The Invisible Network: A New NASA Podcast
The Invisible Network: A New NASA Podcast
We sit on the precipice of a golden age of space exploration — a renaissance of space science and technology. Every day, our missions send millions of bits of data to Earth, unraveling long-held mysteries about the universe, our solar system and even our own planet. But what makes it all possible?

Today we debut a new, limited edition podcast called “The Invisible Network.” It brings you a side of NASA you may have never seen or heard of before — oft overlooked technologies crucial to spaceflight and humanity’s ambitions among the stars.

Communications is the vital link between Earth and space. A collection of far-flung ground stations enabled the Apollo missions: our first steps on the Moon; the Voyager missions: our first brushes with interstellar space; and supported the earliest space and Earth science missions, expanding our knowledge of the stars and of ourselves.

Today, our communications networks are vastly different than those that supported Apollo. Tomorrow’s networks will be even more advanced.
“The Invisible Network” explores technological innovations guiding us into the future. These seemingly un-sexy feats of engineering will allow us to return to the Moon, journey to Mars and venture ever-further into the unknown.

Artist’s rendering of the upcoming Orion missions.
Our podcast’s title, "The Invisible Network," comes from author and former NASA engineer Sunny Tsiao’s book, “Read You Loud and Clear,” published in 2008. Tsiao notes that our communications and tracking programs are often described as “invisible.” Infrastructures, he writes, are seldom recognized, except when they fall short.
If our networks are invisible, perhaps it’s because they work so well.

We hope you’ll join us on our journey into The Invisible Network. Subscribe to the show and share us with a friend. For more information visit nasa.gov/invisible or nasa.gov/scan.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Happy #MoonDay! To celebrate the 49th anniversary of Apollo 11 landing on the Moon, we present you with “Moonlight,” a video by our Goddard science visualizer Ernie Wright set to Debussy’s Clair de Lune. The Apollo missions were a landmark in lunar exploration. The visit and the samples that our Moon walkers collected transformed our understanding of the Moon and the solar system. Now, our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter’s high-resolution data gives an incredibly detailed view of our closest neighbor.
This visualization captures the mood of Claude Debussy's best-known composition, Clair de Lune (which means moonlight in French). The piece was published in 1905 as the third of four movements in the composer's Suite Bergamasque, and unlike the other parts of this work, Clair is quiet, contemplative, and slightly melancholy, evoking the feeling of a solitary walk through a moonlit garden.
“Moonlight” uses a digital 3D model of the Moon built from Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter global elevation maps and image mosaics. The lighting is derived from actual Sun angles during lunar days in 2018. Enjoy and read more HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Science Launching to Station Looks Forward and Back
Some of the earliest human explorers used mechanical tools called sextants to navigate vast oceans and discover new lands. Today, high-tech tools navigate microscopic DNA to discover previously unidentified organisms. Scientists aboard the International Space Station soon will have both types of tools at their disposal.

Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft is scheduled to launch its ninth contracted cargo resupply mission to the space station no earlier than May 21. Sending crucial science, supplies and cargo to the crew of six humans living and working on the orbiting laboratory.
Our Gemini missions conducted the first sextant sightings from a spacecraft, and designers built a sextant into Apollo vehicles as a lost-communications navigation backup. The Sextant Navigation investigation tests use of a hand-held sextant for emergency navigation on missions in deep space as humans begin to travel farther from Earth.

Jim Lovell (far left) demonstrated on Apollo 8 that sextant navigation could return a space vehicle home.

The remoteness and constrained resources of living in space require simple but effective processes and procedures to monitor the presence of microbial life, some of which might be harmful. Biomolecule Extraction and Sequencing Technology (BEST) advances the use of sequencing processes to identify microbes aboard the space station that current methods cannot detect and to assess mutations in the microbial genome that may be due to spaceflight.

Genes in Space 3 performed in-flight identification of bacteria on the station for the first time. BEST takes that one step farther, identifying unknown microbial organisms using a process that sequences directly from a sample with minimal preparation, rather than with the traditional technique that requires growing a culture from the sample.

Adding these new processes to the proven technology opens new avenues for inflight research, such as how microorganisms on the station change or adapt to spaceflight.
The investigation’s sequencing components provide important information on the station’s microbial occupants, including which organisms are present and how they respond to the spaceflight environment -- insight that could help protect humans during future space exploration. Knowledge gained from BEST could also provide new ways to monitor the presence of microbes in remote locations on Earth.
Moving on to science at a scale even smaller than a microbe, the new Cold Atom Lab (CAL) facility could help answer some big questions in modern physics.

CAL creates a temperature ten billion (Yup. BILLION) times colder than the vacuum of space, then uses lasers and magnetic forces to slow down atoms until they are almost motionless. CAL makes it possible to observe these ultra-cold atoms for much longer in the microgravity environment on the space station than would be possible on the ground.

Results of this research could potentially lead to a number of improved technologies, including sensors, quantum computers and atomic clocks used in spacecraft navigation.
A partnership between the European Space Agency (ESA) and Space Application Services (SpaceAps), The International Commercial Experiment, or ICE Cubes Service, uses a sliding framework permanently installed on the space station and “plug-and-play” Experiment Cubes.

The Experiment Cubes are easy to install and remove, come in different sizes and can be built with commercial off-the-shelf components, significantly reducing the cost and time to develop experiments.
ICE Cubes removes barriers that limit access to space, providing more people access to flight opportunities. Potential fields of research range from pharmaceutical development to experiments on stem cells, radiation, and microbiology, fluid sciences, and more.
For daily nerd outs, follow @ISS_Research on Twitter!
Watch the Launch + More!

What’s On Board Briefing
Join scientists and researchers as they discuss some of the investigations that will be delivered to the station on Saturday, May 19 at 1 p.m. EDT at nasa.gov/live. Have questions? Use #askNASA
CubeSat Facebook Live
The International Space Station is often used to deploy small satellites, a low-cost way to test technology and science techniques in space. On board this time, for deployment later this summer, are three CubeSats that will help us monitor rain and snow, study weather and detect and filter radio frequency interference (RFI).
Join us on Facebook Live on Saturday, May 19 at 3:30 p.m. EDT on the NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility page to hear from experts and ask them your questions about these small satellites.
Pre-Launch Briefing
Tune in live at nasa.gov/live as mission managers provide an overview and status of launch operations at 11 a.m. EDT on Sunday, May 20. Have questions? Use #askNASA
LIFTOFF!
Live launch coverage will begin on Monday, May 21 4:00 a.m. on NASA Television, nasa.gov/live, Facebook Live, Periscope, Twitch, Ustream and YouTube. Liftoff is slated for 4:39 a.m.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
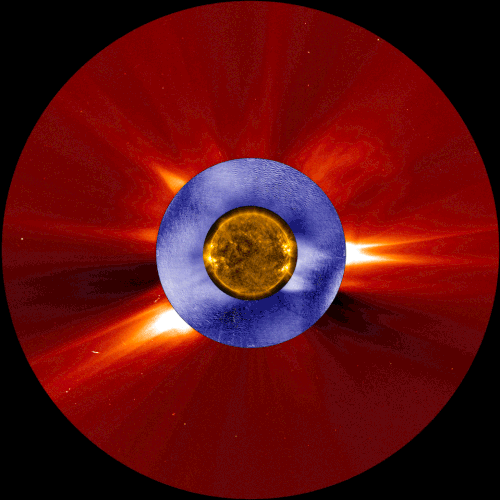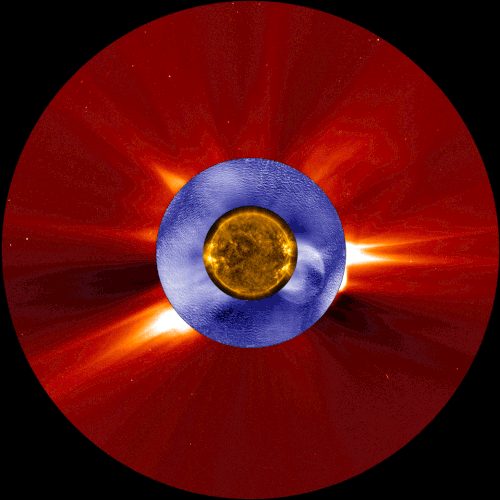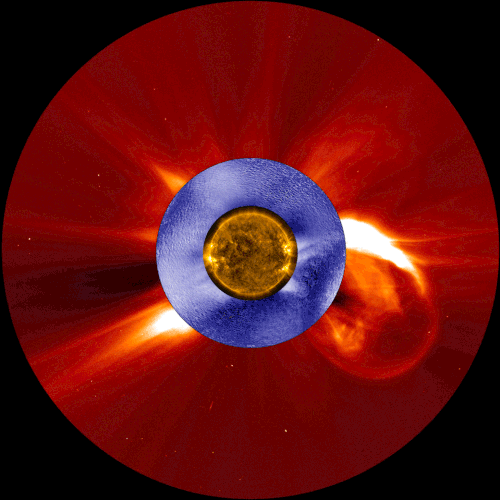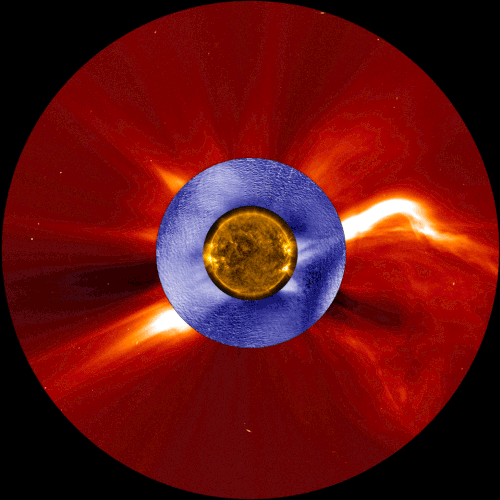
This composite image shows a coronal mass ejection, a type of space weather linked to solar energetic particles, as seen from two space-based solar observatories and one ground-based instrument. The image in gold is from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, the image in blue is from the Manua Loa Solar Observatory’s K-Cor coronagraph, and the image in red is from ESA and NASA’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory.
Our constantly-changing sun sometimes erupts with bursts of light, solar material, or ultra-fast energized particles — collectively, these events contribute to space weather. A new study shows that the warning signs of one type of space weather event can be detected tens of minutes earlier than with current forecasting techniques – critical extra time that could help protect astronauts in space.
Credits: NASA/ESA/SOHO/SDO/Joy Ng and MLSO/K-Cor
Scott Kelly Was the First To…

Astronaut Scott Kelly returned home from his year in space mission on March 1. Spending that much time in space allowed him to rack up some pretty cool milestones. Here are some of his awesome “firsts”:
Firsts on Social Media

While in space, Scott Kelly had the opportunity to host the first NASA TweetChat from space.

The first ever Tumblr AnswerTime from space was hosted by Scott Kelly during his One Year Mission.

Scott Kelly hosted the first NASA Reddit AMA from space.

Before leaving for his year in space, President Obama asked him to Instagram his time on orbit…a Presidential request to Instagram is a first!
Firsts for Scott

During his year in space, Scott conducted his first spacewalk. He hadn’t spacewalked on any of his previous missions, but did so three times during the One Year Mission.
Firsts for an American Astronaut

Most notably, Scott Kelly is the first U.S. astronaut to spend a year in space. His time on orbit also allowed us to conduct the first ever Twins Study on the space station. While Scott was in space, his twin brother Mark Kelly was on Earth. Since their genetic makeup is as close to identical as we can get, this allows a unique research perspective. We can now compare all of the results from Scott in space to his brother Mark on Earth.

During his year in space, Scott had the opportunity to be one of the first astronauts to harvest and eat lettuce grown in the space station’s VEGGIE facility.

Space flowers! Scott was also one of the firsts to help grow and harvest zinnia flowers in the VEGGIE facility. Growing flowering plants in space will help scientists learn more about growing crops for deep-space missions and our journey to Mars.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More than Just Dust in the Wind

From space, we can see a swirling brown mass making its way across the Atlantic – dust from the Sahara Desert – the largest hot desert in the world. It’s a normal phenomenon. Every year, winds carry millions of tons of dust from North Africa, usually during spring and summer in the Northern Hemisphere.

June 2020 has seen a massive plume of dust crossing the ocean. It’s so large it’s visible from one million miles away in space.

Dust clouds this large can affect air quality in regions where the dust arrives. The particles can also scatter the Sun’s light, making sunrises and sunsets more vibrant.

Dust particles in the air are also known as aerosols. We can measure aerosols, including dust, sea salt and smoke, from satellites and also use computer models to study how they move with the wind.

Following the transport of dust from space shows us how one of the driest places on Earth plays a role in fertilizing the Amazon rainforest. There are minerals in Saharan dust, like phosphorous, that exist in commercial fertilizers, helping seed the rainforest.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Our friend - the Moon - is putting on a show tonight!
Look to the sky at 12:44 a.m. EDT to see the first full Moon of summer in the Northern Hemisphere and a partial penumbral eclipse, visible from most of North America. Want more info on this special occurrence? click HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: 5 Things To Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, so let us break it down for you. Here are 5 things to know this week:
1. You Call the Shots

This July, when the Juno mission arrives at Jupiter, it will eye the massive planet with JunoCam. What adds extra interest to this mission is that the public is invited to help Juno scientists choose which images JunoCam will take. Now is the time to get involved.
2. Dawn Delivers

We've seen several images now from the Dawn spacecraft's new, close orbit around Ceres—and they don't disappoint. Exquisitely detailed photos of the dwarf planet reveal craters, cliffs, fractures, canyons and bright spots in many locations. "Everywhere we look in these new low-altitude observations, we see amazing landforms that speak to the unique character of this most amazing world," said the mission's principal investigator.
3. Remembering the Visit to a Sideways World

Jan. 24 is the 30th anniversary of Voyager 2's Uranus flyby. The seventh planet is notable for the extreme tilt of its axis, its lacy ring system and its large family of moons—10 of which were discovered thanks to Voyager's close encounter. In fact, we learned much of what we know about the Uranian system during those few days in 1986.
4. A Decade in the Deep

The New Horizons spacecraft left Earth 10 years ago this week. Its long voyage into deep space is, even now, transforming our understanding of the outer solar system. New data and pictures from the Pluto flyby are still streaming down from the spacecraft. Pending the approval of an extended mission, New Horizons is en route to a 2019 rendezvous with a small, unexplored world in the distant Kuiper Belt.
5. Power at a Distance

Space exploration helped drive the development of practical solar cells, and now solar power has gone farther than ever before. Last week, NASA's Juno spacecraft broke the record for the most distant solar-powered craft when it passed a distance of 493 million miles (793 million kilometers) from the sun. The four-ton Juno spacecraft draws energy from three 30-foot-long (9-meter) solar arrays festooned with 18,698 individual cells.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What are you most excited for in 2020?
Is there any chance that something could go wrong?
How Will We Safely Send the First Humans to the Red Planet?
We’ve been exploring the Red Planet for over 50 years -- Mariner 4 launched on this day (Nov. 28) in 1964 and took the first photos of Mars from space the following summer.

We first explored the surface 40 years ago (Viking, 1976) and have had a continuous scientific presence on Mars for nearly 20 years, starting with the landing of the Pathfinder lander and Sojourner rover on July 4, 1997.
We currently have three orbiters – MAVEN, MRO and Mars Odyssey – and two rovers – Curiosity and Opportunity – actively exploring Mars.
These robotic explorers have already taught us a lot about the Red Planet, and future missions will teach us even more about how humans can live and work on the surface.

After sending humans on space exploration missions for the last 50 years, we have gained the experience and knowledge to send the first people to Mars. We are working across all areas to prepare for that historic day and want to share our progress with you.
Building the ride to Mars: NASA’s Space Launch System.
Our ride to Mars, the Space Launch System, is being built right now to meet the challenges of exploring deep space. When it comes to our journey to Mars and beyond, there are no small steps. Our video series by the same name breaks down those steps to show how SLS will send missions to the Red Planet.

Living on the Space Station will help humans live safely on Mars.
New crew members of Expedition 50 will soon conduct more than 250 experiments on the International Space Station. More than 2,000 experiments have already been done!
Experiments in fields such as biology, Earth science, physical sciences and human research are helping us unlock the knowledge needed to enable humans to live in space for long durations. If you missed the recent launch, check out NASA TV for a replay.

Testing Orion helps crew live and work in space and get home safely.
Scheduled to launch atop the Space Launch System rocket for the first time in 2018, an uncrewed Orion will travel farther into space than any spacecraft built for humans has ever gone before. When Orion returns to Earth, splashing down into the Pacific Ocean, it will take a landing and recovery group to safely return the capsule and crew back to land. A variety of testing on the ground, including to structures and parachutes, is helping make sure Orion can safely carry crew to new destinations in the solar system.

In late October, this recovery group, including NASA’s Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, the U.S. Navy, U.S. Air Force and contractor employees, completed its fifth successful practice run to recover Orion aboard the USS San Diego.

We're using high resolution imagery from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to learn more about potential landing sites for a human mission.
Who knows what surprises the Red Planet holds?
Our Curiosity Rover has discovered all kinds of interesting Mars features including meteorites. How do you learn more about a meteorite? Zap it with lasers, of course.

This golf-ball-sized, iron-nickel meteorite was recently found on Mars where ancient lakebed environments once existed. Named “Egg Rock” for the area in which it was found, it is the first meteorite to be examined using a laser-firing spectrometer.
By studying the conditions on Mars with vehicles like Curiosity, scientists are able to help prepare future astronauts to live on Mars.
How do you prepare the tallest rocket ever built for its first launch?
Another important component in successfully launching the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft on a Journey to Mars is the infrastructure work being done by our Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at Kennedy Space Center.

While efforts at our Vehicle Assembly Building continue, we hope you’ll be making your plans to join us at the launch pad for the first flight of SLS with Orion in 2018!
Preparing for a human journey to Mars
The next Mars rover will launch in 2020, and will investigate a region of Mars where the ancient environment may have been favorable for microbial life, probing the Martian rocks for evidence of past life.

It will collect samples and cache them on the surface for potential return to Earth by a future mission. Mars 2020 will also conduct the first investigation into the usability and availability of Martian resources, including oxygen, in preparation for human missions.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts