Hopefully Not A Total Dumb Question But, YOUR Ultimate Goal As An Astronaut?
Hopefully not a total dumb question but, YOUR ultimate goal as an astronaut?
More Posts from Nasa and Others
An Exo-What...?

Simply put, an exoplanet is a planet that orbits another star. That said, just because a planet orbits a star (like Earth) does not mean that it is automatically stable for life. The planet must be within the habitable zone, which is the area around a star in which water has the potential to be liquid…aka not so close that all the water would evaporate, and not too far away where all the water would freeze.
Recently, with the help of our Kepler spacecraft, scientists have discovered the most Earth-like exoplanet ever, Kepler-452b. Pretty cool! This chart shows 12 other exoplanet discoveries that are less than twice the size of Earth, and live in the habitable zone of their host star. Kepler-452b is special because all previous findings have orbited stars that are smaller and cooler than Earth’s.

You may be thinking, “Okay, so what? There’s an Earth-like planet that spins around a similar sized sun.” Well, Kepler-452b orbits its sun at nearly the same distance from its star as Earth does from our sun, which means that conditions on the plant could be similar to those here on Earth!

We can already guess your next question…”When are we going to Kepler-452b?!” Well, this planet is located in the constellation Cygnus which is 1,400 light-years away, so not anytime soon. However, our Kepler spacecraft continues to search for Earth-like exoplanets and gather important scientific information about them.
21 Years of Amazing Earth Imagery
On April 29, 1999, NASA Earth Observatory started delivering science stories and imagery to the public through the Internet. Today, we turn 21! So much has changed in the past two decades...
One of the most notable changes is the way we view our home planet. Check out some of the beautiful imagery of our planet over the past 21 years.
2000: Pine Island Glacier

Most people will never see Pine Island Glacier in person. Located near the base of the Antarctic Peninsula—the “thumb” of the continent—the glacier lies more than 2,600 kilometers (1,600 miles) from the tip of South America. That’s shorter than a cross-country flight from New York to Los Angeles, but there are no runways on the glacier and no infrastructure. Only a handful of scientists have ever set foot on its ice.
This animation shows a wide view of Pine Island Glacier and the long-term retreat of its ice front. Images were acquired by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on our Terra satellite from 2000 to 2019. Notice that there are times when the front appears to stay in the same place or even advance, though the overall trend is toward retreat. Read more.
2002: The Blue Marble

In February 2002, Earth Observatory published this “blue marble” image based on the most detailed collection of true-color imagery of the entire Earth at that time. Using a collection of satellite-based observations, scientists and visualizers stitched together months of observations of the land surface, oceans, sea ice and clouds into a seamless, true-color mosaic of every square kilometer (.386 square mile) of our planet. Most of the information contained in this image came from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS), illustrating the instrument's outstanding capacity to act as an integrated tool for observing a variety of terrestrial, oceanic and atmospheric features of the Earth. Read more.
2009: Tsauchab River Bed

The Tsauchab River is a famous landmark for the people of Namibia and tourists. Yet few people have ever seen the river flowing with water. In December 2009, an astronaut on the International Space Station caught this glimpse of the Tsauchab River bed jutting into the sea of red dunes. It ends in a series of light-colored, silty mud holes on the dry lake floor.
Like several other rivers around the Namib Desert, the Tsauchab brings sediment down from the hinterland toward the coastal lowland. This sediment is then blown from the river beds, and over tens of millions of years it has accumulated as the red dunes of the Namib Sand Sea. Read more.
2012: Manning Island and Foxe Basin, Canada

Although it may look like a microscope’s view of a thin slice of mineral-speckled rock, this image was actually acquired in space by the Earth Observing-1 satellite in July 2012. It shows a small set of islands and a rich mixture of ice in Foxe Basin, the shallow northern reaches of Hudson Bay.
The small and diverse sizes of the ice floes indicate that they were melting. The darkest colors in the image are open water. Snow-free ice appears gray, while snow-covered ice appears white. The small, dark features on many of the floes are likely melt ponds. Read more.
2013: A Lava Lamp Look at the Atlantic

Stretching from tropical Florida to the doorstep of Europe, this river of water carries a lot of heat, salt, and history. The Gulf Stream is an important part of the global ocean conveyor belt that moves water and heat across the North Atlantic from the equator toward the poles. It is one of the strongest currents on Earth, and one of the most studied.
This image shows a small portion of the Gulf Stream as it appears in infrared imagery. Data for this image was acquired on April 9, 2013, by the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) on the Landsat 8 satellite. TIRS observes in wavelengths of 10.9 micrometers and 12.0 micrometers. The image above is centered at 33.06° North latitude, 73.86° West longitude, about 500 kilometers (300 miles) east of Charleston, South Carolina. Read more.
2016: Curious Ensemble of Wonderful Features

When John Wesley Powell explored the Colorado River in 1869, he made the first thorough survey of one of the last blank spots on the map. The expedition began in May at Green River, Wyoming, and ended three months later at the confluence of the Colorado and Virgin Rivers in present-day Nevada.
About two months into their journey, the nine men of the expedition found themselves in Glen Canyon. As the men traveled along the serpentine river channel, they encountered what Powell later described in Canyons of Colorado as a “curious ensemble of wonderful features.”
From above, the view of Glen Canyon is equally arresting. In 2016, an astronaut aboard the International Space Station took several photographs that were combined to make a long mosaic. The water has an unnatural shade of blue because of sunglint, an optical phenomenon that occurs when sunlight reflects off the surface of water at the same angle that a camera views it. Click here to see the long mosaic.
2019: Lena Delta Shakes Off Water

For most of the year, the Lena River Delta—a vast wetland fanning out from northeast Siberia into the Arctic Ocean—is either frozen over and barren or thawed out and lush. Only briefly will you see it like this.
After seven months encased in snow and ice, the delta emerges for the short Arctic summer. The transition happens fast. The animation above, composed of images from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on our Aqua satellite, shows the transformation from June 3-10, 2019. Read more.
2020: Making Waves in the Andaman Sea

When tides, currents and gravity move water masses over seafloor features, they can create wave actions within the ocean. Oceanographers began studying these internal waves from ships in the 1960s, and the modern era of satellites has made it possible to see them on a grand scale. The Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 captured these images of the Andaman Sea on November 29, 2019. The reflection of the Sun on the ocean—sunglint—helps make the internal waves visible.
Internal waves form because the ocean is layered. Deep water tends to be colder, denser and saltier, while shallower water is often warmer, lighter and fresher. The differences in density and salinity cause layers of the ocean to behave like different fluids. When tides, currents, gravity and Earth’s rotation move these different water masses over seafloor formations (such as ridges or canyons), they create waves within the sea. Read more.
These images were taken from NASA Earth Observatory!
Interested in receiving Earth Observatory's Images of the Day? Subscribe to our newsletters or RSS feeds.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How Well Do you Know Neptune?

Dark, cold and whipped by supersonic winds, Neptune is the last of the hydrogen and helium gas giants in our solar system. More than 30 times as far from the sun as Earth, the planet takes almost 165 Earth years to orbit our sun! In fact, in 2011, Neptune completed its first orbit since its discovery in 1846.

Here are a few things you might not know about the windiest planet:
If the sun were as tall as a typical front door, the Earth would be the size of a nickel and Neptune would be about as big as a baseball.
Neptune orbits our sun, a star. Neptune is the eighth planet from the sun at a distance of about 4.5 billion km (2.8 billion miles) or 30.07 AU.
One day on Neptune takes about 16 hours (the time it takes for Neptune to rotate or spin once)
Neptune makes a complete orbit around the sun (a year in Neptunian time) in about 165 Earth years (60,190 Earth days)
Neptune has six rings
Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to have visited Neptune
Neptune has 13 moons. They are named after various sea gods and nymphs in Greek mythology
Did you know that Neptune has storms?

Similar to Jupiter, Neptune has storms that create gigantic spots in its atmosphere…well, it did. When Voyager 2 flew past Neptune in 1989, it tracked and imaged the “Great Dark Spot” — a storm larger than the entire Earth! When the Hubble Space Telescope imaged Neptune the spot had disappeared, only to be replaced with two smaller storms, which in turn also disappeared.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
The Great Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn

Credits: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Have you noticed two bright objects in the sky getting closer together with each passing night? It’s Jupiter and Saturn doing a planetary dance that will result in the Great Conjunction on Dec. 21. On that day, Jupiter and Saturn will be right next to each other in the sky – the closest they have appeared in nearly 400 years!
Skywatching Tips from NASA

Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
For those who would like to see this phenomenon for themselves, here’s what to do:
Find a spot with an unobstructed view of the sky, such as a field or park. Jupiter and Saturn are bright, so they can be seen even from most cities.
An hour after sunset, look to the southwestern sky. Jupiter will look like a bright star and be easily visible. Saturn will be slightly fainter and will appear slightly above and to the left of Jupiter until December 21, when Jupiter will overtake it and they will reverse positions in the sky.
The planets can be seen with the unaided eye, but if you have binoculars or a small telescope, you may be able to see Jupiter’s four large moons orbiting the giant planet.
How to Photograph the Conjunction

Credits: NASA/Bill Dunford
Saturn and Jupiter are easy to see without special equipment, and can be photographed easily on DSLR cameras and many cell phone cameras. Here are a few tips and tricks:
These planets are visible in the early evening, and you'll have about 1-2 hours from when they are visible, to when they set. A photo from the same location can look completely different just an hour later!
Using a tripod will help you hold your camera steady while taking longer exposures. If you don’t have a tripod, brace your camera against something – a tree, a fence, or a car can all serve as a tripod for a several-second exposure.
The crescent Moon will pass near Jupiter and Saturn a few days before the conjunction. Take advantage of it in your composition!
Get more tips HERE.
Still have questions about the Great Conjunction?
Our NASA expert answered questions from social media on an episode of NASA Science Live on Thursday, Dec. 17. Watch the recording HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Lasers Bring Internet Speeds to Space
Pew. Pew. Lasers in space!
Iconic movie franchises like Star Wars and Star Trek feature futuristic laser technologies, but space lasers aren’t limited to the realm of science fiction. In fact, laser communications technologies are changing the way missions transmit their data. The Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD) blasts into space this weekend, demonstrating the unique – and totally awesome – capabilities of laser communications systems.

Currently, NASA missions rely on radio frequency to send data to Earth. While radio has served the agency well since the earliest days of spaceflight, there are significant benefits to laser systems. Just as the internet has gone from dial-up to high-speed connections, lasers communications’ higher frequency allows missions to send much more information per second than radio systems. With laser communications, it would only take nine days to transmit a complete map of Mars back to Earth, compared to nine weeks with radio frequency systems.

LCRD will demonstrate these enhanced capabilities from 22,000 miles above Earth’s surface. And although the mission uses lasers, these lasers are not visible to the human eye. Once in orbit, the mission will perform experiments using two telescopes on Earth that will relay data through the spacecraft from one site to the other over an optical communications link. These experiments will help NASA and the aerospace community understand the operational challenges of using lasers to communicate to and from space.

On Earth, there are ground stations telescopes that will capture LCRD’s laser signal and send the data to the mission operations center in New Mexico. The two ground stations are located on Haleakalā, Hawaii and Table Mountain, California. These picturesque locations weren’t chosen because they’re beautiful, but rather for their mostly clear skies. Clouds – and other atmospheric disturbances – can disrupt laser signals. However, when those locations do get cloudy, we’ve developed corrective technologies to ensure we receive and successfully decode signals from LCRD.

This demonstration will help NASA, researchers, and space companies learn more about potential future applications for laser communications technologies. In the next few years, NASA will launch additional laser missions to the Moon on Artemis II and to the asteroid belt, even deeper into space. These missions will give us insight on the use of laser communications further in space than ever before.

Ultimately, laser systems will allow us to glean more information from space. This means more galaxy pics, videos of deep space phenomena, and live, 4K videos from astronauts living and working in space.
Laser communications = more data in less time = more discoveries.
If laser communications interests you, check out our Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) Internship Project. This program provides high school, undergrad, graduate, and even Ph.D. candidates with internship opportunities in space communications areas – like laser comm.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
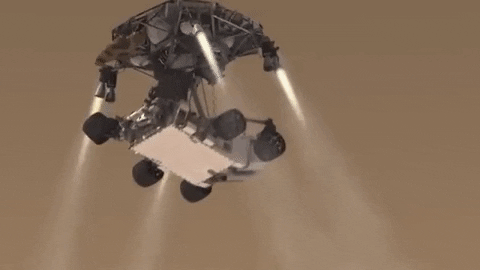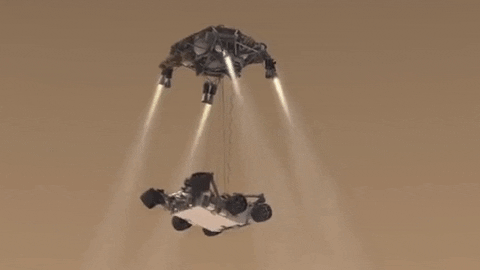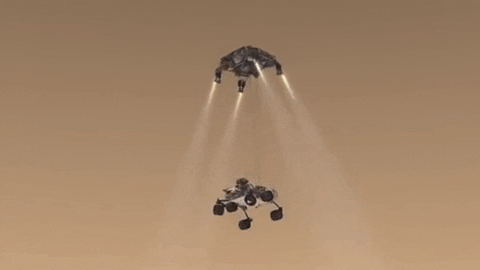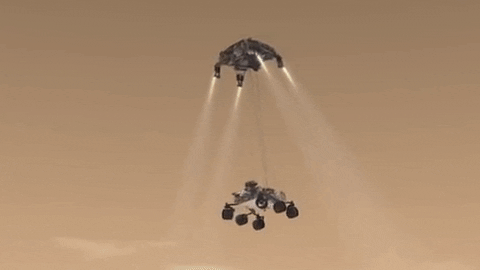
INCOMING! Roving scientist to arrive on Mars.
Save the date! One year from today, Feb. 18, 2021, our next rover is set to land on Mars. Get to know #Mars2020 now! Click here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Game Time: Final Voting for Tournament Earth
The moment has arrived- it's time to decide the NASA Earth Observatory's all-time best image. After four grueling rounds of voting, two contenders remain: Ocean Sand, Bahamas (#5 seed) versus Raikoke Erupts (#6 seed).

The road to the finals has been full of surprises. All top seeds have been knocked out. In one semifinal, Ocean Sand garnered 50.6 percent of the votes to squeak out a win over the overall favorite, Twin Blue Marbles. In the other matchup, Raikoke Erupts trounced Where the Dunes End, 66.5 to 33.5 percent.
Now you have to pick a champion. Will it be a gorgeous, artistic image from the very early years of Earth Observatory or stunning natural-color views of an explosive event from 2019? Which image will you crown as the best in the EO archives: Ocean Sand, Bahamas or Raikoke Erupts? Voting ends on April 28 at 9 a.m. U.S. Eastern Time.
Thank you for helping us celebrate Earth Observatory’s 20th anniversary and the 50th anniversary of Earth Day!
Vote here: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/tournament-earth
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
10 Things: Calling All Pluto Lovers
June 22 marks the 40th anniversary of Charon’s discovery—the dwarf planet Pluto’s largest and first known moon. While the definition of a planet is the subject of vigorous scientific debate, this dwarf planet is a fascinating world to explore. Get to know Pluto’s beautiful, fascinating companion this week.
1. A Happy Accident

Astronomers James Christy and Robert Harrington weren’t even looking for satellites of Pluto when they discovered Charon in June 1978 at the U.S. Naval Observatory Flagstaff Station in Arizona – only about six miles from where Pluto was discovered at Lowell Observatory. Instead, they were trying to refine Pluto's orbit around the Sun when sharp-eyed Christy noticed images of Pluto were strangely elongated; a blob seemed to move around Pluto.
The direction of elongation cycled back and forth over 6.39 days―the same as Pluto's rotation period. Searching through their archives of Pluto images taken years before, Christy then found more cases where Pluto appeared elongated. Additional images confirmed he had discovered the first known moon of Pluto.
2. Forever and Always

Christy proposed the name Charon after the mythological ferryman who carried souls across the river Acheron, one of the five mythical rivers that surrounded Pluto's underworld. But Christy also chose it for a more personal reason: The first four letters matched the name of his wife, Charlene. (Cue the collective sigh.)
3. Big Little Moon

Charon—the largest of Pluto’s five moons and approximately the size of Texas—is almost half the size of Pluto itself. The little moon is so big that Pluto and Charon are sometimes referred to as a double dwarf planet system. The distance between them is 12,200 miles (19,640 kilometers).
4. A Colorful and Violent History

Many scientists on the New Horizons mission expected Charon to be a monotonous, crater-battered world; instead, they found a landscape covered with mountains, canyons, landslides, surface-color variations and more. High-resolution images of the Pluto-facing hemisphere of Charon, taken by New Horizons as the spacecraft sped through the Pluto system on July 14 and transmitted to Earth on Sept. 21, reveal details of a belt of fractures and canyons just north of the moon’s equator.
5. Grander Canyon

This great canyon system stretches more than 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) across the entire face of Charon and likely around onto Charon’s far side. Four times as long as the Grand Canyon, and twice as deep in places, these faults and canyons indicate a titanic geological upheaval in Charon’s past.
6. Officially Official

In April 2018, the International Astronomical Union—the internationally recognized authority for naming celestial bodies and their surface features—approved a dozen names for Charon’s features proposed by our New Horizons mission team. Many of the names focus on the literature and mythology of exploration.
7. Flying Over Charon
This flyover video of Charon was created thanks to images from our New Horizons spacecraft. The “flight” starts with the informally named Mordor (dark) region near Charon’s north pole. Then the camera moves south to a vast chasm, descending to just 40 miles (60 kilometers) above the surface to fly through the canyon system.
8. Strikingly Different Worlds

This composite of enhanced color images of Pluto (lower right) and Charon (upper left), was taken by New Horizons as it passed through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015. This image highlights the striking differences between Pluto and Charon. The color and brightness of both Pluto and Charon have been processed identically to allow direct comparison of their surface properties, and to highlight the similarity between Charon’s polar red terrain and Pluto’s equatorial red terrain.
9. Quality Facetime

Charon neither rises nor sets, but hovers over the same spot on Pluto's surface, and the same side of Charon always faces Pluto―a phenomenon called mutual tidal locking.
10. Shine On, Charon

Bathed in “Plutoshine,” this image from New Horizons shows the night side of Charon against a star field lit by faint, reflected light from Pluto itself on July 15, 2015.
Read the full version of this week’s ‘10 Things to Know’ article on the web HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Rocket Launches and Rising Seas
At NASA, we’re not immune to effects of climate change. The seas are rising at NASA coastal centers – the direct result of warming global temperatures caused by human activity. Several of our centers and facilities were built near the coast, where there aren’t as many neighbors, as a safety precaution. But now the tides have turned and as sea levels rise, these facilities are at greater risk of flooding and storms.

Global sea level is increasing every year by 3.3 millimeters, or just over an eighth of an inch, and the rate of rise is speeding up over time. The centers within range of rising waters are taking various approaches to protect against future damage.

Kennedy Space Center in Florida is the home of historic launchpad 39A, where Apollo astronauts first lifted off for their journey to the Moon. The launchpad is expected to flood periodically from now on.

Like Kennedy, Wallops Flight Facility on Wallops Island, Virginia has its launchpads and buildings within a few hundred feet of the Atlantic Ocean. Both locations have resorted to replenishing the beaches with sand as a natural barrier to the sea.

Native vegetation is planted to help hold the sand in place, but it needs to be replenished every few years.

At the Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, instead of building up the ground, we’re hardening buildings and moving operations to less flood-prone elevations. The center is bounded by two rivers and the Chesapeake Bay.
The effects of sea level rise extend far beyond flooding during high tides. Higher seas can drive larger and more intense storm surges – the waves of water brought by tropical storms.

In 2017, Hurricane Harvey brought flooding to the astronaut training facility at Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Now we have installed flood resistant doors, increased water intake systems, and raised guard shacks to prevent interruptions to operations, which include astronaut training and mission control.

Our only facility that sits below sea level already is Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Onsite pumping systems protected the 43-acre building, which has housed Saturn rockets and the Space Launch System, from Hurricane Katrina. Since then, we’ve reinforced the pumping system so it can now handle double the water capacity.

Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley is going one step farther and gradually relocating farther south and to several feet higher in elevation to avoid the rising waters of the San Francisco Bay.
Understanding how fast and where seas will rise is crucial to adapting our lives to our changing planet.

We have a long-standing history of tracking sea level rise, through satellites like the TOPEX-Poseidon and the Jason series, working alongside partner agencies from the United States and other countries.

We just launched the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite—a U.S.-European partnership—which will use electromagnetic signals bouncing off Earth’s surface to make some of the most accurate measurements of sea levels to date.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What's Up - December 2017
What’s Up For December? Geminid and Ursid meteor showers & winter constellations!

This month hosts the best meteor shower of the year and the brightest stars in familiar constellations.

The Geminds peak on the morning of the 14th, and are active from December 4th through the 17th. The peak lasts for a full 24 hours, meaning more worldwide meteor watchers will get to see this spectacle.

Expect to see up to 120 meteors per hour between midnight and 4 a.m. but only from a dark sky. You'll see fewer after moonrise at 3:30 a.m. local time.

In the southern hemisphere, you won't see as many, perhaps 10-20 per hour, because the radiant never rises above the horizon.

Take a moment to enjoy the circle of constellations and their brightest stars around Gemini this month.

Find yellow Capella in the constellation Auriga.

Next-going clockwise--at 1 o'clock find Taurus and bright reddish Aldebaran, plus the Pleiades.

At two, familiar Orion, with red Betelguese, blue-white Rigel, and the three famous belt stars in-between the two.

Next comes Leo, and its white lionhearted star, Regulus at 7 o'clock.

Another familiar constellation Ursa Major completes the view at 9 o'clock.

There's a second meteor shower in December, the Ursids, radiating from Ursa Minor, the Little Dipper. If December 22nd and the morning of December 23rd are clear where you are, have a look at the Little Dipper's bowl, and you might see about ten meteors per hour. Watch the full What’s Up for December Video:
There are so many sights to see in the sky. To stay informed, subscribe to our What’s Up video series on Facebook. Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 watch reblogged this · 1 year ago
watch reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 ducktaleswoo-oo liked this · 4 years ago
ducktaleswoo-oo liked this · 4 years ago -
 ultra-rare-pegacorn liked this · 5 years ago
ultra-rare-pegacorn liked this · 5 years ago -
 just-peachy-posts reblogged this · 5 years ago
just-peachy-posts reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 just-peachy-posts liked this · 5 years ago
just-peachy-posts liked this · 5 years ago -
 beautisofull liked this · 5 years ago
beautisofull liked this · 5 years ago -
 shailendra65631 reblogged this · 5 years ago
shailendra65631 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 shailendra65631 liked this · 5 years ago
shailendra65631 liked this · 5 years ago -
 cherryobvious liked this · 5 years ago
cherryobvious liked this · 5 years ago -
 adt-space reblogged this · 5 years ago
adt-space reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sadinhoustonn-blog liked this · 5 years ago
sadinhoustonn-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 propinquitine reblogged this · 5 years ago
propinquitine reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 just-my-broken-feelings reblogged this · 5 years ago
just-my-broken-feelings reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 smol-bean-dragon-hoard liked this · 5 years ago
smol-bean-dragon-hoard liked this · 5 years ago -
 spaciegracie07 liked this · 5 years ago
spaciegracie07 liked this · 5 years ago -
 mariacandela705 liked this · 5 years ago
mariacandela705 liked this · 5 years ago -
 whitecatnatalie liked this · 5 years ago
whitecatnatalie liked this · 5 years ago -
 aki-kalchek-blog liked this · 5 years ago
aki-kalchek-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 weird-is-all-ive-got reblogged this · 5 years ago
weird-is-all-ive-got reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 readinginzerogravity liked this · 5 years ago
readinginzerogravity liked this · 5 years ago -
 oshinytomato liked this · 5 years ago
oshinytomato liked this · 5 years ago -
 books-coffe-rain-blog liked this · 5 years ago
books-coffe-rain-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 puppy-n-ottr liked this · 5 years ago
puppy-n-ottr liked this · 5 years ago -
 meliodude liked this · 5 years ago
meliodude liked this · 5 years ago -
 zelink-nalu liked this · 5 years ago
zelink-nalu liked this · 5 years ago -
 eevamaxph liked this · 5 years ago
eevamaxph liked this · 5 years ago -
 lovearcangel liked this · 5 years ago
lovearcangel liked this · 5 years ago -
 16fahri liked this · 5 years ago
16fahri liked this · 5 years ago -
 rosaliachristian liked this · 5 years ago
rosaliachristian liked this · 5 years ago -
 lilyruthconell liked this · 5 years ago
lilyruthconell liked this · 5 years ago -
 mrgneiss liked this · 5 years ago
mrgneiss liked this · 5 years ago -
 delicatemusictale liked this · 5 years ago
delicatemusictale liked this · 5 years ago -
 realspaceships liked this · 5 years ago
realspaceships liked this · 5 years ago -
 tracksuitmafia-bro liked this · 5 years ago
tracksuitmafia-bro liked this · 5 years ago -
 lockvogel liked this · 5 years ago
lockvogel liked this · 5 years ago -
 nonbinnerybuddy liked this · 5 years ago
nonbinnerybuddy liked this · 5 years ago -
 bumblebaubles liked this · 5 years ago
bumblebaubles liked this · 5 years ago -
 darkestdawn liked this · 5 years ago
darkestdawn liked this · 5 years ago -
 terrylhills liked this · 5 years ago
terrylhills liked this · 5 years ago -
 mariareneblog-blog liked this · 5 years ago
mariareneblog-blog liked this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts