Applying Earth Observations Data To The Real World
Applying Earth Observations Data to the Real World
In our DEVELOP Program, participants work on Earth science research projects and are mentored by science advisors from within the agency and from partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities.
This year, our partners ran the gamut from NASA centers to The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Agency (NOAA) to the University of Georgia to state and local governments. The one thing all have in common: using data from our Earth-observing satellites to inform such topics as disaster relief, preserving watershed and marshlands, working municipalities to provide health and study. The program also helps future scientists develop research and presentation skills.
Annually, the participants gather at NASA Headquarters to present their findings. From more than two dozen, we’re highlighting a cross section whose projects covered climate and invasive species in Alaska; health and air quality in Las Cruces; disaster preparation in the Philippines; and air quality in the Shenandoah Valley.
The projects demonstrate to community leaders how our science measurements and predictions can be used to address local policy issues. This year, DEVELOP features more than two dozen projects covering Earth science topics from all corners of the globe.
DEVELOP projects apply Earth observations to agriculture, climate, disasters, ecological forecasting, energy, health and air quality, oceans, water resources and weather. These projects highlight NASA Earth observation capabilities relative to environmental issues and concerns for enhanced policy and decision-making to improve life here on Earth.
DEVELOP projects apply Earth observations to agriculture, climate, disasters, ecological forecasting, energy, health and air quality, oceans, water resources and weather. These projects highlight NASA Earth observation capabilities relative to environmental issues and concerns for enhanced policy and decision-making to improve life here on Earth.
Visit the Develop Project page to learn more about the program and how to apply.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Seven Reasons Why Rover Challenge is Serious Business
Prizes, awards and a year’s worth of bragging rights are at stake during our annual Human Exploration Rover Challenge. Year after year, student teams from across the world design, build and race rovers against the clock and each other.
With a space-themed obstacle course, unique rovers, competitive racing, our exhibits and dozens of international teams… it’s everything cool about STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) and space exploration.
Here are the “must-know” details for this year’s event:
1. Bumps, Bruises and Battle Scars

Our space-themed obstacle course often brings racers to their knees, literally. This daunting three-quarter-mile long course is difficult to traverse and isn’t for the faint of heart. It uses both lunar and Mars-themed obstacles to simulate the types of terrain found on distant planets, asteroids or moons.
Plus, teams must race their rovers in, on and around full-scale rockets and space vehicle exhibits on display at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center – the official visitor center for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, both in Huntsville, Alabama. See just how difficult and wild the course can be in our Flickr gallery.
2. Homemade Wheels Only

Rover teams must design and fabricate their own original, or “homemade” wheels. In-Situ Resource Utilization is an important component for our future missions to Mars, asteroids or other planets.
Astronauts can never simply purchase wheels at the store… and neither can our rover teams. Teams must not use any “off-the-shelf” wheels on their rover. By wheels, this means any component used for contact, traction or mobility on the surface of the obstacle course, including, but not limited to wheels, tracks, treads or belts.
And, as in years past, teams are not allowed to incorporate inflated (or un-inflated) pneumatic tires. Inflated tires would be considered an off-the-shelf product, not eligible under the current rules.
3. New “Sample Retrieval” Component Added

Teams may choose to compete in this optional challenge, collecting four samples (liquid, small pebbles, large rocks and soil) using a mechanical arm or a grabber they design and build. Teams must collect a soil sample and liquid sample while driving their rover, as well as collect rock samples (both large and small) while off the rover, all within a 25-minute time limit. The “Sample Retrieval” challenge highlights our deep-space exploration goals. Teams competing are eligible for the $250 prize awarded to the winner of each high school and college/university division.
4. Caution: Real STEM @work

The sights and sounds of welding, grinding and computer programming are prevalent in this hands-on, experiential activity where students solve similar problems faced by our workforce. Rover Challenge provides a unique test-bed to get students involved in real-world research and development. Their progress and success may glean potential technologies for future exploration of Mars and beyond.
5. Draws Inspiration from Apollo and Journey to Mars

Rover Challenge was inspired by the historic success of the lunar rovers from the Apollo missions, each one built by engineers and scientists at NASA Marshall. While we continue to honor our past achievements, we now highlight future accomplishments on deep-space exploration missions to Mars, asteroids or other planets. The addition of the “Sample Return” component and the Martian obstacles emphasize our commitment toward space exploration.
6. Our International Spirit is Alive and Well

Just like the International Space Station; we bring the best of several nations together to promote and celebrate space exploration. Nearly 80 teams are coming from as far away as Italy, Germany, India, Mexico, Columbia and Russia, as well as more “local” talent from the United States and Puerto Rico. View this year’s registered teams HERE.
7. Real-time Racing on Social Media

From start to finish, each racing rover team will be broadcast, live, on the Marshall Center’s Ustream channel. Plus, enjoy real-time race updates, results and awards by following Rover Challenge Twitter: @RoverChallenge
NASA’s Human Exploration Rover Challenge will take place at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama, April 8-9. For event details, rules, course information and more, please visit: http://www.nasa.gov/roverchallenge
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Hi! The Sun is so bright I need shades... that are ISO 12312-2 compliant! So glad that you are all here and excited about the eclipse. I’m Alexa Halford and ready to answer your questions.
Solar System: 10 Things to Know
Movie Night
Summer break is just around the corner. Hang a sheet from the clothesline in the backyard and fire up the projector for a NASA movie night.
1. Mars in a Minute

Back in the day, movies started with a cartoon. Learn the secrets of the Red Planet in these animated 60 second chunks.
2. Crash of the Titans

Watch two galaxies collide billions of years from now in this high-definition visualization.
3. Tour the Moon in 4K

Wait for the dark of the waning Moon next weekend to take in this 4K tour of our constant celestial companion.
4. Seven Years of the Sun

Watch graceful dances in the Sun’s atmosphere in this series of videos created by our 24/7 Sun-sentinel, the Solar Dynamic Observatory (SDO).
5. Light ‘Em Up

Crank up the volume and learn about NASA science for this short video about some of our science missions, featuring a track by Fall Out Boy.
6. Bennu’s Journey

Follow an asteroid from its humble origins to its upcoming encounter with our spacecraft in this stunning visualization.
7. Lunar Landing Practice
Join Apollo mission pilots as they fly—and even crash—during daring practice runs for landing on the Moon.
8. Earthrise

Join the crew of Apollo 8 as they become the first human beings to see the Earth rise over the surface of the Moon.
9. Musical Descent to Titan

Watch a musical, whimsical recreation of the 2005 Huygens probe descent to Titan, Saturn’s giant moon.
10. More Movies

Our Goddard Scientific Visualization Studio provides a steady stream of fresh videos for your summer viewing pleasure. Come back often and enjoy.
Read the full version of this article on the web HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
A Space Odyssey: 21 Years of Searching for Another Earth
There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours. We must believe that in all worlds there are living creatures and plants and other things we see in this world. – Epicurus, c. 300 B.C.

Are we alone? Are there other planets like ours? Does life exist elsewhere in the universe?
These are questions mankind has been asking for years—since the time of Greek philosophers. But for years, those answers have been elusive, if not impossible to find.
The month of October marks the 21st anniversary of the discovery of the first planet orbiting another sun-like star (aka. an exoplanet), 51 Pegasi b or “Dimidium.” Its existence proved that there were other planets in the galaxy outside our solar system.*

Even more exciting is the fact that astronomers are in hot pursuit of the first discovery of an Earth-like exoplanet orbiting a star other than the sun. The discovery of the so-called "blue dot" could redefine our understanding of the universe and our place in it, especially if astronomers can also find signs that life exists on that planet's surface.
Astronomy is entering a fascinating era where we're beginning to answer tantalizing questions that people have pondered for thousands of years.

Are we alone?
In 1584, when the Catholic monk Giordano Bruno asserted that there were "countless suns and countless earths all rotating around their suns," he was accused of heresy.

But even in Bruno's time, the idea of a plurality of worlds wasn't entirely new. As far back as ancient Greece, humankind has speculated that other solar systems might exist and that some would harbor other forms of life.
Still, centuries passed without convincing proof of planets around even the nearest stars.

Are there other planets like ours?
The first discovery of a planet orbiting a star similar to the sun came in 1995. The Swiss team of Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz of Geneva announced that they had found a rapidly orbiting gas world located blisteringly close to the star 51 Pegasi.

This announcement marked the beginning of a flood of discoveries. Exotic discoveries transformed science fiction into science fact:
a pink planet
worlds with two or even three suns
a gas giant as light as Styrofoam
a world in the shape of an egg
a lava planet

But what about another Earth?
Our first exoplanet mission**, Kepler, launched in 2009 and revolutionized how astronomers understand the universe and our place in it. Kepler was built to answer the question—how many habitable planets exist in our galaxy?

And it delivered: Thousands of planet discoveries poured in, providing statistical proof that one in five sun-like stars (yellow, main-sequence G type) harbor Earth-sized planets orbiting in their habitable zones– where it’s possible liquid water could exist on their surface.

Now, our other missions like the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes point at promising planetary systems (TRAPPIST-1) to figure out whether they are suitable for life as we know it.

Does life exist elsewhere in the universe?
Now that exoplanet-hunting is a mainstream part of astronomy, the race is on to build instruments that can find more and more planets, especially worlds that could be like our own.

Our Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), set for launch in 2017-2018, will look for super-Earth and Earth-sized planets around stars much closer to home. TESS will find new planets the same way Kepler does—via the transit method—but will cover 400 times the sky area.

The James Webb Space Telescope, to launch in 2018, wil be our most powerful space telescope to date. Webb will use its spectrograph to look at exoplanet atmospheres, searching for signs of life.

We still don’t know where or which planets are in the habitable zones of the nearest stars to Earth. Searching out our nearest potentially habitable neighbors will be the next chapter in this unfolding story.

*The first true discovery of extrasolar planets was actually a triplet of dead worlds orbiting the remains of an exploded star, called a pulsar star. Two of three were found by Dr. Alexander Wolszczan in 1992– a full three years before Dimidium’s discovery. But because they are so strange, and can’t support life as we know it, most scientists would reserve the “first” designation for a planet orbiting a normal star.
** The French CoRoT mission, launched in 2006, was the first dedicated exoplanet space mission. It has contributed dozens of confirmed exoplanets to the ranks and boasts a roster of some of the most well-studied planets outside our solar system.
To stay up-to-date on our latest exoplanet discoveries, visit: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Excited about the #CountdownToMars? We've got you covered.
We've created a virtual Mars photo booth, 3D rover experience and more for you to put your own creative touch on wishing Perseverance well for her launch to the Red Planet! Check it out, HERE.
Don’t forget to mark the July 30 launch date on your calendars!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How is Biotechnology Preparing us to Live on the Moon and Mars?
The adventures awaiting astronauts on future long-duration missions have technologists researching sustainable ways to live away from Earth. We’re using what we know from almost 20 years of a continuous human presence on the International Space Station and looking at new technologies to prepare for missions to the Moon and Mars.

Biotechnology – technology that uses living organisms to make products that provide a new use – is key to this research.
With biotechnology, we’re developing new ways to manufacture medicines, build habitats and more in space. Here are some ways biotechnology is advancing spaceflight and how the same research is reaping benefits on Earth.

Healthy astronauts
Planning ways to supply food for a multi-year mission on the Moon or Mars may require making food and nutrients in space. Our scientists are testing an early version of a potential solution: get microorganisms to produce vital nutrients like those usually found in vegetables. Then, whenever they’re needed, astronauts can drink them down.
The microorganisms are genetically engineered to rapidly produce controlled quantities of essential nutrients. Because the microorganisms and their food source both have a long shelf-life at room temperature and only need water to be activated, the system provides a simple, practical way to produce essential nutrients on-demand. The same kind of system designed for space could also help provide nutrition for people in remote areas of our planet.
Our researchers are evaluating the first batches of BioNutrient samples that came back to Earth after an experimental run on the International Space Station.

Because space travel takes a toll on the human body, we’re also researching how biotechnology can be used to advance the field of regenerative medicine.
Related cells that are joined together are collectively referred to as tissue, and these cells work together as organs to accomplish specific functions in the human body. Blood vessels around the cells vascularize, providing nutrients to the tissue to keep it healthy.
Our Vascular Tissue Challenge offers a $500,000 prize to be divided among the first three teams that successfully create thick, metabolically-functional human vascularized organ tissue in a controlled laboratory environment. The vascularized, thick-tissue models resulting from this challenge will function as organ analogs, or models, that can be used to study deep space environmental effects, such as radiation, and to develop strategies to minimize the damage to healthy cells.
Plant factories
Humans have relied on plants’ medicinal qualities for thousands of years for everything from alleviating minor ailments to curing serious diseases. Now, researchers are trying to simplify the process of turning plants into medicine (i.e. how to make it compact and portable). If successful, the cost of biomanufacturing pharmaceuticals on Earth could go down, and plants could produce medicines in space.

Creating medicine on demand isn’t something we typically do, so we’re turning to experts in the field for help. Researchers at the University of California, Davis are transforming plants into mini-medicine factories for future Mars missions. They’re genetically altering an ordinary type of lettuce so that it produces a protein called parathyroid hormone. This hormone is an approved drug for treating osteoporosis, a common condition where bones become weak and brittle.

This type of research is important to long duration spaceflight. When astronauts land on Mars, they will have spent more than half a year in zero gravity on the flight there, and they’ll need to be strong and ready to explore. Having the technologies needed to treat that possibility, and other unanticipated health effects of long duration spaceflight, is crucial.
Growing habitats
Vitamins aren’t the only thing astronauts could be growing on Mars; we’re exploring technologies that could grow structures out of fungi.
An early-stage research project underway at our Ames Research Center is prototyping technologies that could "grow" habitats on the Moon, Mars and beyond out of life – specifically, fungi and the unseen underground threads that make up the main part of the fungus. These tiny threads build complex structures with extreme precision, networking out into larger structures like mushrooms. With the right conditions, they can be coaxed into making new structures – ranging from a material similar to leather to the building blocks for a planetary home.
The myco-architecture project envisions a future where astronauts can construct a habitat out of the lightweight fungi material. Upon arrival, by unfolding a basic structure made up of dormant fungi and simply adding water, the fungi would grow around that framework into a fully functional human habitat – all while being safely contained to avoid contaminating the external environment.

Recycling waste
Once astronauts arrive on the surface of the Moon or a more distant planet, they’ll have to carefully manage garbage. This waste includes some stuff that gets flushed on Earth.
Today, we’re already using a recycling system on the space station to turn urine into drinking water. Poop on the other hand is contained then disposed of on spacecraft returning to Earth. That won’t be possible on more distant journeys, so, we’re turning to biomanufacturing for a practical solution.
Biology can serve as an effective recycling factory. Microorganisms such as yeast and algae feed on all kinds of things classified as “mission waste.” Processing their preferred form of nourishment generates products that can serve as raw materials used to make essential supplies like nutrients, medicines, plastic and fuel.

By taking a careful look at biological processes, we hope to develop new, lightweight systems to leverage that biology to do some helpful in-space manufacturing.
From Space to Earth
Biotechnology is preparing us for longer space missions to the Moon and then Mars – farther from Earth than humans have ever traveled before. As we prepare for those exciting missions, we’re also conducting research on the space station for the primary benefit of everyone on Earth.
January is National Biotechnology Month. To learn more about some of the ways NASA is using biotechnology to solve challenges in space and improve life on Earth, visit this link.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Candy Cane of Cosmic Proportions
Imagine how long it would take to eat a candy cane that’s a thousand trillion miles tall! 😋

Scientists peering into the center of our Milky Way galaxy found this 190-light-year tall “candy cane,” but (sadly) it is not a peppermint treat. It does contain other goodies, though. They have found huge collections of material, called giant molecular clouds, where stars are being born. And there are magnetic fields that might be evidence of a bubble from an outburst in our galactic center long ago.

The full image shows our galaxy’s center in infrared (blue), radio (red) and microwave (“minty” green) light. The picture essentially color codes different ways light is produced. The blue and cyan regions show us cool dust where star formation has just begun. Yellow features show more-established star “factories.” Red reveals places where electrically charged gas interacts with magnetic fields.
This image includes newly published observations using an instrument designed and built at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, called the Goddard-IRAM Superconducting 2-Millimeter Observer (GISMO). It was used with a 30-meter radio telescope located on Pico Veleta, Spain, operated by the Institute for Radio Astronomy in the Millimeter Range headquartered in Grenoble, France. The image shows a region about 750 light-years wide.
Find out more about this image and what we can learn from studying star factories!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
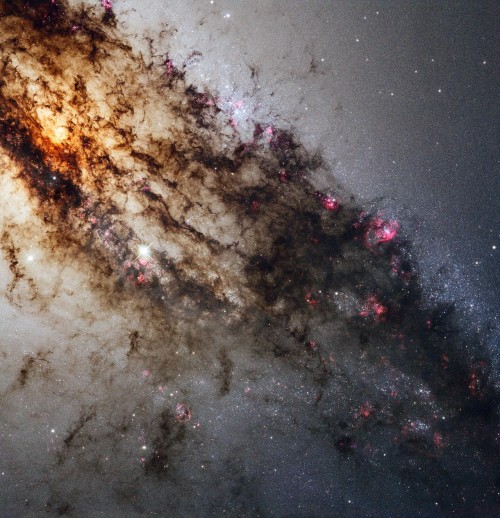
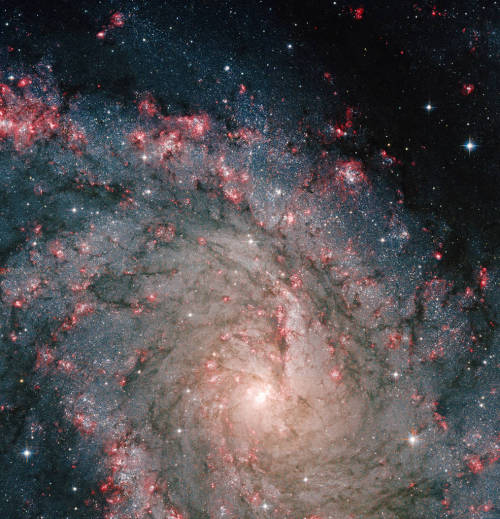
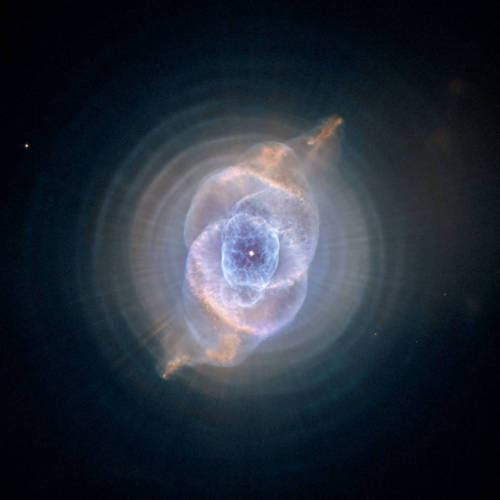
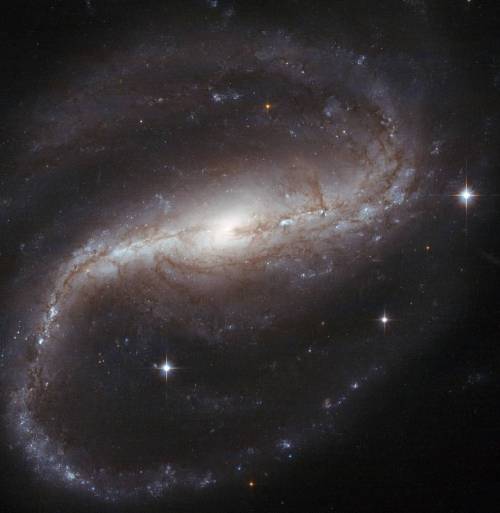
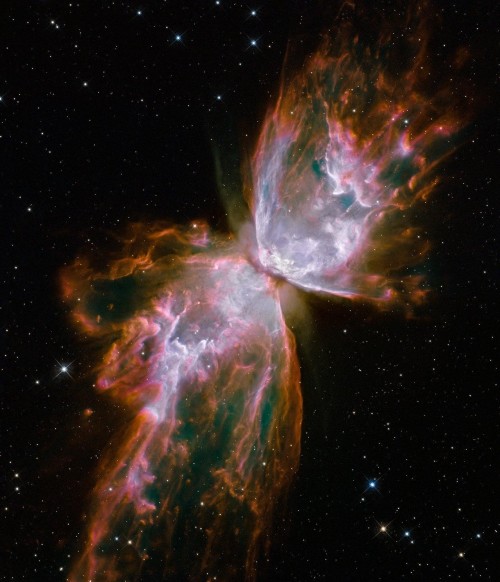






Be your own explorer ✨the cosmos is waiting...
From nearby clouds of gas and dust to remote galaxies that formed billions of years ago, tour the night sky with our Hubble Space Telescope’s new Caldwell catalog. The catalog of star clusters, galaxies and nebulas was first produced to highlight cosmic wonders visible to amateur astronomers. Since then Hubble has taken images of 95 out of the 109 objects, bringing these objects to life in exquisite detail.
While the objects can be observed using modest ground-based telescopes, Hubble’s Caldwell collection has been assembled for astronomers to see the finer details of each object in the night sky.
View the full collection here!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Secrets lie deep within Jupiter, shrouded in the solar system's strongest magnetic field and most lethal radiation belts. On July 4, 2016, our Juno spacecraft will plunge into uncharted territory, entering orbit around the gas giant and passing closer than any spacecraft before. Juno will see Jupiter for what it really is, but first it must pass the trial of orbit insertion. For more information: http://www.nasa.gov/juno and http://missionjuno.swri.edu.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
The Pale Blue Dot and the Golden Record
Almost thirty years ago, on Feb. 14, 1990, our Voyager 1 spacecraft turned back toward its home for one last look. 40 astronomical units (almost 4 billion miles) from the Sun, Voyager snapped the first-ever “family portrait” of our solar system.

One image in particular highlights our own planet’s fragility in the vast cosmic arena that we call home. This image of Earth, a tiny point of light, is contained in a camera artifact that resembles a beam of sunlight.

The late Carl Sagan referred to this image of Earth in the title of his 1994 book, Pale Blue Dot. Sagan wrote: "That's here. That's home. That's us. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you ever heard of, every human being who ever was, lived out their lives. … There is perhaps no better demonstration of the folly of human conceits than this distant image of our tiny world. To me, it underscores our responsibility to deal more kindly with one another, and to preserve and cherish the pale blue dot, the only home we've ever known.”
We placed a message aboard Voyager 1 and 2 — a kind of time capsule intended to communicate a story of our world to extraterrestrials. The Voyager message is carried by a phonograph record: a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth.

The Golden Record includes 115 images and a variety of natural sounds, such as those made by surf, wind and thunder, birds, whales and other animals. Musical selections from different cultures and eras were also added, as well as spoken greetings from Earth-people in fifty-five languages and printed messages from President Carter.
The Golden Record represents the whole of humanity, mounted to a feat of human engineering on a long voyage through interstellar space.

You can listen to the sounds of Earth on the golden record here and take a moment to appreciate our pale blue dot.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 eireni liked this · 4 years ago
eireni liked this · 4 years ago -
 timallenphoto liked this · 7 years ago
timallenphoto liked this · 7 years ago -
 afrodita-niculescu-blog liked this · 7 years ago
afrodita-niculescu-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 lxlteo liked this · 7 years ago
lxlteo liked this · 7 years ago -
 adyteddy-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
adyteddy-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 gowillowi-blog liked this · 7 years ago
gowillowi-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 boostown reblogged this · 7 years ago
boostown reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 queen-gorgo reblogged this · 7 years ago
queen-gorgo reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 queen-gorgo liked this · 7 years ago
queen-gorgo liked this · 7 years ago -
 rafika816 liked this · 7 years ago
rafika816 liked this · 7 years ago -
 hakuna-my-zenyattas liked this · 7 years ago
hakuna-my-zenyattas liked this · 7 years ago -
 sisterofsilence reblogged this · 7 years ago
sisterofsilence reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 gamingonethings liked this · 7 years ago
gamingonethings liked this · 7 years ago -
 darkspark42 liked this · 7 years ago
darkspark42 liked this · 7 years ago -
 analgesicsleep reblogged this · 7 years ago
analgesicsleep reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 roaragainstallwar liked this · 7 years ago
roaragainstallwar liked this · 7 years ago -
 glitchtechscience reblogged this · 7 years ago
glitchtechscience reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 deercoke liked this · 7 years ago
deercoke liked this · 7 years ago -
 aliensteel23 liked this · 7 years ago
aliensteel23 liked this · 7 years ago -
 archaeopteryxwentwoof reblogged this · 7 years ago
archaeopteryxwentwoof reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 archaeopteryxwentwoof liked this · 7 years ago
archaeopteryxwentwoof liked this · 7 years ago -
 fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 7 years ago
fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 wolfbarkbite reblogged this · 7 years ago
wolfbarkbite reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 wolfbarkbite liked this · 7 years ago
wolfbarkbite liked this · 7 years ago -
 dbird051077 liked this · 7 years ago
dbird051077 liked this · 7 years ago -
 jillandjackalope reblogged this · 7 years ago
jillandjackalope reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thekreepykorner-blog liked this · 7 years ago
thekreepykorner-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 moraine-moraine liked this · 7 years ago
moraine-moraine liked this · 7 years ago -
 rdgprof liked this · 7 years ago
rdgprof liked this · 7 years ago -
 lalaarchitecture liked this · 7 years ago
lalaarchitecture liked this · 7 years ago -
 addicted-to-assbutts liked this · 7 years ago
addicted-to-assbutts liked this · 7 years ago -
 chitarra10 reblogged this · 7 years ago
chitarra10 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 juniper-novella liked this · 7 years ago
juniper-novella liked this · 7 years ago -
 naturenestd-blog liked this · 7 years ago
naturenestd-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 classified-ad reblogged this · 7 years ago
classified-ad reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 classified-ad liked this · 7 years ago
classified-ad liked this · 7 years ago -
 charleshdv-blog liked this · 7 years ago
charleshdv-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 alexiakphotos reblogged this · 7 years ago
alexiakphotos reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 alexiakphotos liked this · 7 years ago
alexiakphotos liked this · 7 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts