Another Station Upgrade:
Another Station Upgrade:
Spacewalkers Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins to install new TV cameras
On Thursday, Sept. 1, U.S. astronauts Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins will conduct the station’s 195th American spacewalk. As part of their activities, the pair will install the first of several enhanced high-definition television cameras that will monitor activities outside the station, including the comings and goings of visiting cargo and crew vehicles

Working on the station’s backbone, or truss, Williams and Rubins will retract a thermal radiator that is part of the station’s cooling system.

As was the case for their first spacewalk together on Aug. 19, Williams will be designated as extravehicular crew member 1 (EV1), wearing a spacesuit with a red stripe, while Rubins will be EV2, wearing a suit with no stripes.
Watch LIVE!
Coverage of the spacewalk begins at 6:30 a.m. EDT on Thursday, Sept. 1; with the spacewalk scheduled to begin at 8:05 a.m. EDT. Stream live online HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Celebrating 10 Years of Revolutionary Solar Views
Twin spacecraft give humanity unprecedented views of the entire sun at one time, traveling to the far side of our home star over the course of a 10-year mission.

These two spacecraft are called STEREO, short for Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory. Launched on Oct. 25, 2006, and originally slated for a two-year mission, both spacecraft sent back data for nearly eight years, and STEREO-A still sends information and images from its point of view on the far side of the sun.

STEREO watches the sun from two completely new perspectives. It also provides information invaluable for understanding the sun and its impact on Earth, other worlds, and space itself – collectively known as space weather. On Earth, space weather can trigger things like the aurora and, in extreme cases, put a strain on power systems or damage high-flying satellites.
Because the rest of our sun-watching satellites orbit near our home planet, STEREO’s twin perspectives far from Earth give us a unique opportunity to look at solar events from all sides and understand them in three dimensions.

We use data from STEREO and other missions to understand the space environment throughout the solar system. This helps operators for missions in deep space prepare for the sudden bursts of particles and magnetic field that could pose a danger to their spacecraft.

STEREO has also helped us understand other objects in our solar system – like comets. Watching how a comet’s tail moves gives us clues about the constant stream of particles that flows out from the sun, called the solar wind.

STEREO is an essential piece of our heliophysics fleet, which includes 17 other missions. Together, these spacecraft shed new light on the sun and its interaction with space, Earth, and other worlds throughout the solar system.
To celebrate, we’re hosting a Facebook Live event on Wednesday, Oct. 26. Join us at noon ET on the NASA Sun Science Facebook page to learn more about STEREO and ask questions.
Learn more about how NASA studies the sun at: www.nasa.gov/stereo
Follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Astronaut Journal Entry - Pre-Launch
Currently, six humans are living and working on the International Space Station, which orbits 250 miles above our planet at 17,500mph. Below you will find a real journal entry written by NASA astronaut Scott Tingle.
To read more entires from this series, visit our Space Blogs on Tumblr.

Our crew just finished the final training event before the launch. Tomorrow, at 13:20 local time (Baikonur), we will strap the Soyuz MS-07 spacecraft to our backs and fly it to low Earth orbit. We will spend 2.5 days in low Earth orbit before docking to the MRM-1 docking port on the International Space Station (ISS). There we will begin approximately 168 days of maintenance, service and science aboard one of the greatest engineering marvels that humans have ever created.

Today was bittersweet. Ending a 2-year process of intense training was welcomed by all of us. We are very tired. Seeing our families for the last time was difficult. I am pretty lucky, though. My wife, Raynette, and the kids have grown up around military service and are conditioned to endure the time spent apart during extended calls-to-duty. We are also very much anticipating the good times we will have upon my return in June. Sean and Amy showed me a few videos of them mucking it up at Red Square before flying out to Baikonur. Eric was impressed with the Russian guards marching in to relieve the watch at Red Square. Raynette was taking it all in stride and did not seem surprised by any of it. I think I might have a family of mutants who are comfortable anywhere. Nice! And, by the way, I am VERY proud of all of them!

Tomorrow’s schedule includes a wake-up at 04:00, followed by an immediate medical exam and light breakfast. Upon returning to our quarters, we will undergo a few simple medical procedures that should help make the 2.5-day journey to ISS a little more comfortable. I’ve begun prepping with motion sickness medication that should limit the nausea associated with the first phases of spaceflight. I will continue this effort through docking. This being my first flight, I’m not sure how my body will respond and am taking all precautions to maintain a good working capability. The commander will need my help operating the vehicle, and I need to not be puking into a bag during the busy times. We suit up at 09:30 and then report to the State Commission as “Готовы к Полёту”, or “Ready for Flight”. We’ll enter the bus, wave goodbye to our friends and family, and then head out to the launch pad. Approximately 2 kilometers from the launch pad, the bus will stop.

The crew will get out, pee on the bus’s tire, and then complete the last part of the drive to the launch pad. This is a traditional event first done by Yuri Gagarin during his historic first flight and repeated in his honor to this day. We will then strap in and prepare the systems for launch. Next is a waiting game of approximately 2 hours. Ouch. The crew provided five songs each to help pass the time. My playlist included “Born to Run” (Springsteen), “Sweet Child O’ Mine” (Guns and Roses), “Cliffs of Dover” (Eric Johnson), “More than a Feeling” (Boston), and “Touch the Sky” (Rainbow Bridge, Russian). Launch will happen precisely at 13:20.

I think this sets the stage. It’s 21:30, only 6.5 hours until duty calls. Time to get some sleep. If I could only lower my level of excitement!
Find more ‘Captain’s Log’ entries HERE.
Follow NASA astronaut Scott Tingle on Instagram and Twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Galactic Ghouls and Stellar Screams
A quiet, starry night sky might not seem like a very eerie spectacle, but space can be a creepy place! Monsters lurk in the shadowy depths of the universe, sometimes hidden in plain sight. Many of them are invisible to our eyes, so we have to use special telescopes to see them. Read on to discover some of these strange cosmic beasts, but beware — sometimes fact is scarier than fiction.
Monster Black Holes ⚫

You know those nightmares where no matter how fast you try to run you never seem to get anywhere? Black holes are a sinister possible version of that dream — especially because they’re real! If you get too close to a black hole, there is no possibility of escape.
Just last year our Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope traced an otherworldly ghost particle back to one of these monster black holes, providing additional insight into the many signals we’re picking up from some of the most feared creatures in the cosmic deep.
But it gets worse. Our Hubble Space Telescope revealed that these things are hidden in the hearts of nearly every galaxy in the universe. That means supermassive black holes lurk in the shadows of the night sky in every direction you look!
A Hazy Specter 👻

This fiendish specter lives in the center of the Milky Way, haunting our galaxy’s supermassive black hole. But it’s not as scary as it looks! Our SOFIA observatory captured streamlines tracing a magnetic field that appears to be luring most of the material quietly into orbit around the black hole. In other galaxies, magnetic fields seem to be feeding material into hungry black holes — beware! Magnetic fields might be the answer to why some black holes are starving while others are feasting.
Bats in the Belfry 🦇

The universe has bats in the attic! Hubble spotted the shadow of a giant cosmic bat in the Serpens Nebula. Newborn stars like the one at the center of the bat, called HBC 672, are surrounded by disks of material, which are hard to study directly. The shadows they cast, like the bat, can clue scientists in on things like the disk’s size and density. Our solar system formed from the same type of disk of material, but we can only see the end result of planet building here — we want to learn more about the process!
Jack-o-lantern Sun 🎃

A jack-o-lantern in space?! Our Solar Dynamics Observatory watches the Sun at all times, keeping a close eye on space weather. In October 2014, the observatory captured a chilling image of the Sun with a Halloweenish face!
Skull Comet 💀

On Halloween a few years ago, an eerie-looking object known as 2015 TB145 sped across the night sky. Scientists observing it with our Infrared Telescope Facility determined that it was most likely a dead comet. It’s important to study objects like comets and asteroids because they’re dangerous if they cross Earth’s path — just ask the dinosaurs!
Halloween Treat 🍬

Trick-or-treat! Add a piece of glowing cosmic candy to your Halloween haul, courtesy of Hubble! This image shows the Saturn Nebula, formed from the outer layers ejected by a dying star, destined to be recycled into later generations of stars and planets. Our Sun will experience a similar fate in around five billion years.
Witch’s Broom Nebula 🧹

Massive stars are in for a more fiery fate, as the Witch's Broom Nebula shows. Hubble’s close-up look reveals wisps of gas — shrapnel leftover from a supernova explosion. Astronomers believe that a couple of supernovae occur each century in galaxies like our own Milky Way.
Zombie Stars 🧟

Supernovae usually herald the death of a star, but on a few occasions astronomers have found “zombie stars” left behind after unusually weak supernovae. Our Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) has even spotted a mysterious glow of high-energy X-rays that could be the “howls” of dead stars as they feed on their neighbors.
Intergalactic Ghost Towns 🏚️

The universe is brimming with galaxies, but it’s also speckled with some enormous empty pockets of space, too. These giant ghost towns, called voids, may be some of the largest things in the cosmos, and since the universe is expanding, galaxies are racing even farther away from each other all the time! Be grateful for your place in space — the shadowy patches of the universe are dreadful lonely scenes.
Mysterious Invisible Force 🕵️♀️

Some forces are a lot creepier than floorboards creaking or a door slamming shut unexpectedly when you’re home alone. Dark energy is a mysterious antigravity pressure that our Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope (WFIRST) is going to help us understand. All we know so far is that it’s present everywhere in the cosmos (even in the room with you as you read this) and it controls the fate of the universe, but WFIRST will study hundreds of millions of galaxies to figure out just what dark energy is up to.
Want to learn some fun ways to celebrate Halloween in (NASA) style? Check out this link!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Airglow Can Help Us Understand the Sun’s Influence on Earth
You may have seen the famous blue marble or pale blue dot images showing Earth from 18,000 and 3.7 billion miles away, respectively. But closer to home — some 300 miles above Earth's surface — you might encounter an unfamiliar sight: vibrant swaths of red and green or purple and yellow light emanating from the upper atmosphere.
This light is airglow.

Airglow is created when atoms and molecules in the upper atmosphere, excited by sunlight, emit light to shed excess energy. Or, it can happen when atoms and molecules that have been ionized by sunlight collide with and capture a free electron. In both cases, these atmospheric particles emit light in order to relax again. The process is similar to how auroras are created, but while auroras are driven by high-energy solar wind, airglow is energized by day-to-day solar radiation.

Since sunlight is constant, airglow constantly shines throughout Earth’s atmosphere, and the result is a tenuous bubble of light that closely encases our planet. Its light is too dim to see easily except in orbit or on the ground with clear, dark skies and a sensitive camera — it’s one-tenth as bright as the light given off by all the stars in the night sky.

Airglow highlights a key part of our atmosphere: the ionosphere. Stretching from roughly 50 to 400 miles above Earth’s surface, the ionosphere is an electrified layer of the upper atmosphere generated by extreme ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. It reacts to both terrestrial weather below and solar energy streaming in from above, forming a complex space weather system. Turbulence in this ever-changing sea of charged particles can manifest as disruptions that interfere with Earth-orbiting satellites or communication and navigation signals.

Understanding the ionosphere’s extreme variability is tricky because it requires untangling interactions between the different factors at play — interactions of which we don’t have a clear picture. That’s where airglow comes in. Each atmospheric gas has its own favored airglow color, hangs out at a different height and creates airglow by a different process, so we can use airglow to study different layers of the atmosphere.

Airglow carries information on the upper atmosphere’s temperature, density, and composition, but it also helps us trace how particles move through the region itself. Vast, high-altitude winds sweep through the ionosphere, pushing its contents around the globe — and airglow’s subtle dance follows their lead, highlighting global patterns.

Two NASA missions take advantage of precisely this effect to study the upper atmosphere: ICON — short for Ionospheric Connection Explorer — and GOLD — Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk.
ICON focuses on how charged and neutral gases in the upper atmosphere behave and interact, while GOLD observes what drives change — the Sun, Earth’s magnetic field or the lower atmosphere — in the region.

By imaging airglow, the two missions will enable scientists to tease out how space and Earth’s weather intersect, dictating the region’s complex behavior.
Keep up with the latest in NASA's airglow and upper atmosphere research on Twitter and Facebook or at nasa.gov/sunearth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Which Landsat Image Do You Love?
Feeling competitive? We’ve got a game for you to play in! Tournament Earth: The Landsat Games is happening right now, and as we get to the final entries, the competition is heating up.

You can help us pick the winner by voting for one of the remaining four Landsat images of our home planet! Our competition started with 32 images, divided into categories by what they show: land, water, ice & snow, and human impact.
So, what do you think? Which one of these images is going for gold?
Land
First up, we have an image of the Markha River and surrounding Central Siberian Plateau, acquired in 2020 by Landsat 8. The hypnotic undulations of striping across the landscape carried this image to victory over the rest of the Land images -- a particularly tough category, given that these images all come from Landsat.

Water
It’s not all land, though! The bright blues and greens of this false-color image of the Atchafalaya Delta in Louisiana helped carry it to victory in the Water category. The image, taken in 2020 by Landsat 8, shows a region that’s subject to erosion of land by wind and rising sea levels.

Ice & Snow
Brrr! Did it get cold in here? That’s the finalist from the Ice and Snow category, an image of sea ice around Russia’s New Siberian Islands. The image, collected by Landsat 8 in June 2016, shows sea ice during its annual seasonal breakup.

Human Impact
Humans have been shaping the planet around us for hundreds of years. Some changes, like rice fields in the Sacramento Valley, are visible from space. Landsat 8 collected this false-color image of flooded rice fields in December 2018.

So, now it’s up to you! Which image is your favorite? There can only be one winner of Tournament Earth: The Landsat Games. Get your vote in, and then get ready to watch as we launch the next Landsat satellite, Landsat 9, in September.

The Landsat mission is a partnership between us at NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Together, we’ve been using Landsat satellites to collect nearly 50 years of images of our home planet.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space.
Crab Nebula in technicolor! This new composite view combines data from five different telescopes, showing the celestial object in multiple kinds of light.
The video starts with a composite image of the Crab Nebula, a supernova remnant that was assembled by combining data from five telescopes spanning nearly the entire breadth of the electromagnetic spectrum: the Very Large Array, the Spitzer Space Telescope, the Hubble Space Telescope, the XMM-Newton Observatory, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory.
It then dissolves to the red-colored radio-light view that shows how a neutron star’s fierce “wind” of charged particles from the central neutron star energized the nebula, causing it to emit the radio waves.
The yellow-colored infrared image includes the glow of dust particles absorbing ultraviolet and visible light.
The green-colored Hubble visible-light image offers a very sharp view of hot filamentary structures that permeate this nebula.
The blue-colored ultraviolet image and the purple-colored X-ray image shows the effect of an energetic cloud of electrons driven by a rapidly rotating neutron star at the center of the nebula.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Will the robot be able to send vedio footage?

Hi! The Sun is so bright I need shades... that are ISO 12312-2 compliant! So glad that you are all here and excited about the eclipse. I’m Alexa Halford and ready to answer your questions.
Mission Possible: Redirecting an Asteroid
As part of our Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM), we plan to send a robotic spacecraft to an asteroid tens of millions of miles away from Earth, capture a multi-ton boulder and bring it to an orbit near the moon for future crew exploration.
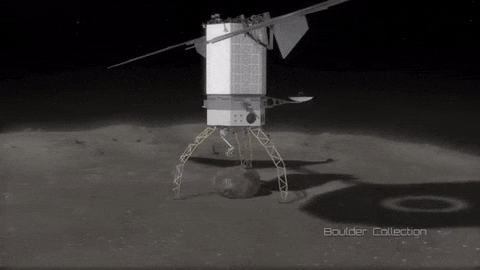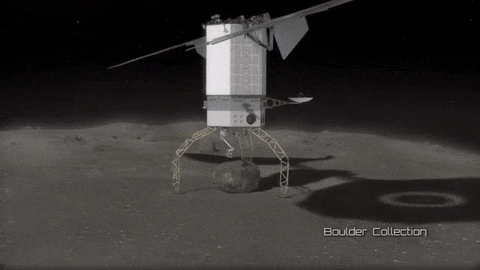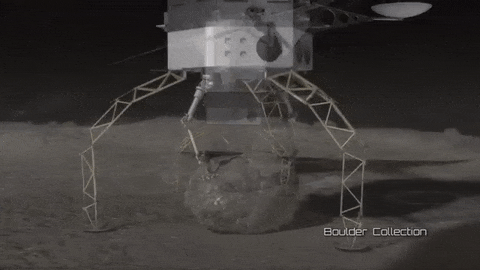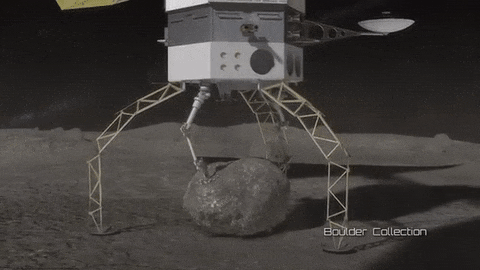
This mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid is part of our plan to advance the new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
How exactly will it work?
The robotic spacecraft, powered by the most advanced solar electric propulsion system, will travel for about 18 months to the target asteroid.

After the spacecraft arrives and the multi-ton boulder is collected from the surface, the spacecraft will hover near the asteroid to create a gravitational attraction that will slightly change the asteroid’s trajectory.

After the enhanced gravity tractor demonstration is compete, the robotic vehicle will deliver the boulder into a stable orbit near the moon. During the transit, the boulder will be further imaged and studied by the spacecraft.

Astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft will launch on the Space Launch System rocket to explore the returned boulder.

Orion will dock with the robotic vehicle that still has the boulder in its grasp.

While docked, two crew members on spacewalks will explore the boulder and collect samples to bring back to Earth for further study.

The astronauts and collected samples will return to Earth in the Orion spacecraft.
How will ARM help us send humans to Mars in the 2030s?

This mission will demonstrate future Mars-level exploration missions closer to home and will fly a mission with technologies and real life operational constraints that we’ll encounter on the way to the Red Planet. A few of the capabilities it will help us test include:
Solar Electric Propulsion – Using advanced Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) technologies is an important part of future missions to send larger payloads into deep space and to the Mars system. Unlike chemical propulsion, which uses combustion and a nozzle to generate thrust, SEP uses electricity from solar arrays to create electromagnetic fields to accelerate and expel charged atoms (ions) to create a very low thrust with a very efficient use of propellant.
Trajectory and Navigation – When we move the massive asteroid boulder using low-thrust propulsion and leveraging the gravity fields of Earth and the moon, we’ll validate critical technologies for the future Mars missions.
Advances in Spacesuits – Spacesuits designed to operate in deep space and for the Mars surface will require upgrades to the portable life support system (PLSS). We are working on advanced PLSS that will protect astronauts on Mars or in deep space by improving carbon dioxide removal, humidity control and oxygen regulation. We are also improving mobility by evaluating advances in gloves to improve thermal capacity and dexterity.
Sample Collection and Containment Techniques – This experience will help us prepare to return samples from Mars through the development of new techniques for safe sample collection and containment. These techniques will ensure that humans do not contaminate the samples with microbes from Earth, while protecting our planet from any potential hazards in the samples that are returned.
Rendezvous and Docking Capabilities – Future human missions to Mars will require new capabilities to rendezvous and dock spacecraft in deep space. We will advance the current system we’ve developed with the international partners aboard the International Space Station.
Moving from spaceflight a couple hundred miles off Earth to the proving ground environment (40,000 miles beyond the moon) will allow us to start accumulating experience farther than humans have ever traveled in space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
1,000 Days in Orbit: MAVEN’s Top 10 Discoveries at Mars
On June 17, our MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission) will celebrate 1,000 Earth days in orbit around the Red Planet.

Since its launch in November 2013 and its orbit insertion in September 2014, MAVEN has been exploring the upper atmosphere of Mars. MAVEN is bringing insight to how the sun stripped Mars of most of its atmosphere, turning a planet once possibly habitable to microbial life into a barren desert world.

Here’s a countdown of the top 10 discoveries from the mission so far:
10. Unprecedented Ultraviolet View of Mars

Revealing dynamic, previously invisible behavior, MAVEN was able to show the ultraviolet glow from the Martian atmosphere in unprecedented detail. Nightside images showed ultraviolet “nightglow” emission from nitric oxide. Nightglow is a common planetary phenomenon in which the sky faintly glows even in the complete absence of eternal light.
9. Key Features on the Loss of Atmosphere

Some particles from the solar wind are able to penetrate unexpectedly deep into the upper atmosphere, rather than being diverted around the planet by the Martian ionosphere. This penetration is allowed by chemical reactions in the ionosphere that turn the charged particles of the solar wind into neutral atoms that are then able to penetrate deeply.
8. Metal Ions

MAVEN made the first direct observations of a layer of metal ions in the Martian ionosphere, resulting from incoming interplanetary dust hitting the atmosphere. This layer is always present, but was enhanced dramatically by the close passage to Mars of Comet Siding Spring in October 2014.
7. Two New Types of Aurora

MAVEN has identified two new types of aurora, termed “diffuse” and “proton” aurora. Unlike how we think of most aurorae on Earth, these aurorae are unrelated to either a global or local magnetic field.
6. Cause of the Aurorae

These aurorae are caused by an influx of particles from the sun ejected by different types of solar storms. When particles from these storms hit the Martian atmosphere, they can also increase the rate of loss of gas to space, by a factor of ten or more.
5. Complex Interactions with Solar Wind

The interactions between the solar wind and the planet are unexpectedly complex. This results due to the lack of an intrinsic Martian magnetic field and the occurrence of small regions of magnetized crust that can affect the incoming solar wind on local and regional scales. The magnetosphere that results from the interactions varies on short timescales and is remarkably “lumpy” as a result.
4. Seasonal Hydrogen

After investigating the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet for a full Martian year, MAVEN determined that the escaping water does not always go gently into space. The spacecraft observed the full seasonal variation of hydrogen in the upper atmosphere, confirming that it varies by a factor of 10 throughout the year. The escape rate peaked when Mars was at its closest point to the sun and dropped off when the planet was farthest from the sun.
3. Gas Lost to Space

MAVEN has used measurements of the isotopes in the upper atmosphere (atoms of the same composition but having different mass) to determine how much gas has been lost through time. These measurements suggest that 2/3 or more of the gas has been lost to space.
2. Speed of Solar Wind Stripping Martian Atmosphere

MAVEN has measured the rate at which the sun and the solar wind are stripping gas from the top of the atmosphere to space today, along with details of the removal process. Extrapolation of the loss rates into the ancient past – when the solar ultraviolet light and the solar wind were more intense – indicates that large amounts of gas have been lost to space through time.
1. Martian Atmosphere Lost to Space

The Mars atmosphere has been stripped away by the sun and the solar wind over time, changing the climate from a warmer and wetter environment early in history to the cold, dry climate that we see today.
Maven will continue its observations and is now observing a second Martian year, looking at the ways that the seasonal cycles and the solar cycle affect the system.
For more information about MAVEN, visit: www.nasa.gov/maven
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 fairytail-ship-obsessed liked this · 4 years ago
fairytail-ship-obsessed liked this · 4 years ago -
 mimovieluvr0216 liked this · 7 years ago
mimovieluvr0216 liked this · 7 years ago -
 clearsnowflake liked this · 8 years ago
clearsnowflake liked this · 8 years ago -
 best-hotels-posts reblogged this · 8 years ago
best-hotels-posts reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 pickk-me liked this · 8 years ago
pickk-me liked this · 8 years ago -
 mhallgath liked this · 8 years ago
mhallgath liked this · 8 years ago -
 sugarmoontangerine liked this · 8 years ago
sugarmoontangerine liked this · 8 years ago -
 yujiro023-blog liked this · 8 years ago
yujiro023-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 merybowie-blog liked this · 8 years ago
merybowie-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 missruckus liked this · 8 years ago
missruckus liked this · 8 years ago -
 tessalynn72-blog liked this · 8 years ago
tessalynn72-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 johzyaz liked this · 8 years ago
johzyaz liked this · 8 years ago -
 nuderefsarebest reblogged this · 8 years ago
nuderefsarebest reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 carlosemiliopir liked this · 8 years ago
carlosemiliopir liked this · 8 years ago -
 alienfrauds liked this · 8 years ago
alienfrauds liked this · 8 years ago -
 konst65 liked this · 8 years ago
konst65 liked this · 8 years ago -
 nuderefsarebest liked this · 8 years ago
nuderefsarebest liked this · 8 years ago -
 analgesicsleep reblogged this · 8 years ago
analgesicsleep reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 nasauniversefan-blog liked this · 8 years ago
nasauniversefan-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 flyingbanana45 liked this · 8 years ago
flyingbanana45 liked this · 8 years ago -
 erielthrym-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
erielthrym-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mrchaoticftl-blog liked this · 8 years ago
mrchaoticftl-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 cool-cat-felix-blog liked this · 8 years ago
cool-cat-felix-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 calrhyo reblogged this · 8 years ago
calrhyo reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 thefourteenthdoctorr liked this · 8 years ago
thefourteenthdoctorr liked this · 8 years ago -
 fishbubbl3 liked this · 8 years ago
fishbubbl3 liked this · 8 years ago -
 daysofterroruponus reblogged this · 8 years ago
daysofterroruponus reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 predictivemarketing-blog liked this · 8 years ago
predictivemarketing-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 curiositytherover reblogged this · 8 years ago
curiositytherover reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 unmightywaffle liked this · 8 years ago
unmightywaffle liked this · 8 years ago -
 vroomkat liked this · 8 years ago
vroomkat liked this · 8 years ago -
 iandallamba liked this · 8 years ago
iandallamba liked this · 8 years ago -
 saitamastamaticsoup reblogged this · 8 years ago
saitamastamaticsoup reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 cheezbot liked this · 8 years ago
cheezbot liked this · 8 years ago -
 k-120 liked this · 8 years ago
k-120 liked this · 8 years ago -
 estamosdentro reblogged this · 8 years ago
estamosdentro reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sweetteadivination-blog liked this · 8 years ago
sweetteadivination-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 kawaiimayhem170 reblogged this · 8 years ago
kawaiimayhem170 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 psikh000 liked this · 8 years ago
psikh000 liked this · 8 years ago -
 bahbrino-blog liked this · 8 years ago
bahbrino-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 nvilyv liked this · 8 years ago
nvilyv liked this · 8 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts