Have You Ever Seen An Eclipse From Space? Check It Out
Have You Ever Seen An Eclipse From Space? Check It Out
On June 21, 2020 an annular solar eclipse passed over parts of Asia and Africa. Eclipses happen when the Moon lines up just right between the Sun and Earth, allowing it to block out part or all of the Sun’s bright face and cast a shadow on Earth.

On that day, the International Space Station was orbiting over Kazakhstan and into China when this picture of the solar eclipse shadowing a portion of the Asian continent was captured by an external high definition camera. In the left foreground, is the H-II Transfer Vehicle-9 from Japan.

Here is another angle as seen from the orbital lab. In the left foreground, is the Progress 74 resupply ship from Russia.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
5 Fun Things To Do Without Gravity
Astronauts onboard the International Space station are typically active for at least 9 1/2 hours per day doing science, exercising and maintaining systems. Excluding scheduled time for sleep and lunch, astronauts have only 4 hours of free time during the work week, and that includes time for meals and general hygiene.
Even with a loaded calendar, the few who have such an opportunity to live in the microgravity environment find ways to make the most of this experience. Here are just a few of their favorite things about living in space:
Flying

One of the most self-explanatory (and most fun!) aspects of living in space for the astronauts is “flying”. In space there is no up or down, so there is no floor or ceiling. There are rails throughout the space station that astronauts use to push themselves among the modules.
Eating

Astronauts actually describe the food on the space station as quite tasty! In part, that’s because they have a large role in choosing their own meals. Over time though, a lot of astronauts experience desensitized taste buds from the shifting fluid to their head. Toward the end of their expedition, spicy foods tend to be their favorites because of this phenomenon.
Drinking

Liquid behaves very differently in space than it does on Earth. Astronauts cannot simply pour a cup of coffee into a mug. Without gravity, it would stick to the walls of the cup and would be very difficult to sip. Most of the time, astronauts fill a bag with liquid and use a special straw with a clamp to keep the contents from flying out.
Playing Games

The space station crew occasionally gets downtime which they can spend however they please. Sometimes they watch a movie, read a book or take photos of Earth from the Cupola windows. Other times they invent games to play with each other, and each crew tends to come up with new games. Sometimes it can be hitting a target, flying from one end of the station to the other fastest or playing zero-gravity sports.
Going Out For A Walk

Preparing and executing a spacewalk can take around 8 to 12 hours, and can be a jam-packed schedule. Spacewalkers have to be focused on the task at hand and sticking to the timeline. That said, they can still catch a spare moment to see the Earth 250 miles below. Many astronauts describe that view from a spacewalk as one of the most beautiful sights in their lives.
Watch Commander Scott Kelly and Flight Engineer Kjell Lindgren perform a spacewalk on Oct. 28 at 8:15 a.m. EDT live on NASA Television.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
SpaceX Dragon: What’s Onboard?
SpaceX is scheduled to launch its Dragon spacecraft into orbit on April 8, which will be the company’s eighth mission under our Commercial Resupply Services contract. This flight will deliver science and supplies to the International Space Station.

The experiments headed to the orbiting laboratory will help us test the use of an expandable space habitat in microgravity, assess the impact of antibodies on muscle wasting in a microgravity environment, use microgravity to seek insight into the interactions of particle flows at the nanoscale level and use protein crystal growth in microgravity to help in the design of new drugs to fight disease. Here’s an in-depth look at each of them:
The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM)

Space is in limited supply on the International Space Station, but with BEAM, the amount of crew space could be expanded! BEAM is an experimental expandable capsule that attaches to the space station. After installation, it will expand to roughly 13-feet long and 10.5 feet in diameter, which would provide a large volume where a crew member could enter. During the two-year test mission, astronauts will enter the module for a few hours three-to-four times a year to retrieve sensor data and conduct assessments of the module’s condition.
Why? Expandable habitats greatly decrease the amount of transport volume at launch for future space missions. They not only take up less room on a rocket, but also provide greatly enhanced space for living and working once they are set up.
The Rodent Research-3-Eli Lilly

The Rodent Research-3-Eli Lilly investigation will use mice as a model for human health to study whether certain drugs might prevent muscle or bone loss while in microgravity.
Why? Crew members experience significant decreases in their bone density and muscle mass during spaceflight if they do not get enough exercise during long-duration missions. The results could expand scientist’s understanding of muscle atrophy and bone loss in space, by testing an antibody that has been known to prevent muscle wasting in mice on Earth.
Microbial Observatory-1
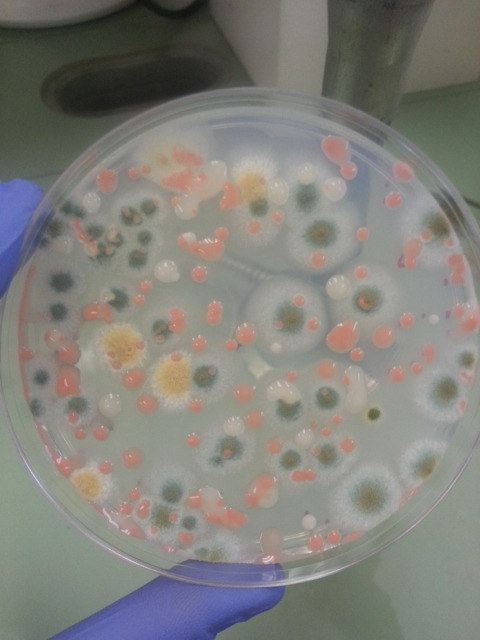
The Microbial Observatory-1 experiment will track and monitor changes to microbial flora over time on the space station.
Why? Obtaining data on these microbial flora could help us understand how such microbes could affect crew health during future long-duration missions.
Micro-10

The Micro-10 investigation will study how the stress of microgravity triggers changes in growth, gene expression, physical responses and metabolism of a fungus called Aspergillus nidulans.
Why? This experiment will study fungi in space for the purpose of potentially developing new medicine for use both in space and on Earth. The stressfull environment of space causes changes to all forms of life, from bacteria and fungi, to animals and people.
Genes in Space-1

Genes in Space-1 is a student-designed experiment that will test whether the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) — which is a fast and relatively inexpensive technique that can amplify or “photocopy” small segments of DNA — could be used to study DNA alterations that crew experience during spaceflight.
Why? In space, the human immune system’s function is altered. Findings from this experiment could help combat some of the DNA changes that crew onboard space station experience while on orbit.
Microchannel Diffusion

Nano science and nanotechnology are the study and application of exceptionally small things and can be used across the fields of medicine, biology, computer science and many others. The way fluid moves is very different on this small scale, so scientists want to know how microparticles might interact. The Microchannel Diffusion investigation simulates these interactions by studying them at a larger scale, the microscopic level. This is only possible on the orbiting laboratory, where Earth’s gravity is not strong enough to interact with the molecules in a sample, so they behave more like they would at the nanoscale.
Why? Nanofluidic sensors could measure the air in the space station, or used to deliver drugs to specific places in the body, among other potential uses. Knowledge learned from this investigation may have implications for drug delivery, particle filtration and future technological applications for space exploration.
The CASIS Protein Crystal Growth 4 (CASIS PCG 4)

CASIS PCG 4 is made up of two investigations that both leverage the microgravity environment in the growth of protein crystals and focus on structure-based drug design (SBDD). Growing crystals in microgravity avoids some of the obstacles they face on Earth, such as sedimentation.
Why? SBDD is an integral component in the drug discovery and development process. It relies on three-dimensional, structural information provided by the protein crystallography to inform the design of more potent, effective and selective drugs.
Watch the Launch!

The Dragon capsule will launch on a Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
Launch coverage begins at 3:15 p.m. EDT, with launch scheduled for 4:43 p.m. Watch live online on NASA Television: nasa.gov/nasatv
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: 5 Things To Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, so let us break it down for you. Here are 5 things to know this week:
1. Dancing with a Star

Our local star, better known as the sun, teems with activity. This month NASA has been tracking regions that burst with magnetic loops. The Solar Dynamics Observatory is one of several space-based assets that keep tabs on the sun daily, watching as charged particles trace the magnetic field, forming bright lines as they emit light in ultraviolet wavelengths.
2. An Idyll for Ida

On Nov. 24, the asteroid Ida makes its closest approach to Earth (at a very safe distance). Ida is the first asteroid found to have its own moon, and the second ever visited by a spacecraft. Its close encounter happened in 1993 as Galileo flew by en route to Jupiter.
3. Moonshine

On Nov. 23, the Cassini spacecraft will fly near Saturn's icy moon Tethys. Several instruments aboard Cassini will collect data, including an eight-frame color image mosaic. Between Nov. 27 and Dec. 2, Cassini will have very limited communications with Earth, because Cassini will enter solar conjunction, when Cassini and Saturn are on the other side of the Sun from Earth.
4. The Moon Will Occult Aldebaran

That may sound ominous, but all it means is that Earth's moon will pass in front of the giant red star Aldebaran on Nov. 26. Aldebaran is the bright "eye" of the constellation Taurus. The event will only be visible in some parts of North America. Details can be found HERE.
5. One Wild Ride, One Year Later

What a year it's been for the Rosetta mission since the Philae lander came to rest on the surface of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko in November 2014. A steady flow of data from the orbiter, together with several days of information sent from the lander, is providing a detailed picture of this remnant from the creation of the solar system.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Does Webb have resolution to look more closely at nearby objects, like Mars or even Earth? Or just far things?
Stars, Sea, and Smoke from the ISS: Tournament Earth 2021
We started Tournament Earth with 32 photos taken by astronauts from the Interantional Space Station and now we are down to 8. All of the #1 seeds are gone. Two #8 seeds are dominating their groups. Who will win? Let's take a closer look at the competitors still in the game. Then remember to vote for your favorites. The champion will be announced on April 13, 2021.
Stars in Motion vs. Cleveland Volcano
This matchup pits smoke against stars, but both have interesting stories.

The International Space Station (ISS) is constantly in motion. For astronaut photographers on board, that motion has consequences. For one, it makes it challenging to take photos. The same motion makes it possible to shoot spectacular photos like the one above. The image is compiled from a series of photographs taken by astronaut Don Pettit while he was onboard the ISS in April 2012. This composite was made from more than 72 individual long-exposure photographs taken over several minutes as the ISS traveled over the Caribbean Sea, across South America, and over the South Atlantic Ocean.

Astronaut Jeff Williams was the first to witness activity at the Cleveland Volcano on May 3, 2006. The Cleveland Volcano is one of the most active in the Aleutian Islands, which extend west-southwest from the Alaska mainland. It is a stratovolcano composed of alternating layers of hardened lava, compacted volcanic ash, and volcanic rocks. The event proved to be short-lived; two hours later, the plume had completely detached from the volcano. The ash cloud height could have been as high as 6,000 meters (20,000 feet) above sea level.
Stargazing from the ISS vs. Cruising Past the Aurora Borealis
This is the most stellar matchup of the tournament, literally. Two beloved star pictures face off in what will be one of the most difficult choices of the tournament.

An astronaut took this broad, short-lens photograph of Earth’s night lights while looking out over the remote reaches of the central equatorial Pacific Ocean. The ISS was passing over the island nation of Kiribati at the time, about 2600 kilometers (1,600 miles) south of Hawaii. Scientists identified the pattern of stars in the photo as our Milky Way galaxy (looking toward its center). The dark patches are dense dust clouds in an inner spiral arm of our galaxy; such clouds can block our view of stars toward the center. The curvature of the Earth crosses the center of the image and is illuminated by a variety of airglow layers in orange, green, and red.

Commonly known as the northern lights, these colorful ribbons of light appear to dance in the sky over the planet’s high latitudes, attracting sky chasers and photographers. Astronaut Randy “Komrade” Bresnik shot this photograph on September 15, 2017, as the space station passed over Ontario, Canada. Curtains of green—the most familiar color of auroras—dominate the light show, with hints of purple and red.
Rolling Through the Appalachians vs. Castellanus Cloud Tower

The Susquehanna River cuts through the folds of the Valley-and-Ridge province of the Appalachian Mountains in this photograph taken from the International Space Station by astronaut Christina Koch. The Valley-and-Ridge province is a section of the larger Appalachian Mountain Belt between the Appalachian Plateau and the Blue Ridge physiographic provinces. The northeast-southwest trending ridges are composed of Early Paleozoic sedimentary rocks. The valleys between them were made of softer rocks (limestone and shales) that were more susceptible to erosion; they are now occupied by farms.

An astronaut aboard the International Space Station took this photograph of a massive vertical cloud formation—known to meteorologists as cumulus castellanus—above Andros Island. The cloud name castellanus comes from the similarity to the crenellated towers or turrets of medieval castles. These clouds develop due to strong vertical air movement typically associated with thunderstorms.
Lake Van, Turkey vs. Typhoon Maysak from the Space Station

While orbiting on the International Space Station, astronaut Kate Rubins shot this photograph of part of Lake Van in Turkey, the largest soda or alkaline lake on Earth. Generally, soda lakes are distinguished by high concentrations of carbonate species. Lake Van is an endorheic lake—it has no outlet, so its water disappears by evaporation—with a pH of 10 and high salinity levels.

This photograph of super typhoon Maysak was taken by European Space Agency astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti as the International Space Station passed near the storm on March 31, 2015. The category 4 typhoon was headed for a possible landfall in the Philippines by the end of the week. It was unusual for the western Pacific to see such a strong storm so early in the year.
See all of the images and vote HERE. Follow @NASAEarth on social media for updates.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

The Summer Solstice Is Here!
Today — June 20, 2024 — is the northern summer solstice. In the Northern Hemisphere, it marks the longest day of the year and the official start to summer.

We experience changing day lengths throughout the year because Earth rotates on a tilted axis as it goes around the Sun. This means during half of the year the North Pole tilts toward the Sun and in the other half it points away.

Solstices occur twice per year, when Earth’s poles are tilted closest to and farthest from the Sun.

The summer solstice is an important day for cultures around the world, especially at latitudes near the North Pole. Indigenous peoples have long marked the summer solstice with dancing and celebrations. Farmers have relied on the solstice to determine when to plant crops. The solstice’s timing also influenced the development of some calendars, like the ancient Roman calendar and the modern Gregorian calendar.
To mark the beginning of summer, here are four ways you can enjoy the Sun and the many wonders of space this season:

1. Check out the “Strawberry Moon”
June is the month of the Strawberry Moon. This name originates with the Algonquin tribes. June is when strawberries are ready for harvest in the northeastern United States, where the Algonquin people traditionally live. The full Strawberry Moon this year happens tomorrow night — June 21, 2024. Grab a pair of binoculars to see it in detail.
2. Celebrate the Heliophysics Big Year!
During the Heliophysics Big Year, we are challenging you to participate in as many Sun-related activities as you can. This month’s theme is performance art. We’re looking at how various kinds of performance artists are moved by the Sun and its influence on Earth. For example, check out this Sun song!
Find out how to get involved here: https://science.nasa.gov/sun/helio-big-year/.

3. Listen to a space-cast
NASA has a ton of great space podcasts. Take a listen to Curious Universe’s Here Comes the Sun series to learn all about our closest star, from how it causes weather in space, to how you can help study it! For even more podcasts, visit our full list here: https://www.nasa.gov/podcasts.

4. Make sunspot cookies
The Sun sometimes has dark patches called sunspots. You can make your own sunspots with our favorite cookie recipe. Real sunspots aren’t made of chocolate, but on these sunspot cookies they are. And they're delicious.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
5 Myths About Becoming an Astronaut
Editor’s Note: This post was updated on March 15, 2024, to reflect new URLs and updated qualifications for applicants.
Have you ever wondered if you have what it takes to become a NASA astronaut? The term “astronaut” derives from the Greek word meaning “star sailor.”
We’re looking for a new class of astronauts to join the NASA team, and if you’re thinking about applying, there are a few things you should know.
Here are a few myths about becoming an astronaut:
MYTH: All astronauts have piloting experience.
FACT: You don’t need to be a pilot to be an astronaut. Flying experience is not a requirement, but it could be beneficial to have.

MYTH: All astronauts have perfect vision.
FACT: It’s OK if you don’t have 20/20 vision. As of September 2007, corrective surgical procedures of the eye (PRK and LASIK), are now allowed, providing at least one year has passed since the date of the procedure with no permanent adverse aftereffects.

MYTH: All astronauts have advanced degrees, like a PhD.
FACT: While a master’s degree from an accredited university is typically necessary to become an astronaut, an exception exists if you have completed a medical degree or test pilot school.

MYTH: Astronauts are required to have military experience to be selected.
FACT: Military experience is not required to become an astronaut.

MYTH: You must be a certain age to be an astronaut.
FACT: There are no age restrictions. Astronaut candidates selected in the past have ranged between the ages of 26 and 46, with the average age being 34.

OK, but what are the requirements?

Basic Qualification Requirements
Applicants must meet the following minimum requirements before submitting an application:
Be a U.S. citizen.
Have completed a master’s degree (or foreign equivalent) in an accredited college or university with major study in an appropriate technical field of engineering, biological science, physical science, computer science, or mathematics.
The master’s degree requirement can also be met by having:
Completed at least two years (36 semester hours or 54 quarter hours) in an accredited PhD or related doctoral degree program (or foreign equivalent) with major study in an appropriate technical field of engineering, biological science, physical science, computer science, or mathematics.
Completed a Doctor of Medicine, Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine, or related medical degree (or foreign equivalent) in an accredited college or university.
Completed or be currently enrolled in a Test Pilot School (TPS) program (nationally or internationally recognized) and will have completed this program by June 2025. (Must submit proof of completion or enrollment.)
If TPS is your only advanced technical degree, you must have also completed a bachelor’s degree or higher (or foreign equivalent) at an accredited college or university with major study in an appropriate technical field of engineering, biological science, physical science, computer science, or mathematics.
Have at least three years of related professional experience obtained after degree completion (or 1,000 Pilot-in-Command hours with at least 850 of those hours in high-performance jet aircraft for pilots). For medical doctors, time in residency can count toward experience and must be completed by June 2025.
Be able to pass the NASA long-duration flight astronaut physical.
Applications for our next astronaut class are open through April 2! Learn more about our Astronaut Selection Program and check out current NASA astronaut Anne McClain’s advice in “An Astronaut’s Guide to Applying to Be an Astronaut.”
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Keep reading
Solar System: 5 Things To Know This Week
We live during one of the great eras of exploration. At this very moment, there are dozens of spacecraft surveying the solar system, from Mars, to Saturn, to Pluto and beyond. What’s more, you can ride along with these expeditions — all you need is an internet connection to see the latest discoveries from deep space. Here are a few essential resources for the armchair astronaut:
1. It’s Like Facebook, but for Planets

Or is it more of a Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Solar System? Whatever you want to call it, our Planets page offers quick rundowns, as well as in-depth guides, for all the major bodies in the solar system. Explore from the sun all they way out to the Oort Cloud.
2. Robots to the Rescue

Saturn looks spectacular through a telescope, but there’s only so much you can learn about it from the ground. Going there in person is tough, too. While we are now preparing to send astronauts beyond Earth orbit, a human mission to Saturn won’t be possible in the near future. That’s where the space robots come in. For example, the Cassini spacecraft studies Saturn and its moons up close, sometimes even doing things like flying right through the geyser plumes of the ice moon Enceladus. See all the solar system missions, past and present, where they went and what they’ve seen HERE.
3. Keep Your Eyes on This One

If you still haven’t tried Eyes on the Solar System, you’re missing out. This online simulation lets you tour the planets and track the past, current and future positions of spacecraft — right in your web browser, all in 3D. Eyes on the Solar System uses real NASA data to help you take a virtual flight across both space and time.
4. Images in the Raw

You don’t have to wait for a news release to see pictures from planetary missions. Some missions allow you to see raw, unprocessed images sent straight from the spacecraft. What these images lack in explanatory captions they make up for in freshness — sometimes you can see pictures from Mars or Saturn that are mere hours old. There’s something exhilarating about being among the first human beings ever to see an alien landscape. Peruse our new raw image pages HERE.
5. Bring It On Home

After you’ve toured the far reaches of the solar system, you can always come home again. When you have spent time studying the harsh conditions of our neighboring planets, the charms of a unique paradise come into sharp focus, the place we call Earth. Watch a real-time video feed from Earth orbit HERE. You can also see a daily global view of our planet from a million miles away HERE. Download THIS Earth Now mobile app to hold the planet in your hands.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
10 Things Einstein Got Right
One hundred years ago, on May 29, 1919, astronomers observed a total solar eclipse in an ambitious effort to test Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity by seeing it in action. Essentially, Einstein thought space and time were intertwined in an infinite “fabric,” like an outstretched blanket. A massive object such as the Sun bends the spacetime blanket with its gravity, such that light no longer travels in a straight line as it passes by the Sun.
This means the apparent positions of background stars seen close to the Sun in the sky – including during a solar eclipse – should seem slightly shifted in the absence of the Sun, because the Sun’s gravity bends light. But until the eclipse experiment, no one was able to test Einstein’s theory of general relativity, as no one could see stars near the Sun in the daytime otherwise.
The world celebrated the results of this eclipse experiment— a victory for Einstein, and the dawning of a new era of our understanding of the universe.
General relativity has many important consequences for what we see in the cosmos and how we make discoveries in deep space today. The same is true for Einstein's slightly older theory, special relativity, with its widely celebrated equation E=mc². Here are 10 things that result from Einstein’s theories of relativity:

1. Universal Speed Limit
Einstein's famous equation E=mc² contains "c," the speed of light in a vacuum. Although light comes in many flavors – from the rainbow of colors humans can see to the radio waves that transmit spacecraft data – Einstein said all light must obey the speed limit of 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second. So, even if two particles of light carry very different amounts of energy, they will travel at the same speed.
This has been shown experimentally in space. In 2009, our Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope detected two photons at virtually the same moment, with one carrying a million times more energy than the other. They both came from a high-energy region near the collision of two neutron stars about 7 billion years ago. A neutron star is the highly dense remnant of a star that has exploded. While other theories posited that space-time itself has a "foamy" texture that might slow down more energetic particles, Fermi's observations found in favor of Einstein.

2. Strong Lensing
Just like the Sun bends the light from distant stars that pass close to it, a massive object like a galaxy distorts the light from another object that is much farther away. In some cases, this phenomenon can actually help us unveil new galaxies. We say that the closer object acts like a “lens,” acting like a telescope that reveals the more distant object. Entire clusters of galaxies can be lensed and act as lenses, too.
When the lensing object appears close enough to the more distant object in the sky, we actually see multiple images of that faraway object. In 1979, scientists first observed a double image of a quasar, a very bright object at the center of a galaxy that involves a supermassive black hole feeding off a disk of inflowing gas. These apparent copies of the distant object change in brightness if the original object is changing, but not all at once, because of how space itself is bent by the foreground object’s gravity.
Sometimes, when a distant celestial object is precisely aligned with another object, we see light bent into an “Einstein ring” or arc. In this image from our Hubble Space Telescope, the sweeping arc of light represents a distant galaxy that has been lensed, forming a “smiley face” with other galaxies.

3. Weak Lensing
When a massive object acts as a lens for a farther object, but the objects are not specially aligned with respect to our view, only one image of the distant object is projected. This happens much more often. The closer object’s gravity makes the background object look larger and more stretched than it really is. This is called “weak lensing.”
Weak lensing is very important for studying some of the biggest mysteries of the universe: dark matter and dark energy. Dark matter is an invisible material that only interacts with regular matter through gravity, and holds together entire galaxies and groups of galaxies like a cosmic glue. Dark energy behaves like the opposite of gravity, making objects recede from each other. Three upcoming observatories -- Our Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope, WFIRST, mission, the European-led Euclid space mission with NASA participation, and the ground-based Large Synoptic Survey Telescope --- will be key players in this effort. By surveying distortions of weakly lensed galaxies across the universe, scientists can characterize the effects of these persistently puzzling phenomena.
Gravitational lensing in general will also enable NASA’s James Webb Space telescope to look for some of the very first stars and galaxies of the universe.

4. Microlensing
So far, we’ve been talking about giant objects acting like magnifying lenses for other giant objects. But stars can also “lens” other stars, including stars that have planets around them. When light from a background star gets “lensed” by a closer star in the foreground, there is an increase in the background star’s brightness. If that foreground star also has a planet orbiting it, then telescopes can detect an extra bump in the background star’s light, caused by the orbiting planet. This technique for finding exoplanets, which are planets around stars other than our own, is called “microlensing.”
Our Spitzer Space Telescope, in collaboration with ground-based observatories, found an “iceball” planet through microlensing. While microlensing has so far found less than 100 confirmed planets, WFIRST could find more than 1,000 new exoplanets using this technique.

5. Black Holes
The very existence of black holes, extremely dense objects from which no light can escape, is a prediction of general relativity. They represent the most extreme distortions of the fabric of space-time, and are especially famous for how their immense gravity affects light in weird ways that only Einstein’s theory could explain.
In 2019 the Event Horizon Telescope international collaboration, supported by the National Science Foundation and other partners, unveiled the first image of a black hole’s event horizon, the border that defines a black hole’s “point of no return” for nearby material. NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, and Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope all looked at the same black hole in a coordinated effort, and researchers are still analyzing the results.

6. Relativistic Jets
This Spitzer image shows the galaxy Messier 87 (M87) in infrared light, which has a supermassive black hole at its center. Around the black hole is a disk of extremely hot gas, as well as two jets of material shooting out in opposite directions. One of the jets, visible on the right of the image, is pointing almost exactly toward Earth. Its enhanced brightness is due to the emission of light from particles traveling toward the observer at near the speed of light, an effect called “relativistic beaming.” By contrast, the other jet is invisible at all wavelengths because it is traveling away from the observer near the speed of light. The details of how such jets work are still mysterious, and scientists will continue studying black holes for more clues.

7. A Gravitational Vortex
Speaking of black holes, their gravity is so intense that they make infalling material “wobble” around them. Like a spoon stirring honey, where honey is the space around a black hole, the black hole’s distortion of space has a wobbling effect on material orbiting the black hole. Until recently, this was only theoretical. But in 2016, an international team of scientists using European Space Agency's XMM-Newton and our Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NUSTAR) announced they had observed the signature of wobbling matter for the first time. Scientists will continue studying these odd effects of black holes to further probe Einstein’s ideas firsthand.
Incidentally, this wobbling of material around a black hole is similar to how Einstein explained Mercury’s odd orbit. As the closest planet to the Sun, Mercury feels the most gravitational tug from the Sun, and so its orbit’s orientation is slowly rotating around the Sun, creating a wobble.

8. Gravitational Waves
Ripples through space-time called gravitational waves were hypothesized by Einstein about 100 years ago, but not actually observed until recently. In 2016, an international collaboration of astronomers working with the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) detectors announced a landmark discovery: This enormous experiment detected the subtle signal of gravitational waves that had been traveling for 1.3 billion years after two black holes merged in a cataclysmic event. This opened a brand new door in an area of science called multi-messenger astronomy, in which both gravitational waves and light can be studied.
For example, our telescopes collaborated to measure light from two neutron stars merging after LIGO detected gravitational wave signals from the event, as announced in 2017. Given that gravitational waves from this event were detected mere 1.7 seconds before gamma rays from the merger, after both traveled 140 million light-years, scientists concluded Einstein was right about something else: gravitational waves and light waves travel at the same speed.

9. The Sun Delaying Radio Signals
Planetary exploration spacecraft have also shown Einstein to be right about general relativity. Because spacecraft communicate with Earth using light, in the form of radio waves, they present great opportunities to see whether the gravity of a massive object like the Sun changes light’s path.
In 1970, our Jet Propulsion Laboratory announced that Mariner VI and VII, which completed flybys of Mars in 1969, had conducted experiments using radio signals — and also agreed with Einstein. Using NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN), the two Mariners took several hundred radio measurements for this purpose. Researchers measured the time it took for radio signals to travel from the DSN dish in Goldstone, California, to the spacecraft and back. As Einstein would have predicted, there was a delay in the total roundtrip time because of the Sun’s gravity. For Mariner VI, the maximum delay was 204 microseconds, which, while far less than a single second, aligned almost exactly with what Einstein’s theory would anticipate.
In 1979, the Viking landers performed an even more accurate experiment along these lines. Then, in 2003 a group of scientists used NASA’s Cassini Spacecraft to repeat these kinds of radio science experiments with 50 times greater precision than Viking. It’s clear that Einstein’s theory has held up!

10. Proof from Orbiting Earth
In 2004, we launched a spacecraft called Gravity Probe B specifically designed to watch Einstein’s theory play out in the orbit of Earth. The theory goes that Earth, a rotating body, should be pulling the fabric of space-time around it as it spins, in addition to distorting light with its gravity.
The spacecraft had four gyroscopes and pointed at the star IM Pegasi while orbiting Earth over the poles. In this experiment, if Einstein had been wrong, these gyroscopes would have always pointed in the same direction. But in 2011, scientists announced they had observed tiny changes in the gyroscopes’ directions as a consequence of Earth, because of its gravity, dragging space-time around it.

BONUS: Your GPS! Speaking of time delays, the GPS (global positioning system) on your phone or in your car relies on Einstein’s theories for accuracy. In order to know where you are, you need a receiver – like your phone, a ground station and a network of satellites orbiting Earth to send and receive signals. But according to general relativity, because of Earth’s gravity curving spacetime, satellites experience time moving slightly faster than on Earth. At the same time, special relativity would say time moves slower for objects that move much faster than others.
When scientists worked out the net effect of these forces, they found that the satellites’ clocks would always be a tiny bit ahead of clocks on Earth. While the difference per day is a matter of millionths of a second, that change really adds up. If GPS didn’t have relativity built into its technology, your phone would guide you miles out of your way!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How often do solar eclipses occur on other planets like Mars or Venus?
Venus doesn’t have a moon so it never has an eclipse. Mars does have a partial eclipse or a transit of one of its moon and you can see photos at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=3888
-
 awk-1 liked this · 1 year ago
awk-1 liked this · 1 year ago -
 lapetitemortgraveyard liked this · 1 year ago
lapetitemortgraveyard liked this · 1 year ago -
 stuzzi liked this · 1 year ago
stuzzi liked this · 1 year ago -
 ctzenb-u liked this · 1 year ago
ctzenb-u liked this · 1 year ago -
 shortwings liked this · 2 years ago
shortwings liked this · 2 years ago -
 the-creature-verse liked this · 2 years ago
the-creature-verse liked this · 2 years ago -
 different-roads liked this · 3 years ago
different-roads liked this · 3 years ago -
 scifisub liked this · 3 years ago
scifisub liked this · 3 years ago -
 odlanorodlanor liked this · 3 years ago
odlanorodlanor liked this · 3 years ago -
 pegasister60 liked this · 3 years ago
pegasister60 liked this · 3 years ago -
 geoboy-world liked this · 3 years ago
geoboy-world liked this · 3 years ago -
 froztox23 liked this · 3 years ago
froztox23 liked this · 3 years ago -
 whatareyoureallyafraidof reblogged this · 3 years ago
whatareyoureallyafraidof reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 the-world-and-space reblogged this · 3 years ago
the-world-and-space reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 broadviewavenue liked this · 4 years ago
broadviewavenue liked this · 4 years ago -
 5ey liked this · 4 years ago
5ey liked this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago -
 naturaleccentricity liked this · 4 years ago
naturaleccentricity liked this · 4 years ago -
 maryambutt reblogged this · 4 years ago
maryambutt reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 maryambutt liked this · 4 years ago
maryambutt liked this · 4 years ago -
 strangesuhi liked this · 4 years ago
strangesuhi liked this · 4 years ago -
 petite-lunas liked this · 4 years ago
petite-lunas liked this · 4 years ago -
 void-tiger reblogged this · 4 years ago
void-tiger reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 void-tiger liked this · 4 years ago
void-tiger liked this · 4 years ago -
 placesm83 reblogged this · 4 years ago
placesm83 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 moonpixxel liked this · 4 years ago
moonpixxel liked this · 4 years ago -
 shyclaws liked this · 4 years ago
shyclaws liked this · 4 years ago -
 arius-starwalker-1412 reblogged this · 4 years ago
arius-starwalker-1412 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 arius-starwalker-1412 liked this · 4 years ago
arius-starwalker-1412 liked this · 4 years ago -
 ap93099782 liked this · 4 years ago
ap93099782 liked this · 4 years ago -
 kenarcadiaking liked this · 4 years ago
kenarcadiaking liked this · 4 years ago -
 arthur--melbin liked this · 4 years ago
arthur--melbin liked this · 4 years ago -
 thetrueroadkill liked this · 4 years ago
thetrueroadkill liked this · 4 years ago -
 nyanzen liked this · 4 years ago
nyanzen liked this · 4 years ago -
 aconfusedwriter liked this · 4 years ago
aconfusedwriter liked this · 4 years ago -
 tictactoetingles liked this · 4 years ago
tictactoetingles liked this · 4 years ago -
 dykem77 liked this · 4 years ago
dykem77 liked this · 4 years ago -
 starborn42 liked this · 4 years ago
starborn42 liked this · 4 years ago -
 rennku liked this · 4 years ago
rennku liked this · 4 years ago -
 black--eyebags liked this · 4 years ago
black--eyebags liked this · 4 years ago -
 marcell017 liked this · 4 years ago
marcell017 liked this · 4 years ago -
 kawaiitrashpile reblogged this · 4 years ago
kawaiitrashpile reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 kawaiitrashpile liked this · 4 years ago
kawaiitrashpile liked this · 4 years ago -
 grandtheoristpeach liked this · 4 years ago
grandtheoristpeach liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts