Are You Scared About Going Up Into Space?
Are you scared about going up into space?
I’m not scared, but I have a healthy amount of nervousness because I don’t know exactly what to expect. I have a lot of great advice, but you don’t know until you actually get there.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Our Favorite Valentines Throughout the Universe
Today is Valentine’s Day. What better way to express that you love someone than with an intergalactic love gram? Check out some of our favorites and send them to all of your cosmic companions:
Your love is galactic

The Hubble Space Telescope revolutionized nearly all areas of astronomical research — and captured some truly lovely images. Here, a pair of intersecting galaxies swirl into the shape of a rose as a result of gravitational tidal pull. What type of roses are you getting for your love — red or galactic?
I think you’re n{ice}

IceBridge is the largest airborne survey of Earth’s polar ice ever flown. It captures 3-D views of Arctic and Antarctic ice sheets, ice shelves and sea ice. This lovely heart-shaped glacier feature was discovered in northwest Greenland during an IceBridge flight in 2017. Which of your lover’s features would you say are the coolest?
You’re absolutely magnetic

Even though we can't see them, magnetic fields are all around us. One of the solar system’s largest magnetospheres belongs to Jupiter. Right now, our Juno spacecraft is providing scientists with their first glimpses of this unseen force. Is your attraction to your loved one magnetic?
You’re MARS-velous

This heart-shaped feature on the Martian landscape was captured by our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. It was created by a small impact crater that blew darker material on the surface away. What impact has your loved one had on you?
I <3 you

From three billion miles away, Pluto sent a “love note” back to Earth, via our New Horizons spacecraft. This stunning image of Pluto's "heart" shows one of the world's most dominant features, estimated to be 1,000 miles (1,600 km) across at its widest point. Will you pass this love note on to someone special in your life?
Light of my life

Our Solar Dynamics Observatory keeps an eye on our closest star that brings energy to you and your love. The observatory helps us understand where the Sun's energy comes from, how the inside of the Sun works, how energy is stored and released in the Sun's atmosphere and much more. Who would you say is your ray of sunshine?
Do any of these cosmic phenomena remind you of someone in your universe? Download these cards here to send to all the stars in your sky.
Want something from the Red Planet to match your bouquet of red roses? Here is our collection of Martian Valentines.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for April 2016?

Jupiter, Mars, the Lyrid meteor shower and 2016’s best views of Mercury are all visible in the sky this month.

Jupiter, where our Juno mission will begin orbiting on July 4, continues to shine almost as brightly this month as last. And eagle-eyed telescope viewers will see a transit, a shadow transit, an occultation and an eclipse of Jupiter’s moons- all in one night: April 6-7.

Io transits first, crossing the planet beginning at 9:52 p.m. EDT. It’s shadow can be seen less than an hour later.

Next Jupiter occults, or eclipses, Europa as Europa slips behind the giant planet at 10:48 p.m. EDT. At 3 a.m. Europa reappears from its eclipse, dramatically leaving the shadow of Jupiter.

Ganymede transits the planet beginning at 1:01 EDT April 7.
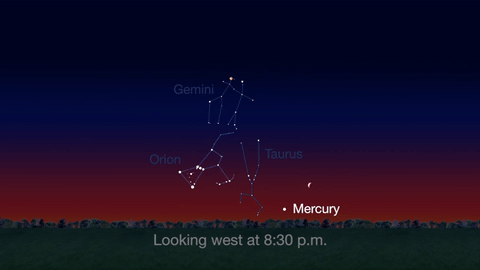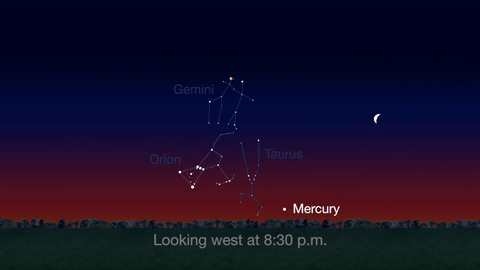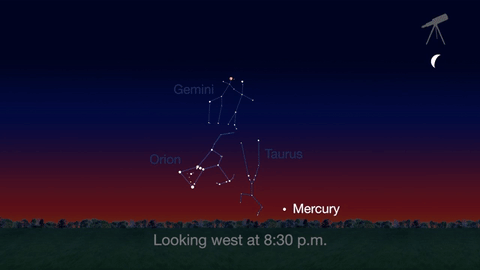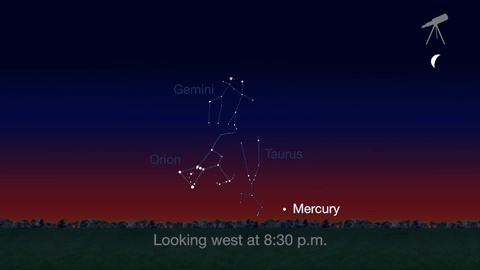
Check out the other planets in April, too! Mercury is always a challenging object to view, but this month you can spot it after sunset about 10 degrees above the horizon. Through a telescope you can see its phase. It will appear like a tiny crescent moon, with about 1/3 of its disk illuminated.

Mars is finally visible before midnight this month. It rises in the southeast at about 10 p.m. by the end of April. The best observing of Mars will be when it is highest in the sky. This means a few hours before dawn. Its brightness and apparent size increase dramatically this month. By month’s end, Mars appears nearly twice as bright as at the beginning of the month.

About mid-month you’ll see Mars near its rival in the sky: the similar-colored red supergiant star Antares. The name “Antares” means “equal to or rival of Mars”.
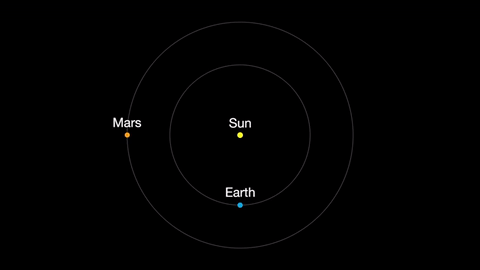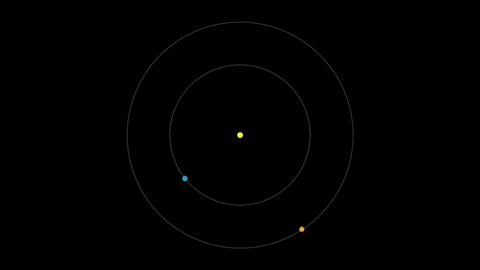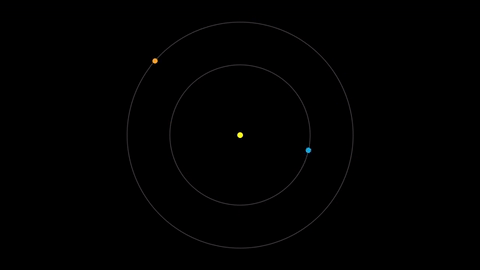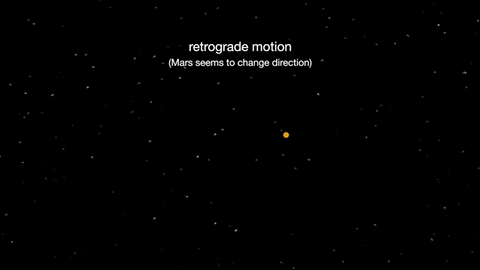
Earth moves almost twice as fast as Mars does, so it often passes Mars in their race around the sun. This causes “retrograde motion”: an illusion we see from our viewpoint on Earth.
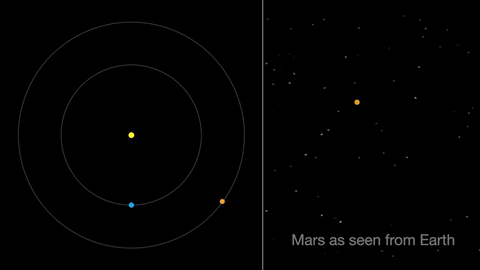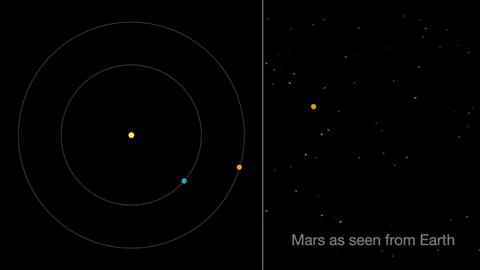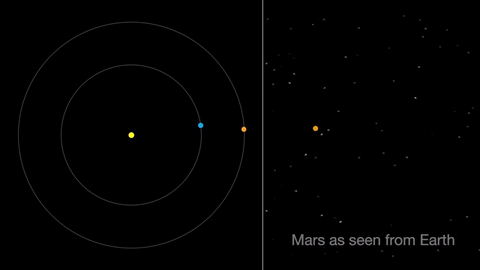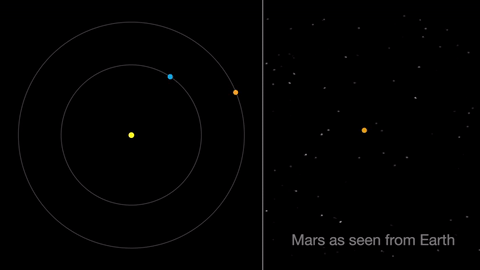
Retrograde motion happens as Earth catches up to Mars, causing Mars to appear slow to slow its eastward motion against the stars. After a few days, when Earth has overtaken Mars, the Red Planet seems to move westward. Eventually, Earth moves far enough around its orbit that Mars appears to be moving eastward again.
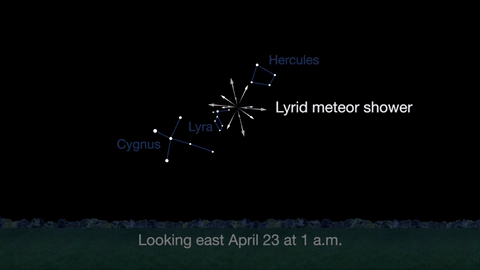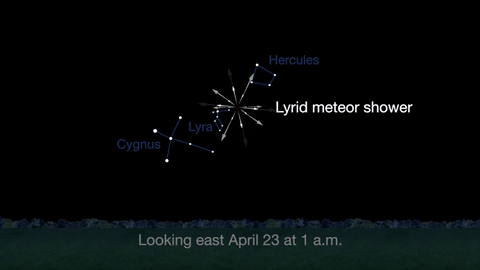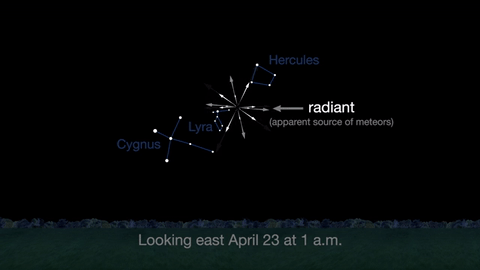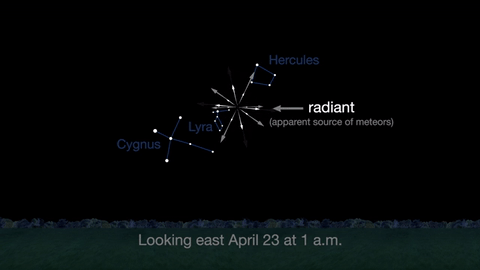
April features one meteor shower, the Lyrids. This year the Lyrids are marred by the full moon. The best time to view will be just before dawn on April 23, when the constellation Lyra is overhead and the moon will be near to setting.
With all of these great things to spot in the sky this month, be sure to get outside and look up!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Jessica Wittner
Jessica Wittner, a lieutenant commander in the U.S. Navy, hails from California. A National Outdoor Leadership School alum, Wittner enjoys riding motorcycles and off-roading. https://go.nasa.gov/49CxwUN
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Behold—the space station of the future! (…from 1973)

This artist’s concept gives a cutaway view of the Skylab orbital workshop, which launched 50 years ago on May 14, 1973. Established in 1970, the Skylab Program's goals were to enrich our scientific knowledge of Earth, the sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials in the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth-resource observations.
Three crews visited Skylab and carried out 270 scientific and technical investigations in the fields of physics, astronomy, and biological sciences. They also proved that humans could live and work in outer space for extended periods of time, laying the groundwork for the International Space Station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Get the latest on women making history at NASA, our Juno mission, the Curiosity rover and move!

1. Women at NASA Making History, Creating the Future
Throughout Women's History Month, we've been presenting profiles of the women who are leading the way in deep space exploration.
+ Meet some of them

2. Juno and the Giant
Our Juno spacecraft made its fifth close flyby over giant Jupiter's mysterious cloud tops.
+ See the latest from the King of Planets

3. When the Road Gets Rough, the Tough Keep Rolling
A routine check of the aluminum wheels on our Curiosity Mars rover has found two small breaks on the rover's left middle wheel tread--the latest sign of wear and tear as the rover continues its journey, now approaching the 10-mile (16 kilometer) mark. But there's no sign the robotic geologist won't keep roving right through its ongoing mission.
+ Get the full report

4. What Do Mars and Dinosaurs Have in Common?
Our research reveals that volcanic activity at the giant Martian volcano Arsia Mons ceased about 50 million years ago, around the time of Earth's Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction, when large numbers of plant and animal species (including dinosaurs) went extinct. However, there's no reason to think the two events were more than a cosmic coincidence.
+ Learn how scientists pieced together the past

5. A Comet in Commotion
Images returned from the European Space Agency's Rosetta mission indicate that during its most recent trip through the inner solar system, the surface of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko was a very active place -- full of growing fractures, collapsing cliffs and massive rolling boulders.
+ See the many faces of Comet #67P

6. Next Generation Space Robot is Ingenious, Versatile--and Cute
The next rovers to explore another planet might bring along a scout. The Pop-Up Flat Folding Explorer Robot (PUFFER) in development at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory was inspired by origami. Its lightweight design is capable of flattening itself, tucking in its wheels and crawling into places rovers can't fit.
+ Meet PUFFER

7. Shadowy Dawn
According to data from our Dawn mission to Ceres, shadowed craters on the dwarf planet may be linked to the history of how the small world has been tilted over time by the gravity of planets like Jupiter.
+ Find out how understanding "cycles of obliquity" might solve solar system mysteries

8. On Orbit and Online
We’re developing a long-term technology demonstration project of what could become the high-speed internet of the sky. The Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD) will help engineers understand the best ways to operate laser communications systems, which could enable much higher data rates for connections between spacecraft and Earth, such as scientific data downlink and astronaut communications.
+ See how it will work

9. A Big Role for Small Sats in Deep Space Exploration
We selected 10 studies to develop mission concepts using CubeSats and other kinds of very small satellites to investigate Venus, Earth's moon, asteroids, Mars and the outer planets. "These small but mighty satellites have the potential to enable transformational science," said Jim Green, director of NASA's Planetary Science Division.
+ Get the small details

10. Rings Around the Red Planet?
It's possible that one of our closest neighbors had rings at one point -- and may have them again someday. At least, that's the theory put forth by NASA-funded scientists at Purdue University.
+ See more details about the once and future rings of Mars
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What Cargo is Launching in October to the International Space Station?
On Monday, Oct. 17, Orbital ATK is scheduled to send new science experiments to the International Space Station.

The Cygnus spacecraft will blast off from our Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia at 7:40 p.m. EDT carrying more than 5,100 pounds of science, supplies and equipment.
Let’s take a look at a few of these experiments:
Cool Flames
Low-temperature fires with no visible flames are known as cool flames. The Cool flames experiment examines these low-temperature combustion of droplets of a variety of fuels and additives in low gravity.

Why are we studying this? Data from this experiment could help scientists develop more efficient advanced engines and new fuels for use in space and on Earth.
Lighting Effects
Light plays a powerful role in our daily, or circadian, rhythms. Astronauts aboard the space station experience multiple cycles of light and dark every 24 hours, which, along with night shifts and the stresses of spaceflight, can affect their sleep quantity and quality.

The Lighting Effects investigation tests a new lighting system aboard the station designed to enhance crew health and keep their body clocks in proper sync with a more regular working and resting schedule.
Why are we studying this? Lighting manipulation has potential as a safe, non-pharmacological way to optimize sleep and circadian regulation on space missions. People on Earth, especially those who work night shifts, could also improve alertness and sleep by adjusting lighting for intensity and wavelength.
EveryWear
A user-friendly tablet app provides astronauts with a new and faster way to collect a wide variety of personal data. The EveryWear experiment tests use of this French-designed technology to record and transmit data on nutrition, sleep, exercise and medications. Astronauts use the app to complete questionnaires and keep medical and clinical logs. They wear a Smartshirt during exercise that records heart activity and body positions and transmits these data to the app. Finally, rather than manually recording everything that they eat, crew members scan barcodes on food packets to collect real-time nutritional data.

Why are we studying this? EveryWear has the potential for use in science experiments, biomedical support and technology demonstrations.
Fast Neturon Spectrometer
Outside the Earth’s magnetic field, astronauts are exposed to space radiation that can reduce immune response, increase cancer risk and interfere with electronics.

The Fast Neutron Spectrometer (FNS) experiment will help scientists understand high-energy neutrons, part of the radiation exposure experienced by crews during spaceflight, by studying a new technique to measure electrically neutral neutron particles.
Why are we studying this? This improved measurement will help protect crews on future exploration missions, like our journey to Mars.
Watch Launch
Ahead of launch, there will be various opportunities to learn more about the mission:

What’s on Board Science Briefing Saturday, Oct. 15 at 4 p.m. EDT Scientists and researchers will discuss some of the experiments being delivered to the station. Watch HERE.
Prelaunch News Briefing Saturday, Oct. 15 at 6 p.m. EDT Mission managers will provide an overview and status of launch operations. Watch HERE.
LAUNCH!!! Monday, Oct. 17 coverage begins at 6:45 p.m. EDT Watch live coverage and liftoff! Launch is scheduled for 7:40 p.m. EDT. Watch HERE.
Facebook Live Starting at 7:25 p.m. EDT you can stream live coverage of the launch on NASA’s Facebook page. Watch HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What are we doing at the Winter Olympics?
This Winter Olympics, our researchers are hoping for what a lot of Olympic athletes want in PyeongChang: precipitation and perfection.
Our researchers are measuring the quantity and type of snow falling on the slopes, tracks and halfpipes at the 2018 PyeongChang Winter Olympics and Paralympic games.

We are using ground instruments, satellite data and weather models to deliver detailed reports of current snow conditions and are testing experimental forecast models at 16 different points near Olympic event venues (shown below). The information is relayed every six hours to Olympic officials to help them account for approaching weather.

We are performing this research in collaboration with the Korea Meteorological Administration, as one of 20 agencies from about a dozen countries and the World Meteorological Organization’s World Weather Research Programme in a project called the International Collaborative Experiments for PyeongChang 2018 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games, or ICE-POP. The international team will make measurements from the start of the Olympics on Feb. 9 through the end of the Paralympics on March 18.

Image Credit: Republic of Korea
South Korea's diverse terrain makes this project an exciting, albeit challenging, endeavor for scientists to study snow events. Ground instruments provide accurate snow observations in easily accessible surfaces, but not on uneven and in hard to reach mountainous terrain. A satellite in space has the ideal vantage point, but space measurements are difficult because snow varies in size, shape and water content. Those variables mean the snowflakes won't fall at the same speed, making it hard to estimate the rates of snowfall. Snowflakes also have angles and planar "surfaces" that make it difficult for satellite radars to read.

The solution is to gather data from space and the ground and compare the measurements. We will track snowstorms and precipitation rates from space using the Global Precipitation Measurement mission, or GPM. The GPM Core Observatory is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency and coordinates with twelve other U.S. and international satellites to provide global maps of precipitation every 30 minutes (shown below).

We will complement the space data with 11 of our instruments observing weather from the ground in PyeongChang. These instruments are contributing to a larger international pool of measurements taken by instruments from the other ICE-POP participants: a total of 70 instruments deployed at the Olympics. We deployed the Dual-frequency, Dual-polarized, Doppler Radar system, usually housed at our Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, to PyeongChang (shown below) that measures the quantity and types of falling snow.

The data will help inform Olympic officials about the current weather conditions, and will also be incorporated into the second leg of our research: improving weather forecast models. Our Marshall Space Flight Center's Short-term Prediction Research and Transition Center (SPoRT) is teaming up with our Goddard Space Flight Center to use an advanced weather prediction model to provide weather forecasts in six-hour intervals over specific points on the Olympic grounds.

The above animation is our Unified Weather Research Forecast model (NU-WRF) based at Goddard. The model output shows a snow event on Jan. 14, 2018 in South Korea. The left animation labeled "precipitation type" shows where rain, snow, ice, and freezing rain are predicted to occur at each forecast time. The right labeled "surface visibility" is a measure of the distance that people can see ahead of them.
The SPoRT team will be providing four forecasts per day to the Korea Meteorological Administration, who will look at this model in conjunction with all the real-time forecast models in the ICE-POP campaign before relaying information to Olympic officials. The NU-WRF is one of five real-time forecast models running in the ICE-POP campaign.
For more information, watch the video below or read the entire story HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Tour NASA with One Direction

You might have heard, One Direction filmed their ‘Drag Me Down’ music video at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, and we know you’re dying to take a tour of everything they saw. So, here we go…
1) Space Exploration Vehicle (SEV)

Even though Louis is roving around Johnson Space Center in our Space Exploration Vehicle, its intended destination is quite different. The SEV will be used for in-space missions and for surface explorations of planetary bodies, including near-Earth asteroids and Mars!
2) Robonaut
Harry and Robonaut bonded during their visit to Johnson Space Center for the filming of their music video. This robot will help humans work and explore in space. Working side by side with humans, or going where the risks are too great for people, robots will make it so we never get ‘dragged down’!
3) Partial Gravity Simulator & Space Station Mockup Bike

You can find Niall floating around in our Partial Gravity Simulator, aka POGO, in the new music video. This tool is used to provide accurate simulations of reduced gravity. Astronauts use this for training and to learn how to perform tasks in space.
While Niall floats with POGO, Liam is training on the International Space Station Mockup Bike, aka CEVIS. This bike provides aerobic exercise and is used to countermeasure the harmful effects of exposure to microgravity while on the space station.
4) Orion Spacecraft

The Orion spacecraft will be the first of its kind that will carry humans to deep space and to Mars! It will be the safest, most advanced spacecraft ever built, and Harry, Niall, Louis and Liam all got to check it out.
5) T-38 Jets

Flying these T-38 jet trainers are an important part of preparing to be an astronaut. Flying and landing them acts as a real-life simulation for practicing spacecraft operations. They can even fly at supersonic up to Mach 1.6, and can put their pilots through more than seven Gs!
Kate Rubins’ Space Station Science Scrapbook
As a child, Kate Rubins dreamed of being an astronaut and a scientist. During the past four months aboard the International Space Station, that dream came full circle. She became the first person to sequence DNA in space, among other research during her recent mission, adding to her already impressive experience. She holds a doctorate in molecular biology, and previously led a lab of 14 researchers studying viruses, including Ebola.

Here’s a look back at Rubins in her element, conducting research aboard your orbiting laboratory.
Kate inside Destiny, the U.S. Laboratory Module
The U.S. national laboratory, called Destiny, is the primary research laboratory for U.S. payloads, supporting a wide range of experiments and studies contributing to health, safety, and quality of life for people all over the world.

Destiny houses the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG), in which Kate worked on the Heart Cells experiment.
Swabbing for Surface Samples
Microbes that can cause illness could present problems for current and future long duration space missions.

Understanding what microbe communities thrive in space habitats could help researchers design antimicrobial technology. Here, Kate is sampling various surfaces of the Kibo module for the Microbe-IV investigation.
Culturing Beating Heart Cells in Space
The Heart Cells investigation uses human skin cells that are induced to become stem cells, which can then differentiate into any type of cell.

Researchers forced the stem cells to grow into human heart cells, which Rubins cultured aboard the space station for one month.

Rubins described seeing the heart cells beat for the first time as “pretty amazing. First of all, there’s a few things that have made me gasp out loud up on board the [space] station. Seeing the planet was one of them, but I gotta say, getting these cells in focus and watching heart cells actually beat has been another pretty big one.”
Innovative Applied Research Experiment from Eli Lilly
The Hard to Wet Surfaces investigation from Eli Lilly, and sponsored by the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS), looks at liquid-solid interactions and how certain pharmaceuticals dissolve, which may lead to more potent and effective medicines in space and on Earth.

Rubins set up vials into which she injected buffer solutions and then set up photography to track how tablets dissolved in the solution in microgravity.
Capturing Dragon
Rubins assisted in the capture of the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft in July. The ninth SpaceX resupply mission delivered more than two thousand pounds of science to the space station.

Biological samples and additional research were returned on the Dragon spacecraft more than a month later.
Sliding Science Outside the Station
Science doesn’t just happen inside the space station. External Earth and space science hardware platforms are located at various places along the outside of the orbiting laboratory.

The Japanese Experiment Module airlock can be used to access the JEM Exposed Facility. Rubins installed the JEM ORU Transfer Interface (JOTI) on the JEM airlock sliding table used to install investigations on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory.
Installing Optical Diagnostic Instrument in the MSG
Rubins installed an optical diagnostic instrument in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) as part of the Selective Optical Diagnostics Instrument (SODI-DCMIX) investigation. Molecules in fluids and gases constantly move and collide.

When temperature differences cause that movement, called the Soret effect, scientists can track it by measuring changes in the temperature and movement of mass in the absence of gravity. Because the Soret effect occurs in underground oil reservoirs, the results of this investigation could help us better understand such reservoirs.
The Sequencing of DNA in Space
When Rubins’ expedition began, DNA had never been sequenced in space. Within just a few weeks, she and the Biomolecule Sequencer team had sequenced their one billionth “base” – the unit of DNA - aboard the orbiting laboratory.

The Biomolecule Sequencer investigation seeks to demonstrate that DNA sequencing in microgravity is possible, and adds to the suite of genomics capabilities aboard the space station.
Studying Fluidic Dynamics with SPHERES
The SPHERES-Slosh investigation examines the way liquids move inside containers in a microgravity environment. The phenomena and mechanics associated with such liquid movement are still not well understood and are very different than our common experiences with a cup of coffee on Earth.

Rockets deliver satellites to space using liquid fuels as a power source, and this investigation plans to improve our understanding of how propellants within rockets behave in order to increase the safety and efficiency of future vehicle designs. Rubins conducted a series of SPHERES-Slosh runs during her mission.
Retrieving Science Samples for Their Return to Earth
Precious science samples like blood, urine and saliva are collected from crew members throughout their missions aboard the orbiting laboratory.

They are stored in the Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) until they are ready to return to Earth aboard a Soyuz or SpaceX Dragon vehicle.
Measuring Gene Expression of Biological Specimens in Space
Our WetLab-2 hardware system is bringing to the space station the technology to measure gene expression of biological specimens in space, and to transmit the results to researchers on Earth at the speed of light.

Rubins ran several WetLab-2 RNA SmartCycler sessions during her mission.
Studying the First Expandable Habitat Module on the Space Station
The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is the first expandable habitat to be installed on the space station. It was expanded on May 28, 2016.

Expandable habitats are designed to take up less room on a spacecraft, but provide greater volume for living and working in space once expanded. Rubins conducted several evaluations inside BEAM, including air and surface sampling.
Better Breathing in Space and Back on Earth
Airway Monitoring, an investigation from ESA (the European Space Agency), uses the U.S. airlock as a hypobaric facility for performing science. Utilizing the U.S. airlock allows unique opportunities for the study of gravity, ambient pressure interactions, and their effect on the human body.

This investigation studies the occurrence and indicators of airway inflammation in crew members, using ultra-sensitive gas analyzers to evaluate exhaled air. This could not only help in spaceflight diagnostics, but that also hold applications on earth within diagnostics of similar conditions, for example monitoring of asthma.
Hot Science with Cool Flames
Fire behaves differently in space, where buoyant forces are removed. Studying combustion in microgravity can increase scientists’ fundamental understanding of the process, which could lead to improvement of fire detection and suppression systems in space and on Earth.

Many combustion experiments are performed in the Combustion Integration Rack (CIR) aboard the space station. Rubins replaced two Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Igniter Tips as part of the CIR igniter replacement operations.
Though Rubins is back on Earth, science aboard the space station continues, and innovative investigations that seek to benefit humans on Earth and further our exploration of the solar system are ongoing. Follow @ISS_Research to keep up with the science happening aboard your orbiting laboratory.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Fun Facts About Mars

Mars is a cold desert world, and is the fourth planet from the sun. It is half the diameter of Earth and has the same amount of dry land. Like Earth, Mars has seasons, polar ice caps, volcanoes, canyons and weather, but its atmosphere is too thin for liquid water to exist for long on the surface. There are signs of ancient floods on the Red Planet, but evidence for water now exists mainly in icy soil and thin clouds.

Earth has one, Mars has two…moons of course! Phobos (fear) and Deimos (panic) are the Red Planet’s two small moons. They are named after the horses that pulled the chariot of the Greek war god Ares, the counterpart to the Roman war god Mars.

The diameter of Mars is 4220 miles (6792 km). That means that the Red Planet is twice as big as the moon, but the Earth is twice as big as Mars.

Since Mars has less gravity than Earth, you would weigh 62% less than you do here on our home planet. Weigh yourself here on the Planets App. What’s the heaviest thing you’ve ever lifted? On Mars, you could have lifted more than twice that! Every 10 pounds on Earth only equals 4 pounds on the Red Planet. Find out why HERE.

Mass is the measurement of the amount of matter something contains. Mars is about 1/10th of the mass of Earth.

Mars and Earth are at their closest point to each other about every two years, with a distance of about 33 million miles between them at that time. The farthest that the Earth and Mars can be apart is: 249 million miles. This is due to the fact that both Mars and Earth have elliptical orbits and Mars’ orbit is tilted in comparison with the Earth’s. They also orbit the sun at different rates.

The temperature on Mars can be as high as 70 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) or as low as about –225 degrees Fahrenheit (-153 degrees Celsius). How hot or cold the surface varies between day and night and among seasons. Mars is colder than Earth because it is farther from the sun.

You know that onions have layers, but did you know that Mars has layers too? Like Earth, Mars has a crust, a mantle and a core. The same stuff even makes up the planet layers: iron and silicate.

Ever wonder why it’s so hard launching things to space? It’s because the Earth has a log of gravity! Gravity makes things have weight, and the greater the gravity, the more it weights. On Mars, things weigh less because the gravity isn’t as strong.

Take a deep breath. What do you think you just breathed in? Mostly Nitrogen, about a fifth of that breath was Oxygen and the rest was a mix of other gases. To get the same amount of oxygen from one Earth breath, you’d have to take around 14,500 breaths on Mars! With the atmosphere being 100 times less dense, and being mostly carbon dioxide, there’s not a whole lot of oxygen to breathe in.

Mars has about 15% of Earth’s volume. To fill Earth’s volume, it would take over 6 Mars’ volumes.
For more fun Mars facts, visit HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 john-erby liked this · 3 years ago
john-erby liked this · 3 years ago -
 2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago
2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago -
 cosmofrog liked this · 5 years ago
cosmofrog liked this · 5 years ago -
 anotherbug2000 liked this · 6 years ago
anotherbug2000 liked this · 6 years ago -
 fridakahloblvd liked this · 7 years ago
fridakahloblvd liked this · 7 years ago -
 neginegiiyahoi liked this · 7 years ago
neginegiiyahoi liked this · 7 years ago -
 dirtycreekwater liked this · 7 years ago
dirtycreekwater liked this · 7 years ago -
 stellar-voyager liked this · 7 years ago
stellar-voyager liked this · 7 years ago -
 cumbercrush liked this · 7 years ago
cumbercrush liked this · 7 years ago -
 decomposing-rey liked this · 7 years ago
decomposing-rey liked this · 7 years ago -
 designarttype liked this · 7 years ago
designarttype liked this · 7 years ago -
 20thcen reblogged this · 7 years ago
20thcen reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 caulfveld liked this · 7 years ago
caulfveld liked this · 7 years ago -
 riperony-blog liked this · 8 years ago
riperony-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 charleshdv-blog liked this · 8 years ago
charleshdv-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 delaiziken reblogged this · 8 years ago
delaiziken reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 justanoldfashiontumblog liked this · 8 years ago
justanoldfashiontumblog liked this · 8 years ago -
 mega-otaku liked this · 8 years ago
mega-otaku liked this · 8 years ago -
 wandering-mech-engineer liked this · 8 years ago
wandering-mech-engineer liked this · 8 years ago -
 agentwhy liked this · 8 years ago
agentwhy liked this · 8 years ago -
 turtleangel94 liked this · 8 years ago
turtleangel94 liked this · 8 years ago -
 babamjan liked this · 8 years ago
babamjan liked this · 8 years ago -
 creamysins liked this · 8 years ago
creamysins liked this · 8 years ago -
 i-need-some-space-man-blog liked this · 8 years ago
i-need-some-space-man-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 rosewineatmidnight liked this · 8 years ago
rosewineatmidnight liked this · 8 years ago -
 madebyfree liked this · 8 years ago
madebyfree liked this · 8 years ago -
 shigawahhhhh liked this · 8 years ago
shigawahhhhh liked this · 8 years ago -
 onyxwolf liked this · 8 years ago
onyxwolf liked this · 8 years ago -
 dinkerton liked this · 8 years ago
dinkerton liked this · 8 years ago -
 lilytardis12 liked this · 8 years ago
lilytardis12 liked this · 8 years ago -
 moominmuffin liked this · 8 years ago
moominmuffin liked this · 8 years ago -
 kinda-funny-sometimes liked this · 8 years ago
kinda-funny-sometimes liked this · 8 years ago -
 page-vacat liked this · 8 years ago
page-vacat liked this · 8 years ago -
 kiraistired liked this · 8 years ago
kiraistired liked this · 8 years ago -
 grrachel-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago
grrachel-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago -
 scienceasfuck liked this · 8 years ago
scienceasfuck liked this · 8 years ago -
 mrsspooky liked this · 8 years ago
mrsspooky liked this · 8 years ago -
 ashtreenomy liked this · 8 years ago
ashtreenomy liked this · 8 years ago -
 maskedmew liked this · 8 years ago
maskedmew liked this · 8 years ago -
 playthehero liked this · 8 years ago
playthehero liked this · 8 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts