Exploring The Invisible: Magnetic Reconnection
Exploring the Invisible: Magnetic Reconnection
People always say that space is a vacuum. That’s true – space is about a thousand times emptier than even the best laboratory vacuums on Earth. Even so, space contains lots of stuff we can’t see. We study this invisible space stuff because we need to understand it to safely send technology and astronauts into space.
The stuff that fills space is mostly plasma, which is gas where particles have separated into positive ions and negative electrons, creating a sea of electrically-charged particles. This plasma also contains something else – magnetic fields.

The particles in space can reach very high speeds, creating radiation. One of the main engines that drives that acceleration to high speeds is called magnetic reconnection. But what is magnetic reconnection?
Magnetic reconnection happens when two oppositely-aligned magnetic fields pinch together and explosively realign. As the lines snap into their new configuration – as in the animation below – the sudden change sends electrons and ions flying at incredible speeds.

Magnetic reconnection releases energy. We can't see the energy itself, but we can see the results: It can set off solar explosions – such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections – or disturbances near Earth that cause auroras.
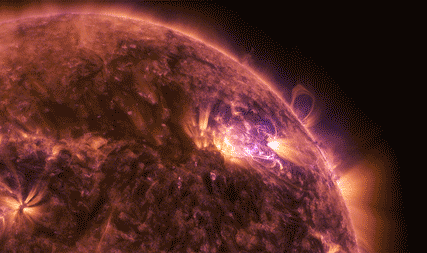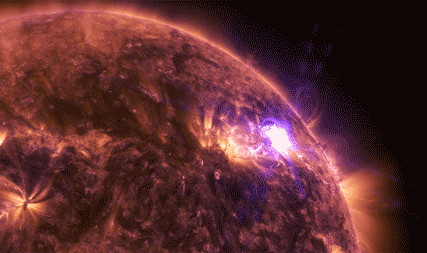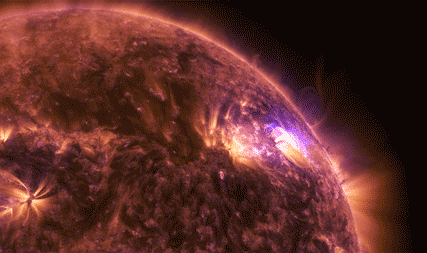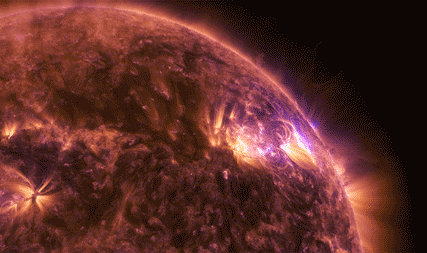
In March 2015, we launched the four Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft on a mission to study magnetic reconnection. Magnetic reconnection only happens in a vacuum with ionized gas. These conditions are vanishingly rare on Earth, so we went to space to study this explosive process.
Because MMS has four separate – but essentially identical – spacecraft, it can watch magnetic reconnection in three dimensions.

The below animation shows what MMS sees – the magnetic fields are magenta, positive ions are purple, and electrons are yellow. The arrows show which the direction the fields and particles are moving.

Like how a research plane flies through a hurricane, MMS flew directly through a magnetic reconnection event in October 2015.
In the data visualization below, you can see the magnetic reconnection happening as the yellow arrows (which represent electrons) explode in all directions. You’ll notice that the magnetic field (represented by magenta arrows) changes direction after the magnetic reconnection, showing that the magnetic field has reconfigured.

Magnetic reconnection transfers energy into Earth’s atmosphere – but it’s not inherently dangerous. Sometimes, the changes in Earth’s magnetic field caused by magnetic reconnection can create electric currents that put a strain on power systems. However, the energy released is more often channeled into auroras, the multicolored lights that most often appear near the North and South Poles.

As the MMS mission continues the four spacecraft can be moved closer together or farther apart, letting us measure magnetic reconnection on all different scales. Each set of observations contributes to explaining different aspects of this invisible phenomenon of magnetic reconnection. Together, the information will help scientists better map out our space environment — crucial information as we journey ever farther beyond our home planet.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
What would be the ideal discovery to make with the Webb Telescope? Or what would you love to find with it?
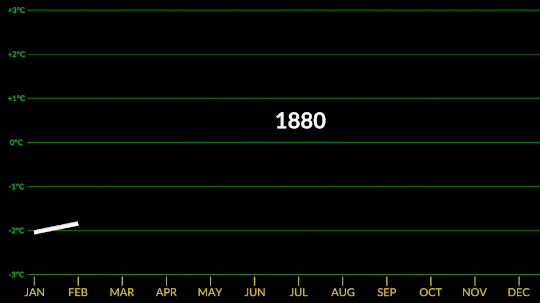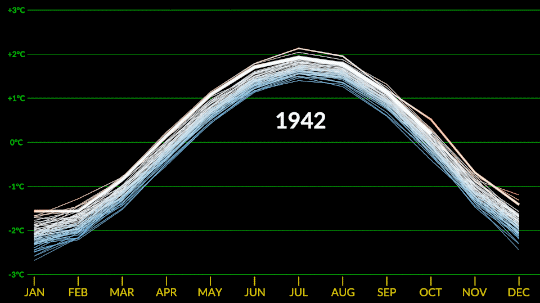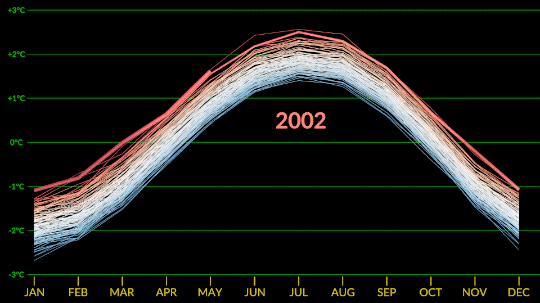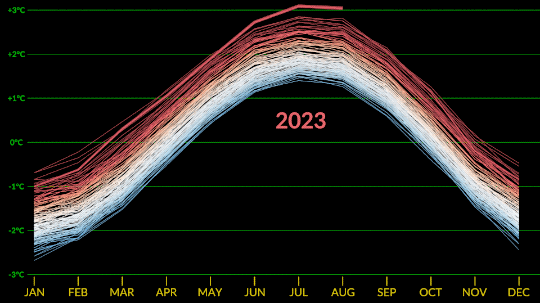
Confirmed: Summer 2023 Hottest in NASA’s Record
All three months of summer 2023 broke records. July 2023 was the hottest month ever recorded, and the hottest July. June 2023 was the hottest June, and August 2023 was the hottest August.
NASA’s temperature record, GISTEMP, starts in 1880, when consistent, modern recordkeeping became possible. Our record uses millions of measurements of surface temperature from weather stations, ships and ocean buoys, and Antarctic research stations. Other agencies and organizations who keep similar global temperature records find the same pattern of long-term warming.
Global temperatures are rising from increased emissions of greenhouse gasses, like carbon dioxide and methane. Over the last 200 years, humans have raised atmospheric CO2 by nearly 50%, primarily through the burning of fossil fuels.
Drivers of climate change, both natural and human-caused, leave distinct fingerprints. Through observations and modeling, NASA researchers confirm that the current warming is the result of human activities, particularly increased greenhouse gas emissions.
Five Orion Technologies That Will Help Us Get Home From Mars
Orion is a key piece of NASA’s journey to Mars. The spacecraft, which was first tested in space last year, will enable crew to travel to deep space on the journey to the Red Planet and bring astronauts home safely. It’s a critical technology we’ll use to help NASA test, demonstrate and hone the skills and capabilities we need to operate farther and farther away from Earth.

Environmental Control and Life Support Systems
Water. Air. A temperate environment. A bathroom. These are some of the things astronauts need to survive the long journey back to Earth from Mars. NASA has developed an environmental control and life support system on the International Space Station and is designing such a system for Orion. The system can recycle carbon dioxide and make it back into useable air and process urine to make it into potable water, for example. Right now on the space station, engineers and astronauts are testing a filtering system for efficiency and reliability on long-duration missions. The investigation uses an amine-based chemical compound combined with the vacuum of space to filter and renew cabin air for breathing. When astronauts travel home from Mars, they won’t be able to count on the arrival of spare parts or extra supplies if something breaks or gets depleted, so engineers are hard at work developing reliable and robust technologies to keep crews alive and healthy in space.

Radiation protection
Astronauts traveling to and from Mars will be far away from the protective shield of Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field, and their spacecraft and its systems will need to be able to protect against the full spectrum of space radiation. NASA is working now to develop protective methods.
Orion will use items already on board to protect the crew and create a temporary shelter in the aft bay of the spacecraft, which is the inside portion closest to the heat shield. This location minimizes the amount of equipment to move around while maximizing the amount of material that can be placed between the crew and the outside environment. The items that will be used include supplies, equipment and launch and re-entry seats as well as water and food. By using the items already on board, the astronauts benefit from additional shielding without adding to Orion’s mass.

Power and Propulsion
A spacecraft needs power and propulsion in space to refine its trajectory during the trip back to Earth. Orion will include a service module capable of helping the spacecraft make any necessary mid-course corrections. A service module provides power, heat rejection, in-space propulsion and water and air for crews, and NASA is working with ESA (European Space Agency) to provide Orion’s service module for its next mission in a partnership that will also bring international cooperation on the journey to Mars. The service module will provide propulsion, batteries and solar arrays to generate power and contain all the air, nitrogen and water for crews.
The ESA-provided element brings together new technology and lightweight materials while also taking advantage of spaceflight-proven hardware. For example, ESA is modeling several key components – like the solar arrays – from technology developed for its Automated Transfer Vehicle-series of cargo vessels, which delivered thousands of pounds of supplies to the space station during five missions between 2008 and 2015. NASA is providing ESA one of the Orbital Maneuvering System pods that allowed space shuttles to move in space to be upgraded and integrated into the service module.

Heat shield
When an uncrewed Orion was tested in space in 2014, the heat shield withstood temperatures of about 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit, or about twice as hot as molten lava. That heat was generated when the spacecraft, traveling at about 20,000 mph back toward our planet, made its way through Earth’s atmosphere, which acts as a braking mechanism to cause friction and slow down a returning spacecraft. Its speed was about 80 percent of what Orion will experience when it comes back from missions near the moon and will need to be even more robust for missions where return speeds, and therefore reentry temperatures, are higher.
Orion’s heat shield is built around a titanium skeleton and carbon fiber skin that provide structural support. A honeycomb structure fits over the skin with thousands of cells that are filled with a material called Avcoat. That layer is 1.6 inches at its thickest and erodes as Orion travels through Earth’s atmosphere.

Parachutes
A spacecraft bringing crews back to Earth after a long trip to Mars will need a parachute system to help it slow down from its high-speed reentry through the atmosphere to a relatively slow speed for splashdown in the ocean. While Earth’s atmosphere will initially slow Orion down from thousands of miles per hour to about 325 mph, its 11 parachutes will deploy in precise sequence to further slow the capsule’s descent. There are three forward bay cover parachutes that pull a protective cover off the top of the capsule, two drogue parachutes that deploy to stabilize the spacecraft, and three pilot parachutes that are used to pull out Orion’s three orange and white main parachutes that are charged with slowing the spacecraft to its final landing speed. The main parachutes are so big that the three of them together nearly cover an entire football field.
Engineers are currently building the Orion spacecraft that will launch on the world’s most powerful rocket, the Space Launch System, and will enable astronauts to travel farther into space than ever before on the journey to Mars.
Visit NASA on the Web for more information about Orion and NASA’s journey to Mars. http://www.nasa.gov/orion
Physical Science...In Space!
Each month, we highlight a different research topic on the International Space Station. In May, our focus is physical science.

The space station is a laboratory unlike any on Earth; on-board, we can control gravity as a variable and even remove it entirely from the equation. Removing gravity reveals fundamental aspects of physics hidden by force-dependent phenomena such as buoyancy-driven convection and sedimentation.

Gravity often masks or distorts subtle forces such as surface tension and diffusion; on space station, these forces have been harnessed for a wide variety of physical science applications (combustion, fluids, colloids, surface wetting, boiling, convection, materials processing, etc).

Other examples of observations in space include boiling in which bubbles do not rise, colloidal systems containing crystalline structures unlike any seen on Earth and spherical flames burning around fuel droplets. Also observed was a uniform dispersion of tin particles in a liquid melt, instead of rising to the top as would happen in Earth’s gravity.

So what? By understanding the fundamentals of combustion and surface tension, we may make more efficient combustion engines; better portable medical diagnostics; stronger, lighter alloys; medicines with longer shelf-life, and buildings that are more resistant to earthquakes.

Findings from physical science research on station may improve the understanding of material properties. This information could potentially revolutionize development of new and improved products for use in everything from automobiles to airplanes to spacecraft.
For more information on space station research, follow @ISS_Research on Twitter!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Ever want to ask a real life astronaut a question? Here’s your chance!
We are kicking off Hispanic Heritage Month a little early this year, and astronaut Serena M. Auñón-Chancellor will be taking your questions in an Answer Time session on Thursday, September 12 from 12pm - 1pm ET here on NASA’s Tumblr! Find out what it’s like to be a NASA astronaut and learn more about her Cuban-American heritage. Make sure to ask your question now by visiting http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Dr. Serena M. Auñón-Chancellor began working with NASA as a Flight Surgeon in 2006 and was later selected as a NASA astronaut in 2009. Her first flight was from Jun 6- Dec. 20, 2018 where she served as Flight Engineer on the International Space Station as a member of Expeditions 56 and 57. During these missions, the crew contributed to hundreds of experiments in biology, biotechnology, physical science and Earth science – including investigations into a new cancer treatment!
She has a Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering from The George Washington University, Washington, D.C and a Doctorate of Medicine from The University of Texas - Health Science Center at Houston.
Dr. Auñón-Chancellor Fun Facts:
She spent 2 months in Antarctica from 2010 to 2011 searching for meteorites as part of the ANSMET expedition.
She served as an Aquanaut on the NEEMO 20 mission in the Aquarius underwater laboratory, which is used to prepare for living and working in space.
She logged 197 days in space during Expeditions 56 and 57.
Follow Serena on Twitter at @AstroSerena and follow NASA on Tumblr for your regular dose of space.
Science Launching to Station Looks Forward and Back
Some of the earliest human explorers used mechanical tools called sextants to navigate vast oceans and discover new lands. Today, high-tech tools navigate microscopic DNA to discover previously unidentified organisms. Scientists aboard the International Space Station soon will have both types of tools at their disposal.

Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft is scheduled to launch its ninth contracted cargo resupply mission to the space station no earlier than May 21. Sending crucial science, supplies and cargo to the crew of six humans living and working on the orbiting laboratory.
Our Gemini missions conducted the first sextant sightings from a spacecraft, and designers built a sextant into Apollo vehicles as a lost-communications navigation backup. The Sextant Navigation investigation tests use of a hand-held sextant for emergency navigation on missions in deep space as humans begin to travel farther from Earth.

Jim Lovell (far left) demonstrated on Apollo 8 that sextant navigation could return a space vehicle home.

The remoteness and constrained resources of living in space require simple but effective processes and procedures to monitor the presence of microbial life, some of which might be harmful. Biomolecule Extraction and Sequencing Technology (BEST) advances the use of sequencing processes to identify microbes aboard the space station that current methods cannot detect and to assess mutations in the microbial genome that may be due to spaceflight.

Genes in Space 3 performed in-flight identification of bacteria on the station for the first time. BEST takes that one step farther, identifying unknown microbial organisms using a process that sequences directly from a sample with minimal preparation, rather than with the traditional technique that requires growing a culture from the sample.

Adding these new processes to the proven technology opens new avenues for inflight research, such as how microorganisms on the station change or adapt to spaceflight.
The investigation’s sequencing components provide important information on the station’s microbial occupants, including which organisms are present and how they respond to the spaceflight environment -- insight that could help protect humans during future space exploration. Knowledge gained from BEST could also provide new ways to monitor the presence of microbes in remote locations on Earth.
Moving on to science at a scale even smaller than a microbe, the new Cold Atom Lab (CAL) facility could help answer some big questions in modern physics.

CAL creates a temperature ten billion (Yup. BILLION) times colder than the vacuum of space, then uses lasers and magnetic forces to slow down atoms until they are almost motionless. CAL makes it possible to observe these ultra-cold atoms for much longer in the microgravity environment on the space station than would be possible on the ground.

Results of this research could potentially lead to a number of improved technologies, including sensors, quantum computers and atomic clocks used in spacecraft navigation.
A partnership between the European Space Agency (ESA) and Space Application Services (SpaceAps), The International Commercial Experiment, or ICE Cubes Service, uses a sliding framework permanently installed on the space station and “plug-and-play” Experiment Cubes.

The Experiment Cubes are easy to install and remove, come in different sizes and can be built with commercial off-the-shelf components, significantly reducing the cost and time to develop experiments.
ICE Cubes removes barriers that limit access to space, providing more people access to flight opportunities. Potential fields of research range from pharmaceutical development to experiments on stem cells, radiation, and microbiology, fluid sciences, and more.
For daily nerd outs, follow @ISS_Research on Twitter!
Watch the Launch + More!

What’s On Board Briefing
Join scientists and researchers as they discuss some of the investigations that will be delivered to the station on Saturday, May 19 at 1 p.m. EDT at nasa.gov/live. Have questions? Use #askNASA
CubeSat Facebook Live
The International Space Station is often used to deploy small satellites, a low-cost way to test technology and science techniques in space. On board this time, for deployment later this summer, are three CubeSats that will help us monitor rain and snow, study weather and detect and filter radio frequency interference (RFI).
Join us on Facebook Live on Saturday, May 19 at 3:30 p.m. EDT on the NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility page to hear from experts and ask them your questions about these small satellites.
Pre-Launch Briefing
Tune in live at nasa.gov/live as mission managers provide an overview and status of launch operations at 11 a.m. EDT on Sunday, May 20. Have questions? Use #askNASA
LIFTOFF!
Live launch coverage will begin on Monday, May 21 4:00 a.m. on NASA Television, nasa.gov/live, Facebook Live, Periscope, Twitch, Ustream and YouTube. Liftoff is slated for 4:39 a.m.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
@flood123789: What does it feel like to drink a lot of water in zero gravity
i cannot wait for my first solar eclipse! what's your favorite part about these eclipses, alexa?
I’ve never seen totality as the last time it was in the US was before I was born. My favourite part of seeing videos and photos is definitely viewing the solar corona! But I’m looking forward to this one so that I can see sunspots during the partial eclipse! It’s these spots that are often the active regions on the Sun that produce solar storms that can ultimately drive the aurora here on Earth!
Five Ways the International Space Station’s National Lab Enables Commercial Research
A growing number of commercial partners use the International Space Station National Lab. With that growth, we will see more discoveries in fundamental and applied research that could improve life on the ground.

Space Station astronaut Kate Rubins was the first person to sequence DNA in microgravity.
Since 2011, when we engaged the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS) to manage the International Space Station (ISS) National Lab, CASIS has partnered with academic researchers, other government organizations, startups and major commercial companies to take advantage of the unique microgravity lab. Today, more than 50 percent of CASIS’ experiments on the station represent commercial research.
Here’s a look at five ways the ISS National Lab is enabling new opportunities for commercial research in space.
1. Supporting Commercial Life Sciences Research

One of the main areas of focus for us in the early origins of the space station program was life sciences, and it is still a major priority today. Studying the effects of microgravity on astronauts provides insight into human physiology, and how it evolves or erodes in space. CASIS took this knowledge and began robust outreach to the pharmaceutical community, which could now take advantage of the microgravity environment on the ISS National Lab to develop and enhance therapies for patients on Earth. Companies such as Merck, Eli Lilly & Company, and Novartis have sent several experiments to the station, including investigations aimed at studying diseases such as osteoporosis, and examining ways to enhance drug tablets for increased potency to help patients on Earth. These companies are trailblazers for many other life science companies that are looking at how the ISS National Lab can advance their research efforts.
2. Enabling Commercial Investigations in Material and Physical Sciences

Over the past few years, CASIS and the ISS National Lab also have seen a major push toward material and physical sciences research by companies interested in enhancing their products for consumers. Examples range from Proctor and Gamble’s investigation aimed at increasing the longevity of daily household products, to Milliken’s flame-retardant textile investigation to improve protective clothing for individuals in harm’s way, and companies looking to enhance materials for household appliances. Additionally, CASIS has been working with a variety of companies to improve remote sensing capabilities in order to better monitor our oceans, predict harmful algal blooms, and ultimately, to better understand our planet from a vantage point roughly 250 miles above Earth.
3. Supporting Startup Companies Interested in Microgravity Research

CASIS has funded a variety of investigations with small startup companies (in particular through seed funding and grant funding from partnerships and funded solicitations) to leverage the ISS National Lab for both research and test-validation model experiments. CASIS and The Boeing Company recently partnered with MassChallenge, the largest startup accelerator in the world, to fund three startup companies to conduct microgravity research.
4. Enabling Validation of Low-Earth Orbit Business Models

The ISS National Lab helps validate low-Earth orbit business models. Companies such as NanoRacks, Space Tango, Made In Space, Techshot, and Controlled Dynamics either have been funded by CASIS or have sent instruments to the ISS National Lab that the research community can use, and that open new channels for inquiry. This has allowed the companies that operate these facilities to validate their business models, while also building for the future beyond station.
5. Demonstrating the Commercial Value of Space-based Research
We have been a key partner in working with CASIS to demonstrate to American businesses the value of conducting research in space. Through outreach events such as our Destination Station, where representatives from the International Space Station Program Science Office and CASIS select cities with several major companies and meet with the companies to discuss how they could benefit from space-based research. Over the past few years, this outreach has proven to be a terrific example of building awareness on the benefits of microgravity research.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
@yesrazorbladecupcakes: Do you guys ever just goof off?
-
 4s14 liked this · 1 year ago
4s14 liked this · 1 year ago -
 whitestnoise liked this · 3 years ago
whitestnoise liked this · 3 years ago -
 partygrenade1420 liked this · 5 years ago
partygrenade1420 liked this · 5 years ago -
 kangleywa liked this · 6 years ago
kangleywa liked this · 6 years ago -
 nukleara reblogged this · 6 years ago
nukleara reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 nukleara liked this · 6 years ago
nukleara liked this · 6 years ago -
 q-v-butts liked this · 6 years ago
q-v-butts liked this · 6 years ago -
 becblanc reblogged this · 6 years ago
becblanc reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 sparkofstorm reblogged this · 6 years ago
sparkofstorm reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 theinquisitivereceptacle reblogged this · 6 years ago
theinquisitivereceptacle reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 mynwworld-blog liked this · 6 years ago
mynwworld-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 bilt2tumble reblogged this · 6 years ago
bilt2tumble reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 averageinside liked this · 6 years ago
averageinside liked this · 6 years ago -
 migueltri reblogged this · 7 years ago
migueltri reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 cosmos-ayira reblogged this · 7 years ago
cosmos-ayira reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 cosmos-ayira liked this · 7 years ago
cosmos-ayira liked this · 7 years ago -
 spacetimewithstuartgary reblogged this · 7 years ago
spacetimewithstuartgary reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 migueltri liked this · 7 years ago
migueltri liked this · 7 years ago -
 dulce-bomboncito-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
dulce-bomboncito-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 dulce-bomboncito-blog liked this · 7 years ago
dulce-bomboncito-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 theprominens liked this · 7 years ago
theprominens liked this · 7 years ago -
 hatenik reblogged this · 7 years ago
hatenik reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 hatenik liked this · 7 years ago
hatenik liked this · 7 years ago -
 the-blvck-wolf reblogged this · 7 years ago
the-blvck-wolf reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 burnt-to-ashes reblogged this · 7 years ago
burnt-to-ashes reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 crvplace liked this · 7 years ago
crvplace liked this · 7 years ago -
 larryrickard liked this · 7 years ago
larryrickard liked this · 7 years ago -
 manuel82 liked this · 7 years ago
manuel82 liked this · 7 years ago -
 prettygoodmamgu liked this · 7 years ago
prettygoodmamgu liked this · 7 years ago -
 gabosaurius liked this · 7 years ago
gabosaurius liked this · 7 years ago -
 gabosaurius reblogged this · 7 years ago
gabosaurius reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 lordblackjesus reblogged this · 7 years ago
lordblackjesus reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 waceycah liked this · 7 years ago
waceycah liked this · 7 years ago -
 bozont liked this · 7 years ago
bozont liked this · 7 years ago -
 aspensmonster liked this · 7 years ago
aspensmonster liked this · 7 years ago -
 andromeda1023 reblogged this · 7 years ago
andromeda1023 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 andromeda1023 liked this · 7 years ago
andromeda1023 liked this · 7 years ago -
 cliffsteele reblogged this · 7 years ago
cliffsteele reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 justinrezz liked this · 7 years ago
justinrezz liked this · 7 years ago -
 vestigial-wanderer liked this · 7 years ago
vestigial-wanderer liked this · 7 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts