Science Launching To Station Looks Forward And Back
Science Launching to Station Looks Forward and Back
Some of the earliest human explorers used mechanical tools called sextants to navigate vast oceans and discover new lands. Today, high-tech tools navigate microscopic DNA to discover previously unidentified organisms. Scientists aboard the International Space Station soon will have both types of tools at their disposal.

Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft is scheduled to launch its ninth contracted cargo resupply mission to the space station no earlier than May 21. Sending crucial science, supplies and cargo to the crew of six humans living and working on the orbiting laboratory.
Our Gemini missions conducted the first sextant sightings from a spacecraft, and designers built a sextant into Apollo vehicles as a lost-communications navigation backup. The Sextant Navigation investigation tests use of a hand-held sextant for emergency navigation on missions in deep space as humans begin to travel farther from Earth.

Jim Lovell (far left) demonstrated on Apollo 8 that sextant navigation could return a space vehicle home.

The remoteness and constrained resources of living in space require simple but effective processes and procedures to monitor the presence of microbial life, some of which might be harmful. Biomolecule Extraction and Sequencing Technology (BEST) advances the use of sequencing processes to identify microbes aboard the space station that current methods cannot detect and to assess mutations in the microbial genome that may be due to spaceflight.

Genes in Space 3 performed in-flight identification of bacteria on the station for the first time. BEST takes that one step farther, identifying unknown microbial organisms using a process that sequences directly from a sample with minimal preparation, rather than with the traditional technique that requires growing a culture from the sample.

Adding these new processes to the proven technology opens new avenues for inflight research, such as how microorganisms on the station change or adapt to spaceflight.
The investigation’s sequencing components provide important information on the station’s microbial occupants, including which organisms are present and how they respond to the spaceflight environment -- insight that could help protect humans during future space exploration. Knowledge gained from BEST could also provide new ways to monitor the presence of microbes in remote locations on Earth.
Moving on to science at a scale even smaller than a microbe, the new Cold Atom Lab (CAL) facility could help answer some big questions in modern physics.

CAL creates a temperature ten billion (Yup. BILLION) times colder than the vacuum of space, then uses lasers and magnetic forces to slow down atoms until they are almost motionless. CAL makes it possible to observe these ultra-cold atoms for much longer in the microgravity environment on the space station than would be possible on the ground.

Results of this research could potentially lead to a number of improved technologies, including sensors, quantum computers and atomic clocks used in spacecraft navigation.
A partnership between the European Space Agency (ESA) and Space Application Services (SpaceAps), The International Commercial Experiment, or ICE Cubes Service, uses a sliding framework permanently installed on the space station and “plug-and-play” Experiment Cubes.

The Experiment Cubes are easy to install and remove, come in different sizes and can be built with commercial off-the-shelf components, significantly reducing the cost and time to develop experiments.
ICE Cubes removes barriers that limit access to space, providing more people access to flight opportunities. Potential fields of research range from pharmaceutical development to experiments on stem cells, radiation, and microbiology, fluid sciences, and more.
For daily nerd outs, follow @ISS_Research on Twitter!
Watch the Launch + More!

What’s On Board Briefing
Join scientists and researchers as they discuss some of the investigations that will be delivered to the station on Saturday, May 19 at 1 p.m. EDT at nasa.gov/live. Have questions? Use #askNASA
CubeSat Facebook Live
The International Space Station is often used to deploy small satellites, a low-cost way to test technology and science techniques in space. On board this time, for deployment later this summer, are three CubeSats that will help us monitor rain and snow, study weather and detect and filter radio frequency interference (RFI).
Join us on Facebook Live on Saturday, May 19 at 3:30 p.m. EDT on the NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility page to hear from experts and ask them your questions about these small satellites.
Pre-Launch Briefing
Tune in live at nasa.gov/live as mission managers provide an overview and status of launch operations at 11 a.m. EDT on Sunday, May 20. Have questions? Use #askNASA
LIFTOFF!
Live launch coverage will begin on Monday, May 21 4:00 a.m. on NASA Television, nasa.gov/live, Facebook Live, Periscope, Twitch, Ustream and YouTube. Liftoff is slated for 4:39 a.m.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
What are three things you would want everyone to know about your work?
10 Things to Know About Parker Solar Probe
On Aug. 12, 2018, we launched Parker Solar Probe to the Sun, where it will fly closer than any spacecraft before and uncover new secrets about our star. Here's what you need to know.

1. Getting to the Sun takes a lot of power
At about 1,400 pounds, Parker Solar Probe is relatively light for a spacecraft, but it launched to space aboard one of the most powerful rockets in the world, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy. That's because it takes a lot of energy to go to the Sun — in fact, 55 times more energy than it takes to go to Mars.
Any object launched from Earth starts out traveling at about the same speed and in the same direction as Earth — 67,000 mph sideways. To get close to the Sun, Parker Solar Probe has to shed much of that sideways speed, and a strong launch is good start.

2. First stop: Venus!
Parker Solar Probe is headed for the Sun, but it's flying by Venus along the way. This isn't to see the sights — Parker will perform a gravity assist at Venus to help draw its orbit closer to the Sun. Unlike most gravity assists, Parker will actually slow down, giving some orbital energy to Venus, so that it can swing closer to the Sun.
One's not enough, though. Parker Solar Probe will perform similar maneuvers six more times throughout its seven-year mission!

3. Closer to the Sun than ever before
At its closest approach toward the end of its seven-year prime mission, Parker Solar Probe will swoop within 3.83 million miles of the solar surface. That may sound pretty far, but think of it this way: If you put Earth and the Sun on opposite ends of an American football field, Parker Solar Probe would get within four yards of the Sun's end zone. The current record-holder was a spacecraft called Helios 2, which came within 27 million miles, or about the 30 yard line. Mercury orbits at about 36 million miles from the Sun.
This will place Parker well within the Sun's corona, a dynamic part of its atmosphere that scientists think holds the keys to understanding much of the Sun's activity.

4. Faster than any human-made object
Parker Solar Probe will also break the record for the fastest spacecraft in history. On its final orbits, closest to the Sun, the spacecraft will reach speeds up to 430,000 mph. That's fast enough to travel from New York to Tokyo in less than a minute!

5. Dr. Eugene Parker, mission namesake
Parker Solar Probe is named for Dr. Eugene Parker, the first person to predict the existence of the solar wind. In 1958, Parker developed a theory showing how the Sun’s hot corona — by then known to be millions of degrees Fahrenheit — is so hot that it overcomes the Sun’s gravity. According to the theory, the material in the corona expands continuously outwards in all directions, forming a solar wind.
This is the first NASA mission to be named for a living person, and Dr. Parker watched the launch with the mission team from Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

6. Unlocking the secrets of the solar wind
Even though Dr. Parker predicted the existence of the solar wind 60 years ago, there's a lot about it we still don't understand. We know now that the solar wind comes in two distinct streams, fast and slow. We've identified the source of the fast solar wind, but the slow solar wind is a bigger mystery.
Right now, our only measurements of the solar wind happen near Earth, after it has had tens of millions of miles to blur together, cool down and intermix. Parker's measurements of the solar wind, just a few million miles from the Sun's surface, will reveal new details that should help shed light on the processes that send it speeding out into space.

7. Studying near-light speed particles
Another question we hope to answer with Parker Solar Probe is how some particles can accelerate away from the Sun at mind-boggling speeds — more than half the speed of light, or upwards of 90,000 miles per second. These particles move so fast that they can reach Earth in under half an hour, so they can interfere with electronics on board satellites with very little warning.

8. The mystery of the corona's high heat
The third big question we hope to answer with this mission is something scientists call the coronal heating problem. Temperatures in the Sun's corona, where Parker Solar Probe will fly, spike upwards of 2 million degrees Fahrenheit, while the Sun's surface below simmers at a balmy 10,000 F. How the corona gets so much hotter than the surface remains one of the greatest unanswered questions in astrophysics.
Though scientists have been working on this problem for decades with measurements taken from afar, we hope measurements from within the corona itself will help us solve the coronal heating problem once and for all.

9. Why won't Parker Solar Probe melt?
The corona reaches millions of degrees Fahrenheit, so how can we send a spacecraft there without it melting?
The key lies in the distinction between heat and temperature. Temperature measures how fast particles are moving, while heat is the total amount of energy that they transfer. The corona is incredibly thin, and there are very few particles there to transfer energy — so while the particles are moving fast (high temperature), they don’t actually transfer much energy to the spacecraft (low heat).
It’s like the difference between putting your hand in a hot oven versus putting it in a pot of boiling water (don’t try this at home!). In the air of the oven, your hand doesn’t get nearly as hot as it would in the much denser water of the boiling pot.

10. Engineered to thrive in an extreme environment
Make no mistake, the environment in the Sun's atmosphere is extreme — hot, awash in radiation, and very far from home — but Parker Solar Probe is engineered to survive.
The spacecraft is outfitted with a cutting-edge heat shield made of a carbon composite foam sandwiched between two carbon plates. The heat shield is so good at its job that, even though the front side will receive the full brunt of the Sun's intense light, reaching 2,500 F, the instruments behind it, in its shadow, will remain at a cozy 85 F.
Even though Parker Solar Probe's solar panels — which provide the spacecraft's power — are retractable, even the small bit of surface area that peeks out near the Sun is enough to make them prone to overheating. So, to keep its cool, Parker Solar Probe circulates a single gallon of water through the solar arrays. The water absorbs heat as it passes behind the arrays, then radiates that heat out into space as it flows into the spacecraft’s radiator.
For much of its journey, Parker Solar Probe will be too far from home and too close to the Sun for us to command it in real time — but don't worry, Parker Solar Probe can think on its feet. Along the edges of the heat shield’s shadow are seven sensors. If any of these sensors detect sunlight, they alert the central computer and the spacecraft can correct its position to keep the sensors — and the rest of the instruments — safely protected behind the heat shield.
Read the web version of this week’s “Solar System: 10 Things to Know” article HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
10 Ways the Webb Telescope ‘Trains’ for Space
The James Webb Space Telescope will peer at the first stars and galaxies as a cosmic time machine, look beyond to distant worlds, and unlock the mysteries of the universe. But before it can do any of those things, it needs to “train” for traveling to its destination — 1 million miles away from Earth!
So how does Webb get ready for space while it’s still on the ground? Practice makes perfect. Different components of the telescope were first tested on their own, but now a fully-assembled Webb is putting all of its training together. Here are 10 types of tests that Webb went through to prepare for its epic journey:
1. Sounding Off
A rocket launch is 100 times more intense and four times louder than a rock concert! (That’s according to Paul Geithner, Webb’s deputy project manager – technical.) To simulate that level of extreme noise, Webb’s full structure was blasted with powerful sound waves during its observatory-level acoustic testing in August.

2. Shaking It Up
Webb will also have to withstand a super-bumpy ride as it launches — like a plane takeoff, but with a lot more shaking! The observatory was carefully folded into its launch position, placed onto a shaker table, and vibrated from 5 to 100 times per second to match the speeds of Webb’s launch vehicle, an Ariane 5 rocket.

3. All Systems Go
In July, Webb performed a rigorous test of its software and electrical systems as a fully connected telescope. Each line of code for Webb was tested and then retested as different lines were combined into Webb’s larger software components. To complete this test, Webb team members were staffed 24 hours a day for 15 consecutive days!

4. Hanging Out
After launch, Webb is designed to unfold (like origami in reverse) from its folded launch position into its operational form. Without recharging, the telescope’s onboard battery would only last a few hours, so it will be up to Webb’s 20-foot solar array to harness the Sun’s energy for all of the telescope’s electrical needs. To mimic the zero-gravity conditions of space, Webb technicians tested the solar array by hanging it sideways.

5. Time to Stretch
The tower connects the upper and lower halves of Webb. Once Webb is in space, the tower will extend 48 inches (1.2 meters) upward to create a gap between the two halves of the telescope. Then all five layers of Webb’s sunshield will slowly unfurl and stretch out, forming what will look like a giant kite in space. Both the tower and sunshield will help different sections of Webb maintain their ideal temperatures.

For these steps, engineers designed an ingenious system of cables, pulleys and weights to counter the effects of Earth’s gravity. 6. Dance of the Mirrors
Unfolding Webb’s mirrors will involve some dance-like choreography. First, a support structure will gracefully unfold to place the circular secondary mirror out in front of the primary mirror. Although small, the secondary mirror will play a big role: focusing light from the primary mirror to send to Webb’s scientific instruments.

Next, Webb’s iconic primary mirror will fully extend so that all 18 hexagonal segments are in view. At 6.5 meters (21 feet 4-inches) across, the mirror’s massive size is key for seeing in sharp detail. Like in tower and sunshield testing, the Webb team offloaded the weight of both mirrors with cables, pulleys and weights so that they unfolded as if weightless in space.

7. Do Not Disturb
Before a plane takeoff, it’s important for us to turn off our cell phones to make sure that their electromagnetic waves won’t interfere with navigation signals. Similarly, Webb had to test that its scientific instruments wouldn’t disrupt the electromagnetic environment of the spacecraft. This way, when we get images back from Webb, we’ll know that we’re seeing actual objects in space instead of possible blips caused by electromagnetic interference. These tests took place in the Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Lab, which looks like a futuristic sound booth! Instead of absorbing sound, however, the walls of this chamber help keep electromagnetic waves from bouncing around.

8. Phoning Earth
How will Webb know where to go and what to look at? Thanks to Webb’s Ground Segment Tests, we know that we’ll be able to “talk” to Webb after liftoff. In the first six hours after launch, the telescope needs to seamlessly switch between different communication networks and stations located around the world. Flight controllers ran through these complex procedures in fall 2018 to help ensure that launch will be a smooth success.

After Webb reaches its destination, operators will use the Deep Space Network, an international array of giant radio antennas, to relay commands that tell Webb where to look. To test this process when Webb isn’t in space yet, the team used special equipment to imitate the real radio link that will exist between the observatory and the network.
9. Hot and Cold
Between 2017 and 2019, Webb engineers separately tested the two halves of the telescope in different thermal vacuum chambers, which are huge, climate-controlled rooms drained of air to match the vacuum of space. In testing, the spacecraft bus and sunshield half were exposed to both boiling hot and freezing cold temperatures, like the conditions that they’ll encounter during Webb’s journey.
But Webb’s mirrors and instruments will need to be colder than cold to operate! This other half of Webb was tested in the historic Chamber A, which was used to test Apollo Moon mission hardware and specifically upgraded to fit Webb. Over about 100 days, Chamber A was gradually cooled down, held at cryogenic temperatures (about minus 387 F, or minus 232.8 C), and then warmed back up to room temperature.

10. Cosmic Vision
When the Hubble Space Telescope was first sent into space, its images were blurry due to a flaw with its mirror. This error taught us about the importance of comprehensively checking Webb’s “eyes” before the telescope gets out of reach.
Besides training for space survival, Webb also spent time in Chamber A undergoing mirror alignment and optical testing. The team used a piece of test hardware that acted as a source of artificial starlight to verify that light would travel correctly through Webb’s optical system.

Whew! That’s a lot of testing under Webb’s belt! Webb is set to launch in October 2021 from Kourou, French Guiana. But until then, it’s still got plenty of training left, including a final round of deployment tests before being shipped to its launch location.
Learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope HERE, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How Do Cargo Spacecraft Work?

Today is the day that our commercial partner, Orbital ATK, has set for the launch of its fourth contracted mission to the International Space Station. The Cygnus spacecraft will carry more than 7,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory.
How Does it Launch?

This mission is the first Cygnus mission to utilize NASA’s Kennedy Space Center and launch from the Cape Canaveral Air Force base in Cape Canaveral, Florida.
The cargo will be launched inside the Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft using a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
But how does it get there? Is there someone on the ground controlling and directing it to the space station? Surprisingly, no. After launch, the Cygnus spacecraft is automated until it gets near the station. At that point, the robotic controllers use the CanadArm2 to reach out and grapple it (grab), and then berth (connect) it to the station.
What’s Inside?

In order to keep the thousands of pounds of supplies, science and hardware from moving during launch and in flight, the cargo is packed in bags and strapped to the walls.
The new experiments arriving to the space station will challenge and inspire future scientists and explorers. A few of the highlights are:
The Packed Bed Reactor Experiment (PBRE) - This experiment (image below) will study the behavior of gases and liquids when they flow simultaneously through a column filled with fixed porous media. The findings from this will be of interest in many chemical and biological processing systems as well as many geophysical applications.

BASS-M (Burning and Suppression of Solids – Milliken) - This experiment (image below) will evaluate flame retardant and/or resistant textiles as a mode of personal protection from fire-related hazards. Studying this in microgravity will aid in better designs for future textiles and benefit those who wear flame retardant and/or resistant protective apparel such as military personnel and civilian workers in the electrical and energy industries.

Space Automated Bioproduct Lab (SABL) - This equipment is a single locker-sized facility (image below) that will enable a wide variety of fundamental, applied and commercial life sciences research. It will also benefit K-16 education-based investigations aboard the space station. Research will be supported on microorganisms (bacteria, yeast, algae, fungi, viruses, etc.), animal cells and tissues and small plant and animal organisms.

Nodes Satellites – These satellites (image below) will be deployed from the space station to demonstrate new network capabilities critical to the operation of swarms of spacecraft. They will show the ability of multi-spacecraft swarms to receive and distribute ground commands, exchange information periodically and more.

Holiday Surprises - With the upcoming holidays the crew’s family has the opportunity to send Christmas gifts to their family members on the International Space Station.

What About After?
The spacecraft will spend more than a month attached to the space station before it’s detached for re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere in January 2016, disposing of about 3,000 pounds of trash. It will disintegrate while entering the atmosphere.

Want to Watch Launch?
Launch coverage begins at 4:30 p.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 3 on NASA Television. Cygnus is set to lift off on the Atlas V at 5:55 p.m., the beginning of a 30-minute launch window, from Space Launch Complex 41.
In addition to launch coverage, a post-launch briefing will be held approximately two hours after launch. All briefings will air live on NASA TV.
UPDATE: Due to poor weather conditions, today’s launch has been scrubbed and moved to tomorrow at 5:33 p.m. EST. The forecast for tomorrow calls for a 30% chance of acceptable conditions at launch time. Continuous countdown coverage will be available on NASA Television starting at 4:30 p.m.

UPDATE 2: The uncrewed Cygnus cargo ship launched at 4:44 p.m. EST on Sunday, Dec. 6 on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to begin its three-day journey to the orbiting laboratory.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Happy International Women’s Day!

Today we celebrate International Women’s Day, a day in which we honor and recognize the contributions of women…both on Earth and in space.

Since the beginning, women have been essential to the progression and success of America’s space program.

Throughout history, women have had to overcome struggles in the workplace. The victories for gender rights were not achieved easily or quickly, and our work is not done.

Today, we strive to make sure that our legacy of inclusion and excellence lives on.

We have a long-standing cultural commitment to excellence that is largely driven by data, including data about our people. And our data shows progress is driven by questioning our assumptions and cultural prejudices – by embracing and nurturing all talent we have available, regardless of gender, race or other protected status, to build a workforce as diverse as our mission. This is how we, as a nation, will take the next giant leap in exploration.

As a world leader in science, aeronautics, space exploration and technology, we have a diverse mission that demands talent from every corner of America, and every walk of life.

So, join us today, and every day, as we continue our legacy of inclusion and excellence.

Happy International Women’s Day!
Learn more about the inspiring woman at NASA here: https://women.nasa.gov/
5 Training Requirements for New Astronauts
After evaluating a record number of applications, we will introduce our newest class of astronaut candidates on June 7!

Upon reporting to duty at our Johnson Space Center in Houston, the new astronaut candidates will complete two years of training before they are eligible to be assigned to a mission.
Here are the five training criteria they must check off to graduate from astronaut candidate to astronaut:
1. T-38 Jets

Astronauts have been training in T-38 jets for more than 35 years because the sleek, white jets require crew members to think quickly in dynamic situations and to make decisions that have real consequences. This type of mental experience is critical to preparing for the rigors of spaceflight. To check off this training criteria, astronaut candidates must be able to safely operate in the T-38 as either a pilot or back seater.
2. International Space Station Systems

We are currently flying astronauts to the International Space Station every few months. Astronauts aboard the space station are conducting experiments benefitting humanity on Earth and teaching us how to live longer in space. Astronaut candidates learn to operate and maintain the complex systems aboard the space station as part of their basic training.
3. Spacewalks

Spacewalks are the hardest thing, physically and mentally, that astronauts do. Astronaut candidates must demonstrate the skills to complete complex spacewalks in our Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (giant pool used to simulate weightlessness). In order to do so, they will train on the life support systems within the spacesuit, how to handle emergency situations that can arise and how to work effectively as a team to repair the many critical systems aboard the International Space Station to keep it functioning as our science laboratory in space.
4. Robotics

Astronaut candidates learn the coordinate systems, terminology and how to operate the space station’s robotic arm. They train in Canada for a two week session where they develop more complex robotics skills including capturing visiting cargo vehicles with the arm. The arm, built by the Canadian Space Agency, is capable of handling large cargo and hardware, and helped build the entire space station. It has latches on either end, allowing it to be moved by both flight controllers on the ground and astronauts in space to various parts of the station.
5. Russian Language

The official languages of the International Space Station are English and Russian, and all crewmembers – regardless of what country they come from – are required to know both. NASA astronauts train with their Russian crew mates and launch on the Russian Soyuz vehicle, so it makes sense that they should be able to speak Russian. Astronaut candidates start learning the language at the beginning of their training. They train on this skill every week, as their schedule allows, to keep in practice.
Now, they are ready for their astronaut pin!
After completing this general training, the new astronaut candidates could be assigned to missions performing research on the International Space Station, launching from American soil on spacecraft built by commercial companies, and launching on deep space missions on our new Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket.

Watch the Astronaut Announcement LIVE!
We will introduce our new astronaut candidates at 2 p.m. EDT Wednesday, June 7, from our Johnson Space Center in Houston.
Watch live online at nasa.gov/live or on NASA’s Facebook Page.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More than Just Dust in the Wind

From space, we can see a swirling brown mass making its way across the Atlantic – dust from the Sahara Desert – the largest hot desert in the world. It’s a normal phenomenon. Every year, winds carry millions of tons of dust from North Africa, usually during spring and summer in the Northern Hemisphere.

June 2020 has seen a massive plume of dust crossing the ocean. It’s so large it’s visible from one million miles away in space.

Dust clouds this large can affect air quality in regions where the dust arrives. The particles can also scatter the Sun’s light, making sunrises and sunsets more vibrant.

Dust particles in the air are also known as aerosols. We can measure aerosols, including dust, sea salt and smoke, from satellites and also use computer models to study how they move with the wind.

Following the transport of dust from space shows us how one of the driest places on Earth plays a role in fertilizing the Amazon rainforest. There are minerals in Saharan dust, like phosphorous, that exist in commercial fertilizers, helping seed the rainforest.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
June 10 Solar Eclipse in the Northern Hemisphere!
On June 10, people in parts of the northern hemisphere will have the chance to witness a solar eclipse.

Watch the full visualization of the eclipse.
The June 10 eclipse is an annular solar eclipse, meaning that the Sun will never be completely covered by the Moon. The Moon’s orbit around the Earth is not a perfect circle, so throughout each month, the Moon’s distance from Earth varies. During an annular eclipse, the Moon is far enough away from Earth that the Moon appears smaller than the Sun in the sky. Since the Moon does not block the entire view of the Sun, it will look like a dark disk on top of a larger, bright disk. This creates what looks like a ring of fire around the Moon.
People in the narrow path of annularity — which, for this eclipse, cuts through Canada, Greenland, and northern Russia — will see the ring of fire effect as the Moon passes across the Sun.

Credit: Dale Cruikshank
Outside this path of annularity, many people in the northern hemisphere have a chance to see a partial solar eclipse. The partial eclipse will fall on parts of the eastern United States, as well as northern Alaska. Some locations will only see a very small piece of the Sun covered, while locations closer to the path of annularity can see the Moon cover most of the Sun.
To learn which times the eclipse may be visible in certain areas, you can click anywhere on the map here. (Note that the maximum obscuration and maximum eclipse timing noted on this map may occur before sunrise in many locations.)

This solar eclipse is a pair with the total lunar eclipse that happened on May 26.
Both solar and lunar eclipses happen when the Sun, Moon, and Earth line up in the same plane — a lunar eclipse happens when Earth is in the middle and casts its shadow on the Moon, and a solar eclipse happens when the Moon is in the middle and casts its shadow on Earth. The Moon’s orbit is tilted, so it’s usually too high or too low for this alignment to work out.

The May 26 lunar eclipse was a supermoon lunar eclipse, meaning that the full moon happened while the Moon was near its closest point to Earth, making the Moon appear larger in the sky. The solar eclipse happens at the opposite point of the Moon’s orbit, during the new moon — and in this case, the new moon happens near the Moon’s farthest point from Earth, making the Moon appear smaller and resulting in an annular (rather than total) solar eclipse.
How to watch the eclipse
From anywhere: Watch the eclipse online with us! Weather permitting, we’ll be sharing live telescope views of the partial eclipse courtesy of Luc Boulard of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada Sudbury Centre. Tune in starting at 5 a.m. EDT on June 10 at nasa.gov/live.
From the path of the annular or partial eclipse: Be sure to take safety precuations if you plan to watch in person!
It is never safe to look directly at the Sun's rays, even if the Sun is partly or mostly obscured, like during a partial or annular eclipse — doing so can severely harm your eyes. If you’re planning to watch the eclipse on June 10, you should use solar viewing glasses or an indirect viewing method at all points during the eclipse if you want to face the Sun. Solar viewing glasses, sometimes called eclipse glasses, are NOT regular sunglasses; regular sunglasses are not safe for viewing the Sun.

If you don’t have solar viewing or eclipse glasses, you can use an alternate indirect method like a pinhole projector. Pinhole projectors shouldn’t be used to look at the Sun; instead, they’re an easy way to project an image of the Sun onto a surface. Read more about how to create a pinhole projector.
This is a sunrise eclipse in the contiguous U.S. At locations in the lower 48 states that can see the partial eclipse, the show starts before sunrise, when the Sun is still below the horizon. That means the best chance to see the eclipse in these locations will be during and shortly after sunrise, when the Sun is very low in the sky. In northern Alaska, the eclipse happens in the very early hours of June 10 when the Sun is low on the horizon.
Bottom line: If you’re trying to watch the eclipse in the contiguous U.S., look for a location with a clear view of the horizon to the northeast, and plan to watch starting at sunrise with your solar filter or indirect viewer.
The next two eclipses in the continental U.S. are in 2023 and 2024. The annular solar eclipse of Oct. 14, 2023, will cut from Oregon to Texas, and the total solar eclipse of April 8, 2024, will pass from Texas to Maine. Keep up with the latest on eclipses and eclipse science at nasa.gov/eclipse.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
May the Four Forces Be With You!
May the force be with you? Much to learn you still have, padawan. In our universe it would be more appropriate to say, “May the four forces be with you.”
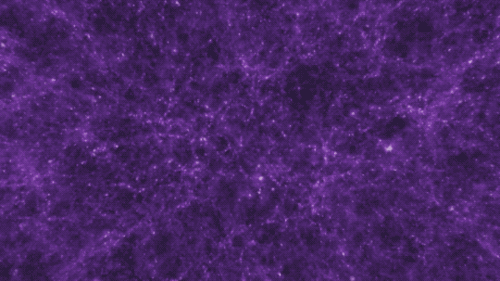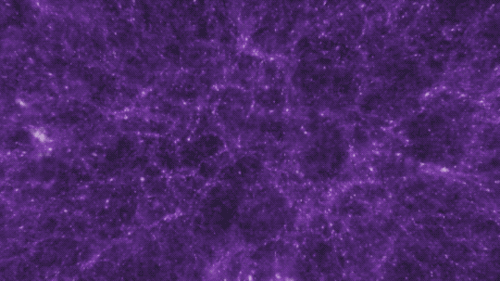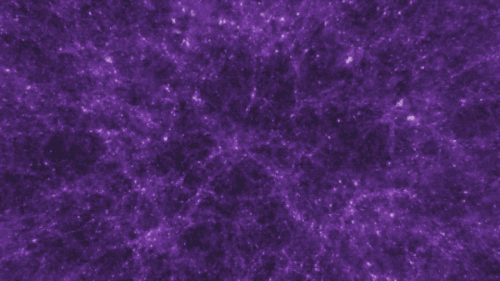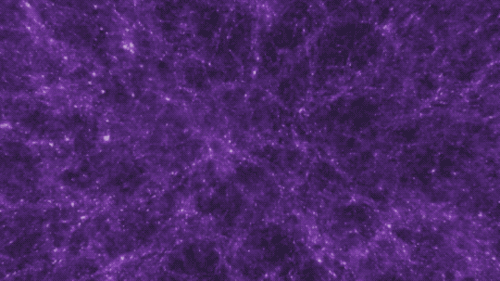
There are four fundamental forces that bind our universe and its building blocks together. Two of them are easy to spot — gravity keeps your feet on the ground while electromagnetism keeps your devices running. The other two are a little harder to see directly in everyday life, but without them, our universe would look a lot different!
Let’s explore these forces in a little more detail.
Gravity: Bringing the universe together

If you jump up, gravity brings you back down to Earth. It also keeps the solar system together … and our galaxy, and our local group of galaxies and our supercluster of galaxies.
Gravity pulls everything together. Everything, from the bright centers of the universe to the planets farthest from them. In fact, you (yes, you!) even exert a gravitational force on a galaxy far, far away. A tiny gravitational force, but a force nonetheless.

Credit: NASA and the Advanced Visualization Laboratory at the National Center for Supercomputing and B. O'Shea, M. Norman
Despite its well-known reputation, gravity is actually the weakest of the four forces. Its strength increases with the mass of the two objects involved. And its range is infinite, but the strength drops off as the square of the distance. If you and a friend measured your gravitational tug on each other and then doubled the distance between you, your new gravitational attraction would just be a quarter of what it was. So, you have to be really close together, or really big, or both, to exert a lot of gravity.
Even so, because its range is infinite, gravity is responsible for the formation of the largest structures in our universe! Planetary systems, galaxies and clusters of galaxies all formed because gravity brought them together.
Gravity truly surrounds us and binds us together.
Electromagnetism: Lighting the way
You know that shock you get on a dry day after shuffling across the carpet? The electricity that powers your television? The light that illuminates your room on a dark night? Those are all the work of electromagnetism. As the name implies, electromagnetism is the force that includes both electricity and magnetism.
Electromagnetism keeps electrons orbiting the nucleus at the center of atoms and allows chemical compounds to form (you know, the stuff that makes up us and everything around us). Electromagnetic waves are also known as light. Once started, an electromagnetic wave will travel at the speed of light until it interacts with something (like your eye) — so it will be there to light up the dark places.

Like gravity, electromagnetism works at infinite distances. And, also like gravity, the electromagnetic force between two objects falls as the square of their distance. However, unlike gravity, electromagnetism doesn't just attract. Whether it attracts or repels depends on the electric charge of the objects involved. Two negative charges or two positive charges repel each other; one of each, and they attract each other. Plus. Minus. A balance.
This is what happens with common household magnets. If you hold them with the same “poles” together, they resist each other. On the other hand, if you hold a magnet with opposite poles together — snap! — they’ll attract each other.
Electromagnetism might just explain the relationship between a certain scruffy-looking nerf-herder and a princess.
Strong Force: Building the building blocks

Credit: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
The strong force is where things get really small. So small, that you can’t see it at work directly. But don’t let your eyes deceive you. Despite acting only on short distances, the strong force holds together the building blocks of the atoms, which are, in turn, the building blocks of everything we see around us.
Like gravity, the strong force always attracts, but that’s really where their similarities end. As the name implies, the force is strong with the strong force. It is the strongest of the four forces. It brings together protons and neutrons to form the nucleus of atoms — it has to be stronger than electromagnetism to do it, since all those protons are positively charged. But not only that, the strong force holds together the quarks — even tinier particles — to form those very protons and neutrons.
However, the strong force only works on very, very, very small distances. How small? About the scale of a medium-sized atom’s nucleus. For those of you who like the numbers, that’s about 10-15 meters, or 0.000000000000001 meters. That’s about a hundred billion times smaller than the width of a human hair! Whew.
Its tiny scale is why you don’t directly see the strong force in your day-to-day life. Judge a force by its physical size, do you?
Weak Force: Keeping us in sunshine

If you thought it was hard to see the strong force, the weak force works on even smaller scales — 1,000 times smaller. But it, too, is extremely important for life as we know it. In fact, the weak force plays a key role in keeping our Sun shining.
But what does the weak force do? Well … that requires getting a little into the weeds of particle physics. Here goes nothing! We mentioned quarks earlier — these are tiny particles that, among other things, make up protons and neutrons. There are six types of quarks, but the two that make up protons and neutrons are called up and down quarks. The weak force changes one quark type into another. This causes neutrons to decay into protons (or the other way around) while releasing electrons and ghostly particles called neutrinos.
So for example, the weak force can turn a down quark in a neutron into an up quark, which will turn that neutron into a proton. If that neutron is in an atom’s nucleus, the electric charge of the nucleus changes. That tiny change turns the atom into a different element! Such reactions are happening all the time in our Sun, giving it the energy to shine.
The weak force might just help to keep you in the (sun)light.

All four of these forces run strong in the universe. They flow between all things and keep our universe in balance. Without them, we’d be doomed. But these forces will be with you. Always.
You can learn more about gravity from NASA’s Space Place and follow NASAUniverse on Twitter or Facebook to learn about some of the cool cosmic objects we study with light.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s your favorite part of the job?
-
 epitafio-desconocido liked this · 4 years ago
epitafio-desconocido liked this · 4 years ago -
 andrejupiter liked this · 4 years ago
andrejupiter liked this · 4 years ago -
 galestral liked this · 5 years ago
galestral liked this · 5 years ago -
 fernandanajerd liked this · 6 years ago
fernandanajerd liked this · 6 years ago -
 ash-moztaza liked this · 6 years ago
ash-moztaza liked this · 6 years ago -
 atukjomcx liked this · 6 years ago
atukjomcx liked this · 6 years ago -
 qaqswdefr-blog liked this · 6 years ago
qaqswdefr-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 hyourinmaruice reblogged this · 6 years ago
hyourinmaruice reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 quantumwoow-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
quantumwoow-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 6 years ago
fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 littleplasticspaceship reblogged this · 6 years ago
littleplasticspaceship reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 saltymusician-blog liked this · 6 years ago
saltymusician-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 smokenhose liked this · 6 years ago
smokenhose liked this · 6 years ago -
 kherukemet reblogged this · 6 years ago
kherukemet reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 kherukemet liked this · 6 years ago
kherukemet liked this · 6 years ago -
 adventuretrips3-blog liked this · 6 years ago
adventuretrips3-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 clockworkambigram reblogged this · 6 years ago
clockworkambigram reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 maggietann reblogged this · 6 years ago
maggietann reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 maggietann liked this · 6 years ago
maggietann liked this · 6 years ago -
 grin-a-wolfish-grin liked this · 6 years ago
grin-a-wolfish-grin liked this · 6 years ago -
 monet-paints-moineau reblogged this · 6 years ago
monet-paints-moineau reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 waterbro5566-blog liked this · 6 years ago
waterbro5566-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 nocti-x-blog liked this · 6 years ago
nocti-x-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 wrongfooted liked this · 6 years ago
wrongfooted liked this · 6 years ago -
 randyranks reblogged this · 6 years ago
randyranks reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 nasalangley liked this · 6 years ago
nasalangley liked this · 6 years ago -
 nofollowers1 liked this · 6 years ago
nofollowers1 liked this · 6 years ago -
 secretlysweetstud-blog liked this · 6 years ago
secretlysweetstud-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 alternageek reblogged this · 6 years ago
alternageek reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 bir-kedisever reblogged this · 6 years ago
bir-kedisever reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 lonelystewsack-blog liked this · 6 years ago
lonelystewsack-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 realf-blog liked this · 6 years ago
realf-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 stormbear reblogged this · 6 years ago
stormbear reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 naseralyosofi-blog liked this · 6 years ago
naseralyosofi-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 greenminister liked this · 6 years ago
greenminister liked this · 6 years ago -
 actualbenis liked this · 6 years ago
actualbenis liked this · 6 years ago -
 snadwick liked this · 6 years ago
snadwick liked this · 6 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts