A Wrinkle In Space-Time: The Eclipse That “Proved” Einstein Right
A Wrinkle in Space-Time: The Eclipse That “Proved” Einstein Right
One hundred years ago a total solar eclipse turned an obscure scientist into a household name. You might have heard of him — his name is Albert Einstein. But how did a solar eclipse propel him to fame?
First, it would be good to know a couple things about general relativity. (Wait, don’t go! We’ll keep this to the basics!)

A decade before he finished general relativity, Einstein published his special theory of relativity, which demonstrates how space and time are interwoven as a single structure he dubbed “space-time.” General relativity extended the foundation of special relativity to include gravity. Einstein realized that gravitational fields can be understood as bends and curves in space-time that affect the motions of objects including stars, planets — and even light.
For everyday situations the centuries-old description of gravity by Isaac Newton does just fine. However, general relativity must be accounted for when we study places with strong gravity, like black holes or neutron stars, or when we need very precise measurements, like pinpointing a position on Earth to within a few feet. That makes it hard to test!

A prediction of general relativity is that light passing by an object feels a slight "tug", causing the light's path to bend slightly. The more mass the object has, the more the light will be deflected. This sets up one of the tests that Einstein suggested — measuring how starlight bends around the Sun, the strongest source of gravity in our neighborhood. Starlight that passes near the edge of the Sun on its way to Earth is deflected, altering by a small amount where those stars appear to be. How much? By about the width of a dime if you saw it at a mile and a quarter away! But how can you observe faint stars near the brilliant Sun? During a total solar eclipse!

That’s where the May 29, 1919, total solar eclipse comes in. Two teams were dispatched to locations in the path of totality — the places on Earth where the Moon will appear to completely cover the face of the Sun during an eclipse. One team went to South America and another to Africa.
On eclipse day, the sky vexed both teams, with rain in Africa and clouds in South America. The teams had only mere minutes of totality during which to take their photographs, or they would lose the opportunity until the next total solar eclipse in 1921! However, the weather cleared at both sites long enough for the teams to take images of the stars during totality.

The teams took two sets of photographs of the same patch of sky – one set during the eclipse and another set a few months before or after, when the Sun was out of the way. By comparing these two sets of photographs, researchers could see if the apparent star positions changed as predicted by Einstein. This is shown with the effect exaggerated in the image above.
A few months after the eclipse, when the teams sorted out their measurements, the results demonstrated that general relativity correctly predicted the positions of the stars. Newspapers across the globe announced that the controversial theory was proven (even though that’s not quite how science works). It was this success that propelled Einstein into the public eye.

The solar eclipse wasn’t the first test of general relativity. For more than two centuries, astronomers had known that Mercury’s orbit was a little off. Its perihelion — the point during its orbit when it is closest to the Sun — was changing faster than Newton’s laws predicted. General relativity easily explains it, though, because Mercury is so close to the Sun that its orbit is affected by the Sun’s dent in space-time, causing the discrepancy.
In fact, we still test general relativity today under different conditions and in different situations to see whether or not it holds up. So far, it has passed every test we’ve thrown at it.
Curious to know where we need general relativity to understand objects in space? Tune into our Tumblr tomorrow to find out!

You can also read more about how our understanding of the universe has changed during the past 100 years, from Einstein's formulation of gravity through the discovery of dark energy in our Cosmic Times newspaper series.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Juno Spacecraft: What Do We Hope to Learn?

The Juno spacecraft has been traveling toward its destination since its launch in 2011, and is set to insert Jupiter’s orbit on July 4. Jupiter is by far the largest planet in the solar system. Humans have been studying it for hundreds of years, yet still many basic questions about the gas world remain.

The primary goal of the Juno spacecraft is to reveal the story of the formation and evolution of the planet Jupiter. Understanding the origin and evolution of Jupiter can provide the knowledge needed to help us understand the origin of our solar system and planetary systems around other stars.

Have We Visited Jupiter Before? Yes! In 1995, our Galileo mission (artist illustration above) made the voyage to Jupiter. One of its jobs was to drop a probe into Jupiter’s atmosphere. The data showed us that the composition was different than scientists thought, indicating that our theories of planetary formation were wrong.
What’s Different About This Visit? The Juno spacecraft will, for the first time, see below Jupiter’s dense clover of clouds. [Bonus Fact: This is why the mission was named after the Roman goddess, who was Jupiter’s wife, and who could also see through the clouds.]

Unlocking Jupiter’s Secrets
Specifically, Juno will…
Determine how much water is in Jupiter’s atmosphere, which helps determine which planet formation theory is correct (or if new theories are needed)
Look deep into Jupiter’s atmosphere to measure composition, temperature, cloud motions and other properties
Map Jupiter’s magnetic and gravity fields, revealing the planet’s deep structure
Explore and study Jupiter’s magnetosphere near the planet’s poles, especially the auroras – Jupiter’s northern and southern lights – providing new insights about how the planet’s enormous
Juno will let us take a giant step forward in our understanding of how giant planets form and the role these titans played in putting together the rest of the solar system.
For updates on the Juno mission, follow the spacecraft on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Tumblr.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
7 Things to Know about the Perseverance Mars Rover

We’re set to launch the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover mission from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on July 30. The rover is loaded with scientific instruments and advanced technology, making it the largest, heaviest and most sophisticated vehicle ever sent to the Red Planet.
What is Perseverance’s mission and what will it do on Mars? Here are seven things to know:
1. Perseverance draws on the NASA – and scientific – spirit of overcoming challenges

Not only does it have to launch during a pandemic and land on a treacherous planet, it has to carry out its science goals:
Searching for signs of past microbial life
Mapping out the planet’s geology and climate
Collecting rock and other samples for future return to Earth
Paving the way for human exploration
We chose the name Perseverance from among the 28,000 essays submitted during the "Name the Rover" contest. Because of the coronavirus pandemic, the months leading up to the launch in particular have required creative problem solving, teamwork and determination.
2. Perseverance builds on the lessons from other Mars rovers

In 1997, our first Mars rover – Sojourner – showed that a robot could rove on the Red Planet. Spirit and Opportunity, which both landed in 2004, found evidence that Mars once had water before becoming a frozen desert.
Curiosity found evidence that Mars’ Gale Crater was home to a lake billions of years ago and that there was an environment that may have sustained microbial life. Perseverance aims to answer the age-old question – are there any signs that life once existed on Mars?
3. Perseverance will land in a place with high potential to find signs of ancient life

The rover will land in Jezero Crater, a 28-mile wide basin north of the Martian equator. A space rock hit the surface long ago, creating the large hole. Between 3 and 4 billion years ago, a river flowed into a body of water in Jezero the size of Lake Tahoe.
4. Perseverance will also collect important data about Mars’ geology and climate

Mars orbiters have collected images and other data about Jezero Crater from about 200 miles above, but finding signs of past life will need much closer inspection. A rover like Perseverance can look for those signs that may be related to ancient life and analyze the context in which they were found to see if the origins were biological.
5. Perseverance is the first leg of a round trip to Mars

This is the first rover to bring a sample-gathering system to Mars that will package promising samples of rocks and other materials for future return to Earth. NASA and ESA are working on the Mars Sample Return campaign, so we can analyze the rocks and sediment with tools too large and complex to send to space.
6. Perseverance will pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet

Two packages -- one that helps the rover autonomously avoid hazards during landing (TRN) and another that gathers crucial data during the trip through Mars’ atmosphere (MEDLI2) – will help future human missions land safely and with larger payloads on other worlds.
There are two instruments that will specifically help astronauts on the Red Planet. One (MEDA) will provide key information about the planet’s weather, climate and dust activity, while a technology demonstration (MOXIE) aims to extract oxygen from Mars’ mostly carbon-dioxide atmosphere.
7. You get to ride along

Perseverance and other parts of the Mars 2020 spacecraft feature 23 cameras, which is more than any other interplanetary mission in history. Raw images from the camera are set to be released on the mission website.
There are also three silicon chips with the names of nearly 11 million people who signed up to send their names to Mars.
And you can continue to follow the mission on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
That’s a Wrap - September
Each month, the International Space Station focuses on an area of research. In September, the research focus was biology, encompassing cells, plants, animals, genetics, biochemistry, human physiology and more.
Benefits from this research are vast and include: combating diseases, reducing our environmental footprint, feeding the world’s population and developing cleaner energy.
Here’s a recap of some topics we studied this month:
Cells

Scientists studied T-cells in orbit to better understand how human immune systems change as they age. For an immune cell, the microgravity environment mimics the aging process. Because spaceflight-induced and aging-related immune suppression share key characteristics, researchers expect the results from this study will be relevant for the general population.
NASA to Napa

We raised a glass to the space station to toast how the study of plants in space led to air purification technology that keeps the air clean in wine cellars and is also used in homes and medical facilities to help prevent mold.
One-Year Mission

This month also marked the halfway point of the One-Year Mission. NASA Astronaut Scott Kelly and Roscosmos Cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko reached the midpoint on Sept. 15. This mission will result in valuable data about human health and the effects of microgravity on the body.
Microbes

Since microbes can threaten crew health and jeopardize equipment, scientists study them on astronauts’ skin and aboard the space station. Samples like saliva, blood, perspiration and swaps of equipment are collected to determine how microgravity, environment, diet and stress affect the microorganisms.
Model Organisms

Model organisms have characteristics that allow them to easily be maintained, reproduced and studied in a laboratory. Scientists investigate roundworms, medaka fish and rodents on the station because of this reason. They can also provide insight into the basic cellular and molecular mechanisms of the human body.
For more information about research on the International Space Station, go HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
New Rose-Colored Glasses for the Roman Space Telescope
Big news for our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope! Thanks to some new “shades” – an infrared filter that will help us see longer wavelengths of light – the mission will be able to spot water ice on objects in the outer solar system, see deeper into clouds of gas and dust, and peer farther across space. We’re gearing up for some super exciting discoveries!
Rocks on the rocks
You probably know that our solar system includes planets, the Sun, and the asteroid belt in between Mars and Jupiter – but did you know there’s another ‘belt’ of small objects out past Neptune? It’s called the Kuiper belt, and it’s home to icy bodies that were left over from when our solar system formed.

A lot of the objects there are like cosmic fossils – they haven’t changed much since they formed billions of years ago. Using its new filter, Roman will be able to see how much water ice they have because the ice absorbs specific wavelengths of infrared light, providing a “fingerprint” of its presence. This will give us a window into the solar system’s early days.
Upgraded heat vision
Clouds of dust and gas drift throughout our galaxy, sometimes blocking our view of the stars behind them. It’s hard for visible light to penetrate this dusty haze because the particles are the same size or even larger than the light’s wavelength. Since infrared light travels in longer waves, it hardly notices the tiny particles and can pass more easily through dusty regions.

With Roman’s new filter, we’ll be able to see through much thicker dust clouds than we could have without the upgrade. It’ll be much easier to study the structure of our home galaxy, the Milky Way.

Roman’s expanded view will also help us learn more about brown dwarfs – objects that are more massive than planets, but not massive enough to light up like stars. The mission will find them near the heart of the galaxy, where stars explode more often.
These star explosions, called supernovae, are so extreme that they create and disperse new elements. So near the center of the galaxy, there should be higher amounts of elements that aren’t as common farther away, where supernovae don’t happen as often.
Astronomers think that may affect how stars and planets form. Using the new filter, Roman will probe the composition of brown dwarfs to help us understand more.
Baby galaxies
Roman’s upgraded filter will also help us see farther across space. As light travels through our expanding universe, its wavelength becomes stretched. The longer it travels before reaching us, the longer its wavelength becomes. Roman will be able to see so far back that we could glimpse some of the first stars and galaxies that ever formed. Their light will be so stretched that it will mostly arrive as infrared instead of visible light.

We’re still not sure how the very first galaxies formed because we’ve found so few of these super rare and faint beasts. But Roman will have such a big view of the universe and sharp enough vision that it could help us find a lot more of them. Then astronomers can zoom in on them with missions like our James Webb Space Telescope for a closer look.
Roman will help us explore these cosmic questions and many more! Learn more about the mission here: https://roman.gsfc.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Top 5 Things to Know This Week
Here are five things you need to know about our amazing solar system this week:
1. Perpetual Pluto-palooza

The New Horizons spacecraft continues its ongoing download of data and images from the July 14 flyby of the Pluto system. In the latest weekly release, the new images don’t disappoint, showing fine details in an exotic landscape. The New Horizons team has also described a wide range of findings about the dwarf planet’s system in its first science paper. Learn more HERE.
2. Encounter at Enceladus

The Cassini spacecraft has returned the closest images ever showing the north polar region of Saturn’s intriguing ice moon Enceladus. Scientists expected the area to be heavily cratered, but the new high-resolution Cassini images also show a landscape of stark contrasts, crisscrossed by a spidery network of gossamer-thin cracks that slice through the craters. The robotic spacecraft buzzed by the moon during the first of what will be three close encounters this year -- the last of the long mission. Next up: on Oct. 28 Cassini will deep dive right through Enceladus’ famous ice geyser plume! Learn more HERE.
3. We’re Giving You the Whole World, Every Day
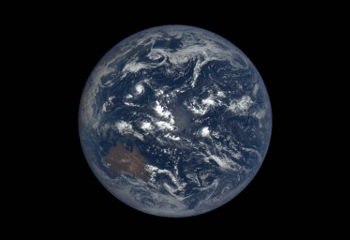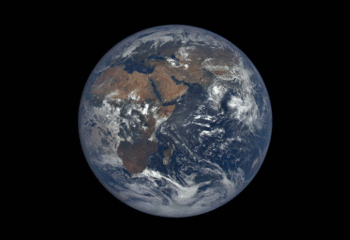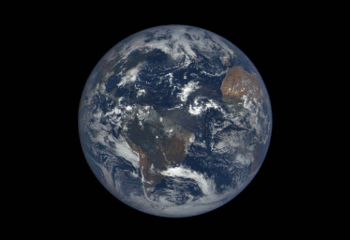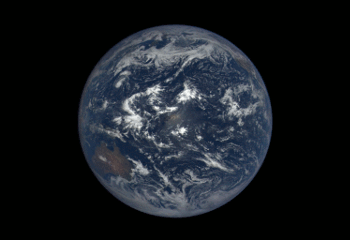
We have worked with NOAA to launch a new website that shows the full, sunlit side of the Earth on a daily basis. The images come from our camera a million miles away aboard the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR). Each daily sequence of images shows the Earth as it rotates, revealing the entire planet over the course of a day. Take a look HERE.
4. Going Big at Jupiter

We have large, new maps of Jupiter, thanks to data from the Wide Field Camera 3 on our Hubble Space Telescope. The big images provide a detailed look at how the giant planet’s features change over time. In fact, the maps are just the first in a planned series of yearly portraits of the solar system’s four outer planets. The views come as we prepare for the Juno mission to arrive at Jupiter in little less than a year.
5. Catch a Falling Star

Meteors aren’t really falling stars, just dust and rock from deep space meeting a fiery end in Earth’s atmosphere -- but they’re a sight to behold if you can catch a glimpse. The Orionid meteors appear every year around this time, when Earth travels through an area of space littered with debris from Halley’s Comet. This year the peak will occur on the night of Wednesday, Oct. 21, into the morning of Thursday, Oct. 22. Find out how to watch HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Rocket Fuel in Her Blood: The Story of JoAnn Morgan
As the Apollo 11 mission lifted off on the Saturn V rocket, propelling humanity to the surface of the Moon for the very first time, members of the team inside Launch Control Center watched through a window.
The room was crowded with men in white shirts and dark ties, watching attentively as the rocket thrust into the sky. But among them sat one woman, seated to the left of center in the third row in the image below. In fact, this was the only woman in the launch firing room for the Apollo 11 liftoff.

This is JoAnn Morgan, the instrumentation controller for Apollo 11. Today, this is what Morgan is most known for. But her career at NASA spanned over 45 years, and she continued to break ceiling after ceiling for women involved with the space program.
“It was just meant to be for me to be in the launching business,” she says. “I’ve got rocket fuel in my blood.”

Morgan was inspired to join the human spaceflight program when Explorer 1 was launched into space in 1958, the first satellite to do so from the United States. Explorer 1 was instrumental in discovering what has become known as the Van Allen radiation belt.
“I thought to myself, this is profound knowledge that concerns everyone on our planet,” she says. “This is an important discovery, and I want to be a part of this team. I was compelled to do it because of the new knowledge, the opportunity for new knowledge.”

The opportunity came when Morgan spotted an advertisement for two open positions with the Army Ballistic Missile Agency. The ad listed two Engineer’s Aide positions available for two students over the summer.
“Thank God it said ‘students’ and not ‘boys’” says Morgan, “otherwise I wouldn’t have applied.”
After Morgan got the position, the program was quickly rolled into a brand-new space exploration agency called NASA. Dr. Kurt Debus, the first director of Kennedy Space Center (KSC), looked at Morgan’s coursework and provided Morgan with a pathway to certification. She was later certified as a Measurement and Instrumentation Engineer and a Data Systems Engineer.

There was a seemingly infinite amount of obstacles that Morgan was forced to overcome — everything from obscene phone calls at her station to needing a security guard to clear out the men’s only restroom.
“You have to realize that everywhere I went — if I went to a procedure review, if I went to a post-test critique, almost every single part of my daily work — I’d be the only woman in the room,” reflects Morgan. “I had a sense of loneliness in a way, but on the other side of that coin, I wanted to do the best job I could.”

To be the instrumentation controller in the launch room for the Apollo 11 liftoff was as huge as a deal as it sounds. For Morgan, to be present at that pivotal point in history was ground-breaking: “It was very validating. It absolutely made my career.”

Much like the Saturn V rocket, Morgan’s career took off. She was the first NASA woman to win a Sloan Fellowship, which she used to earn a Master of Science degree in management from Stanford University in California. When she returned to NASA, she became a divisions chief of the Computer Systems division.

From there, Morgan excelled in many other roles, including deputy of Expendable Launch Vehicles, director of Payload Projects Management and director of Safety and Mission Assurance. She was one of the last two people who verified the space shuttle was ready to launch and the first woman at KSC to serve in an executive position, associate director of the center.

To this day, Morgan is still one of the most decorated women at KSC. Her numerous awards and recognitions include an achievement award for her work during the activation of Apollo Launch Complex 39, four exceptional service medals and two outstanding leadership medals. In 1995, she was inducted into the Florida Women's Hall of Fame.
After serving as the director of External Relations and Business Development, she retired from NASA in August 2003.

Today, people are reflecting on the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, looking back on photos of the only woman in the launch firing room and remembering Morgan as an emblem of inspiration for women in STEM. However, Morgan’s takeaway message is to not look at those photos in admiration, but in determination to see those photos “depart from our culture.”
“I look at that picture of the firing room where I’m the only woman. And I hope all the pictures now that show people working on the missions to the Moon and onto Mars, in rooms like Mission Control or Launch Control or wherever — that there will always be several women. I hope that photos like the ones I’m in don’t exist anymore.”

Follow Women@NASA for more stories like this one, and make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Rare Full Moon on Christmas Day
Not since 1977 has a full moon dawned in the skies on Christmas. But this year, a bright full moon will be an added gift for the holidays.

This full moon, the last of the year, is called the Full Cold Moon because it occurs during the beginning of winter.
Make sure you get outside to check out this rare event because it won’t happen again until 2034!

Here are a few fun facts about the event and our moon:
The moon’s peak this year will occur at 6:11 a.m. EST
As you gaze up at the Christmas moon, take note that we have a spacecraft currently orbiting Earth’s moon. Our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) mission has been investigating the lunar surface since 2009
More than 100 spacecraft have been launched to explore the moon
Our moon is the only celestial body beyond Earth that has been visited by human beings..so far!
Twelve human beings have walked on the surface of the moon
The moon makes a complete orbit around Earth in 27 Earth days and rotates or spins at the same rate. This causes the moon to keep the same side, or face, towards Earth during the course of its orbit
The moon is the brightest and largest feature in the night sky. Venus is second
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Infrared is Beautiful
Why was James Webb Space Telescope designed to observe infrared light? How can its images hope to compare to those taken by the (primarily) visible-light Hubble Space Telescope? The short answer is that Webb will absolutely capture beautiful images of the universe, even if it won’t see exactly what Hubble sees. (Spoiler: It will see a lot of things even better.)

The James Webb Space Telescope, or Webb, is our upcoming infrared space observatory, which will launch in 2019. It will spy the first luminous objects that formed in the universe and shed light on how galaxies evolve, how stars and planetary systems are born, and how life could form on other planets.
What is infrared light?
This may surprise you, but your remote control uses light waves just beyond the visible spectrum of light—infrared light waves—to change channels on your TV.
Infrared light shows us how hot things are. It can also show us how cold things are. But it all has to do with heat. Since the primary source of infrared radiation is heat or thermal radiation, any object that has a temperature radiates in the infrared. Even objects that we think of as being very cold, such as an ice cube, emit infrared.
There are legitimate scientific reasons for Webb to be an infrared telescope. There are things we want to know more about, and we need an infrared telescope to learn about them. Things like: stars and planets being born inside clouds of dust and gas; the very first stars and galaxies, which are so far away the light they emit has been stretched into the infrared; and the chemical fingerprints of elements and molecules in the atmospheres of exoplanets, some of which are only seen in the infrared.
In a star-forming region of space called the 'Pillars of Creation,' this is what we see with visible light:

And this is what we see with infrared light:

Infrared light can pierce through obscuring dust and gas and unveil a more unfamiliar view.
Webb will see some visible light: red and orange. But the truth is that even though Webb sees mostly infrared light, it will still take beautiful images. The beauty and quality of an astronomical image depends on two things: the sharpness of the image and the number of pixels in the camera. On both of these counts, Webb is very similar to, and in many ways better than, Hubble. Webb will take much sharper images than Hubble at infrared wavelengths, and Hubble has comparable resolution at the visible wavelengths that Webb can see.

Webb’s infrared data can be translated by computer into something our eyes can appreciate – in fact, this is what we do with Hubble data. The gorgeous images we see from Hubble don’t pop out of the telescope looking fully formed. To maximize the resolution of the images, Hubble takes multiple exposures through different color filters on its cameras.
The separate exposures, which look black and white, are assembled into a true color picture via image processing. Full color is important to image analysis of celestial objects. It can be used to highlight the glow of various elements in a nebula, or different stellar populations in a galaxy. It can also highlight interesting features of the object that might be overlooked in a black and white exposure, and so the images not only look beautiful but also contain a lot of useful scientific information about the structure, temperatures, and chemical makeup of a celestial object.
This image shows the sequences in the production of a Hubble image of nebula Messier 17:

Here’s another compelling argument for having telescopes that view the universe outside the spectrum of visible light – not everything in the universe emits visible light. There are many phenomena which can only be seen at certain wavelengths of light, for example, in the X-ray part of the spectrum, or in the ultraviolet. When we combine images taken at different wavelengths of light, we can get a better understanding of an object, because each wavelength can show us a different feature or facet of it.
Just like infrared data can be made into something meaningful to human eyes, so can each of the other wavelengths of light, even X-rays and gamma-rays.
Below is an image of the M82 galaxy created using X-ray data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory, infrared data from the Spitzer Space Telescope, and visible light data from Hubble. Also note how aesthetically pleasing the image is despite it not being just optical light:

Though Hubble sees primarily visible light, it can see some infrared. And despite not being optimized for it, and being much less powerful than Webb, it still produced this stunning image of the Horsehead Nebula.

It’s a big universe out there – more than our eyes can see. But with all the telescopes now at our disposal (as well as the new ones that will be coming online in the future), we are slowly building a more accurate picture. And it’s definitely a beautiful one. Just take a look...
…At this Spitzer infrared image of a shock wave in dust around the star Zeta Ophiuchi.

…this Spitzer image of the Helix Nebula, created using infrared data from the telescope and ultraviolet data from the Galaxy Evolution Explorer.

…this image of the “wing” of the Small Magellanic Cloud, created with infrared data from Spitzer and X-ray data from Chandra.

...the below image of the Milky Way’s galactic center, taken with our flying SOFIA telescope. It flies at more than 40,000 feet, putting it above 99% of the water vapor in Earth's atmosphere-- critical for observing infrared because water vapor blocks infrared light from reaching the ground. This infrared view reveals the ring of gas and dust around a supermassive black hole that can't be seen with visible light.

…and this Hubble image of the Mystic Mountains in the Carina Nebula.

Learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope HERE, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Image Credits Eagle Nebula: NASA, ESA/Hubble and the Hubble Heritage Team Hubble Image Processing - Messier 17: NASA/STScI Galaxy M82 Composite Image: NASA, CXC, JHU, D.Strickland, JPL-Caltech, C. Engelbracht (University of Arizona), ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Horsehead Nebula: NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Zeta Ophiuchi: NASA/JPL-Caltech Helix Nebula: NASA/JPL-Caltech Wing of the Small Magellanic Cloud X-ray: NASA/CXC/Univ.Potsdam/L.Oskinova et al; Optical: NASA/STScI; Infrared: NASA/JPL-Caltech Milky Way Circumnuclear Ring: NASA/DLR/USRA/DSI/FORCAST Team/ Lau et al. 2013 Mystic Mountains in the Carina Nebula: NASA/ESA/M. Livio & Hubble 20th Anniversary Team (STScI)
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
A Ring of Fire Eclipse in the Southern Hemisphere
On Feb. 26, a “ring of fire” will be visible in the sky above parts of the Southern Hemisphere, including Chile, Argentina and Angola. This is called an annular eclipse.

Credit: Dale Cruikshank
If you live within the viewing area, even though most of the sun will be obscured by the moon, it’s essential to observe eye safety. This includes using a proper solar filter or an indirect viewing method during ALL phases of this eclipse.

See full graphic
What is an annular eclipse? During any type of solar eclipse, the sun, moon, and Earth line up, allowing the moon to cast its shadow on Earth’s surface in a partial or total solar eclipse.

Download this animation
An annular eclipse is the product of almost the same celestial geometry as a total solar eclipse – that is, from the perspective of some place on Earth, the moon crosses in front of the sun's center.
But an annular eclipse is different in one important way – the moon is too far from Earth to obscure the sun completely, leaving the sun’s edges exposed and producing the “ring of fire” effect for which annular eclipses are known. Because the moon’s orbit is slightly oblong, its distance from Earth – and therefore its apparent size compared to the sun’s – is constantly changing.

An annular eclipse seen in extreme ultraviolet light – a type of light invisible to humans – by the Hinode spacecraft on Jan. 4, 2011.
Any time part, or all, of the sun’s surface is exposed – whether during an annular eclipse, a partial eclipse, or just a regular day – it’s essential to use a proper solar filter or an indirect viewing method to view the sun. You can NEVER look directly at the sun, and an annular eclipse is no exception!

If you live in the Southern Hemisphere or near the equator, check this interactive map for partial eclipse times.
If you live in North America, you’ll have a chance to see an eclipse later this year. On Aug. 21, 2017, a total solar eclipse will cross the US – the first total solar eclipse in the contiguous US in nearly 40 years! The path of totality for the August eclipse runs from coast to coast.

Within this narrow path of totality, the moon will completely obscure the sun – unlike an annular eclipse – revealing the sun’s outer atmosphere. People in other parts of North America will see a partial solar eclipse, weather permitting. Find out what you can see during the Aug. 21, 2017, eclipse in your area with our maps, and explore the rest of eclipse2017.nasa.gov for more information.
For more eclipse science, visit www.nasa.gov/eclipse.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Ad Astra, John Glenn (1921-2016)
An astronaut.
A pilot.
A husband.
A father.
A United States Senator.
An American hero.
An original.

John Glenn (1921-2016) was all those things and more. When he rocketed into space on Feb. 20, 1962, to become the first American to orbit Earth, the flight set the nation on course to meet ever-more ambitious goals.
The life and career of Senator Glenn eclipses those of many. In spite of his accomplishments, he was a humble and gracious man (and 4-term U.S. senator).
During Glenn’s first flight, a scheduled 30-minute test to determine whether Glenn could fly the capsule manually became a matter of life and death when the automatic system malfunctioned after the first orbit.

"I went to manual control and continued in that mode during the second and third orbits, and during re-entry," Glenn recalled later. "The malfunction just forced me to prove very rapidly what had been planned over a longer period of time." Another problem seemed even more serious -- telemetry indicated the spacecraft's heat shield was loose. It seemed possible that Glenn and the spacecraft would be incinerated on re-entry. Glenn left the retrorocket pack in place to steady the heat shield during re-entry. "It made for a very spectacular re-entry from where I was sitting," he said. Big chunks of the burning material came flying by the window.

He wasn't sure whether the flaming debris was the rocket pack or the heat shield breaking up. "Fortunately," he told an interviewer," it was the rocket pack -- or I wouldn't be answering these questions."

In the words of President Obama, who awarded him the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2012: “When John Glenn blasted off from Cape Canaveral atop an Atlas rocket in 1962, he lifted the hopes of a nation. And when his Friendship 7 spacecraft splashed down a few hours later, the first American to orbit the Earth reminded us that with courage and a spirit of discovery there's no limit to the heights we can reach together. With John's passing, our nation has lost an icon and Michelle and I have lost a friend. John spent his life breaking barriers, from defending our freedom as a decorated Marine Corps fighter pilot in World War II and Korea, to setting a transcontinental speed record ... The last of America's first astronauts has left us, but propelled by their example we know that our future here on Earth compels us to keep reaching for the heavens. On behalf of a grateful nation, Godspeed, John Glenn.”

Glenn left the Astronaut Corps in 1964 and resigned from the Marine Corps in 1965. And, after some time in private industry ran for and was elected ti the U.S. Senate in 1974, carrying all 88 counties of Ohio. He was re-elected in 1980 with the largest margin in Ohio history. Ohio returned him to the Senate for a third term in 1986. In 1992 he was elected again, becoming the first popularly elected senator from his state to win four consecutive terms. During his last term he was the ranking member of both the Governmental Affairs Committee and the Subcommittee on Air/Land Forces in the Senate Armed Services Committee. He also served on the Select Committee on Intelligence and the Special Committee on Aging. He was considered one of the Senate's leading experts on technical and scientific matters, and won wide respect for his work to prevent the spread of weapons of mass destruction.

In 1998, Glenn flew on the STS-95 Discovery shuttle flight, a 9-day mission during which the crew supported a variety of research payloads including deployment of the Spartan solar-observing spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, and Glenn's investigations on space flight and the aging process.
NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden remembers, “Senator Glenn's legacy is one of risk and accomplishment, of history created and duty to country carried out under great pressure with the whole world watching.”
Today, we honor him for all that he stood for and continues to stand for -- grace under pressure, humility, ability, strength.
Godspeed, John Glenn.
-
 gonuclear liked this · 7 months ago
gonuclear liked this · 7 months ago -
 stitchlingbelle reblogged this · 11 months ago
stitchlingbelle reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 esacesalbit liked this · 1 year ago
esacesalbit liked this · 1 year ago -
 broad-skies liked this · 2 years ago
broad-skies liked this · 2 years ago -
 tenshot liked this · 2 years ago
tenshot liked this · 2 years ago -
 misan-thropist reblogged this · 2 years ago
misan-thropist reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 avi6174 liked this · 3 years ago
avi6174 liked this · 3 years ago -
 writingawaymylife liked this · 4 years ago
writingawaymylife liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts