Thedevilpriv-blog - De Todo El Mundo

More Posts from Thedevilpriv-blog and Others
“Es tan duro verse al espejo. No hay nada allí.”
— Andy Warhol (via elcielosobremi)

Amor ¿Cómo no atarme a tu universo? ¿Cómo no perder la razón por tus besos? ¿Cómo no caer ante ti?, si en ti encuentro todo, no me falta nada, mi mirada te dice: “estoy jodidamente enamorado”; te amo “hasta la madre”, tú eres mi universo y yo tan solo un planeta. Eres el amor de mi pinche vida.
Alguien sabe como transferir el dinero que tengo en mi mente a mi cuenta bancaria???
<3
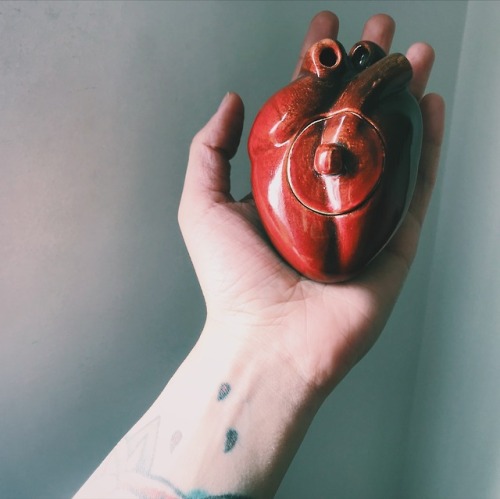

A lo mejor el amor de mi vida es una mujer y yo aquí, jugandole a lo homosexual.
Study Looks for DNA Changes to Measure Parkinson’s Disease

Neurons derived from a patient with Parkinson’s disease. Courtesy of Regis Grailhe, Nasia Antoniou and Rebecca Matsas, Institut Pasteur Korea/Nikon Small World.
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Arizona State University (ASU) have received funding from The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research (MJFF) to launch a multi-year, $1.7-million effort to identify blood-based biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease (PD), which could improve care and accelerate new treatments for the neurodegenerative disorder, which affects nearly 1 million Americans, with 60,000 new cases diagnosed annually.
“The exact cause of Parkinson’s is unknown, but evidence points to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Right now, there is no objective test or biomarker for PD, which increases the risk of misdiagnosis and delayed treatment,” said Paula Desplats, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Neurosciences at UC San Diego School of Medicine and co-principal investigator of the new study with Travis Dunckley, PhD, assistant research professor at ASU’s Biodesign Institute.
The new study will analyze nearly 2,500 blood samples collected longitudinally over three years in the MJFF-sponsored Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI). These samples include donations from patients diagnosed with idiopathic (cause unknown) PD; PD patients and asymptomatic individuals who carry a genetic mutation in the PD-implicated LRKK2 gene; at-risk populations of people with REM sleep behavior disorder and/or smell loss; as well as healthy control subjects. Researchers will analyze DNA methylation, an epigenetic modification of the DNA that can change genetic activity without changing the underlying sequence. DNA methylation is critical to turning genes on and off and affects a vast range of cellular functions and fundamental development.
“This epigenetic analysis could help us better understand the pathology of Parkinson’s disease, pointing to biomarker candidates and, potentially, novel therapeutic targets,” said Samantha Hutten, PhD, MJFF senior associate director of research partnerships. “In addition, this DNA methylation data grows the value of the PPMI clinical, imaging and biological database, the most robust in Parkinson’s research.”
“Study Looks for DNA Changes to Measure Parkinson’s Disease“
Pienso que si hubiera sido mujer, usaría café como perfume.
Villegas P.
-
 escape-to-heaven01 liked this · 1 week ago
escape-to-heaven01 liked this · 1 week ago -
 werewolfmack liked this · 2 weeks ago
werewolfmack liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 maraschino-cherries reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
maraschino-cherries reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 shaheerah reblogged this · 1 month ago
shaheerah reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 pleasefollowxmndy96instead liked this · 2 months ago
pleasefollowxmndy96instead liked this · 2 months ago -
 ktyclws reblogged this · 3 months ago
ktyclws reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 hobbit-wannabe reblogged this · 3 months ago
hobbit-wannabe reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 enciende-la-mente reblogged this · 3 months ago
enciende-la-mente reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 a-bike-guy liked this · 3 months ago
a-bike-guy liked this · 3 months ago -
 barbiee-girll reblogged this · 3 months ago
barbiee-girll reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 soniciselectricc reblogged this · 3 months ago
soniciselectricc reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 bubble--cheeks reblogged this · 4 months ago
bubble--cheeks reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 soniciselectricc reblogged this · 4 months ago
soniciselectricc reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 mathi-arts-things liked this · 4 months ago
mathi-arts-things liked this · 4 months ago -
 morewildandfree liked this · 5 months ago
morewildandfree liked this · 5 months ago -
 hello-surfer2018 liked this · 5 months ago
hello-surfer2018 liked this · 5 months ago -
 allysonytx reblogged this · 5 months ago
allysonytx reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 anna0vu7g liked this · 6 months ago
anna0vu7g liked this · 6 months ago -
 annaw6izj liked this · 6 months ago
annaw6izj liked this · 6 months ago -
 annawptga liked this · 6 months ago
annawptga liked this · 6 months ago -
 annawlacm liked this · 6 months ago
annawlacm liked this · 6 months ago -
 soniciselectricc liked this · 6 months ago
soniciselectricc liked this · 6 months ago -
 vjlva reblogged this · 7 months ago
vjlva reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 vjlva liked this · 7 months ago
vjlva liked this · 7 months ago -
 superchat liked this · 7 months ago
superchat liked this · 7 months ago -
 kawaiidesu reblogged this · 7 months ago
kawaiidesu reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 kawaiidesu liked this · 7 months ago
kawaiidesu liked this · 7 months ago -
 erotic-tinaa liked this · 8 months ago
erotic-tinaa liked this · 8 months ago -
 microeskandalo reblogged this · 8 months ago
microeskandalo reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 o-ceanssss reblogged this · 8 months ago
o-ceanssss reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 emotionally--scarred reblogged this · 8 months ago
emotionally--scarred reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 emotionally--scarred liked this · 8 months ago
emotionally--scarred liked this · 8 months ago -
 maybeseptemberbaby liked this · 8 months ago
maybeseptemberbaby liked this · 8 months ago -
 cantexistloudenoughforyou liked this · 9 months ago
cantexistloudenoughforyou liked this · 9 months ago -
 alex-one-o-one reblogged this · 9 months ago
alex-one-o-one reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 alex-one-o-one liked this · 9 months ago
alex-one-o-one liked this · 9 months ago -
 iamnamelessvit reblogged this · 9 months ago
iamnamelessvit reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 s-h-y-y-a-n-n-e liked this · 9 months ago
s-h-y-y-a-n-n-e liked this · 9 months ago -
 el0win reblogged this · 10 months ago
el0win reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 el0win liked this · 10 months ago
el0win liked this · 10 months ago -
 heartsnecksandthingsthatbreak liked this · 10 months ago
heartsnecksandthingsthatbreak liked this · 10 months ago -
 eroticconcrete reblogged this · 10 months ago
eroticconcrete reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 l1v1ng-deadg1rl liked this · 10 months ago
l1v1ng-deadg1rl liked this · 10 months ago -
 alchemistangel777 reblogged this · 10 months ago
alchemistangel777 reblogged this · 10 months ago