologinforthis reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 semiprofessional-cryptid reblogged this · 1 month ago
semiprofessional-cryptid reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 semiprofessional-cryptid liked this · 1 month ago
semiprofessional-cryptid liked this · 1 month ago -
 hederigerenthag liked this · 1 month ago
hederigerenthag liked this · 1 month ago -
 hotcheetos-te-amo reblogged this · 1 month ago
hotcheetos-te-amo reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 hotcheetos-te-amo liked this · 1 month ago
hotcheetos-te-amo liked this · 1 month ago -
 criscura reblogged this · 1 month ago
criscura reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 criscura liked this · 1 month ago
criscura liked this · 1 month ago -
 chiefofboatwatsonstittymug reblogged this · 1 month ago
chiefofboatwatsonstittymug reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 schaferhunde-blog liked this · 1 month ago
schaferhunde-blog liked this · 1 month ago -
 ever-nights liked this · 2 months ago
ever-nights liked this · 2 months ago -
 vitrazik liked this · 2 months ago
vitrazik liked this · 2 months ago -
 mariannetheflash liked this · 2 months ago
mariannetheflash liked this · 2 months ago -
 tanelorn8615 reblogged this · 2 months ago
tanelorn8615 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 henry-fox-biggest-stan liked this · 2 months ago
henry-fox-biggest-stan liked this · 2 months ago -
 gothgleek reblogged this · 3 months ago
gothgleek reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 lokalypso liked this · 3 months ago
lokalypso liked this · 3 months ago -
 capnmetalheadlives reblogged this · 3 months ago
capnmetalheadlives reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 capnmetalheadlives liked this · 3 months ago
capnmetalheadlives liked this · 3 months ago -
 neurodecadence reblogged this · 3 months ago
neurodecadence reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 stumblios-grumblios reblogged this · 3 months ago
stumblios-grumblios reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 wheresmyfuckintea reblogged this · 3 months ago
wheresmyfuckintea reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 coweatman liked this · 3 months ago
coweatman liked this · 3 months ago -
 sparkly-heretic liked this · 3 months ago
sparkly-heretic liked this · 3 months ago -
 allwithinilly liked this · 3 months ago
allwithinilly liked this · 3 months ago -
 rainb0w-em0kid liked this · 3 months ago
rainb0w-em0kid liked this · 3 months ago -
 teamfreewillonbakerstreet777 reblogged this · 3 months ago
teamfreewillonbakerstreet777 reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 ythastogonow reblogged this · 3 months ago
ythastogonow reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 caligulasperi liked this · 3 months ago
caligulasperi liked this · 3 months ago -
 nmpositive reblogged this · 3 months ago
nmpositive reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 betterthanyou liked this · 3 months ago
betterthanyou liked this · 3 months ago -
 smiling-pile-of-crap reblogged this · 3 months ago
smiling-pile-of-crap reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 sorryforbeingpremium liked this · 3 months ago
sorryforbeingpremium liked this · 3 months ago -
 agentalysswolf reblogged this · 3 months ago
agentalysswolf reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 taxchurchesfundhealthcare reblogged this · 3 months ago
taxchurchesfundhealthcare reblogged this · 3 months ago
Once I was made of stardust. Now I am made of flesh and I can experience our agreed-upon reality and said reality is exciting and beautiful and terrifying and full of interesting things to compile on a blog! / 27 / ENTP / they-them / Divination Wizard / B.E.y.O.N.D. department of Research and Development / scientist / science enthusiast / [fantasyd20 character]
162 posts