Five Things You Need To Know About The Deep Space Atomic Clock
Five Things You Need to Know About the Deep Space Atomic Clock

We are set to send a new technology to space that will change the way we navigate spacecraft — even how we’ll send astronauts to Mars and beyond. Built by our Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, the Deep Space Atomic Clock is a technology demonstration that will help spacecraft navigate autonomously. No larger than a toaster oven, the instrument will be tested in Earth orbit for one year, with the goal of being ready for future missions to other worlds.
Here are five key facts to know about our Deep Space Atomic Clock:
1) It works a lot like GPS

The Deep Space Atomic Clock is a sibling of the atomic clocks you interact with every day on your smart phone. Atomic clocks aboard satellites enable your phone's GPS application to get you from point A to point B by calculating where you are on Earth, based on the time it takes the signal to travel from the satellite to your phone.
But spacecraft don't have GPS to help them find their way in deep space; instead, navigation teams rely on atomic clocks on Earth to determine location data. The farther we travel from Earth, the longer this communication takes. The Deep Space Atomic Clock is the first atomic clock designed to fly onboard a spacecraft that goes beyond Earth's orbit, dramatically improving the process.
2) It will help our spacecraft navigate autonomously

Today, we navigate in deep space by using giant antennas on Earth to send signals to spacecraft, which then send those signals back to Earth. Atomic clocks on Earth measure the time it takes a signal to make this two-way journey. Only then can human navigators on Earth use large antennas to tell the spacecraft where it is and where to go.
If we want humans to explore the solar system, we need a better, faster way for the astronauts aboard a spacecraft to know where they are, ideally without needing to send signals back to Earth. A Deep Space Atomic Clock on a spacecraft would allow it to receive a signal from Earth and determine its location immediately using an onboard navigation system.
3) It loses only 1 second in 9 million years

Any atomic clock has to be incredibly precise to be used for this kind of navigation: A clock that is off by even a single second could mean the difference between landing on Mars and missing it by miles. In ground tests, the Deep Space Atomic Clock proved to be up to 50 times more stable than the atomic clocks on GPS satellites. If the mission can prove this stability in space, it will be one of the most precise clocks in the universe.
4) It keeps accurate time using mercury ions

Your wristwatch and atomic clocks keep time in similar ways: by measuring the vibrations of a quartz crystal. An electrical pulse is sent through the quartz so that it vibrates steadily. This continuous vibration acts like the pendulum of a grandfather clock, ticking off how much time has passed. But a wristwatch can easily drift off track by seconds to minutes over a given period.
An atomic clock uses atoms to help maintain high precision in its measurements of the quartz vibrations. The length of a second is measured by the frequency of light released by specific atoms, which is same throughout the universe. But atoms in current clocks can be sensitive to external magnetic fields and temperature changes. The Deep Space Atomic Clock uses mercury ions - fewer than the amount typically found in two cans of tuna fish - that are contained in electromagnetic traps. Using an internal device to control the ions makes them less vulnerable to external forces.
5) It will launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket

The Deep Space Atomic Clock will fly on the Orbital Test Bed satellite, which launches on the SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket with around two dozen other satellites from government, military and research institutions. The launch is targeted for June 24, 2019 from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and will be live-streamed here: https://www.nasa.gov/live
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Greenland Refrozen
It won’t be until summertime that a significant amount of melt shows up across the Greenland Ice Sheet. For now, most indications of meltwater ponds and lakes are leftovers from past seasons that have since refrozen.

These photographs were snapped during research flights for NASA’s Operation IceBridge—now in its final year after a decade of airborne missions to map polar ice.

This second image was acquired on April 18, 2019, with the Continuous Airborne Mapping by Optical Translator (CAMBOT) system. The system takes downward-looking images throughout a flight, which can later be used by scientists to interpret other data. This image shows part of a large, frozen lake on Storstrømmen Glacier. This lake also thaws in summertime, which is why it shows up as blue ice.
Lakes atop a glacier, or “supraglacial lakes,” are somewhat stable in terms of their location, according to Joe MacGregor, NASA project scientist for Operation IceBridge. The lake on Storstrømmen is visible in satellite data at least as far back as May 2012. On occasion, water in lakes like this can drain away through a vertical shaft known as a “moulin.” Scientists initially wondered if the dark circular area on the right side of this image could be a moulin, but closer inspection suggested it is just a deeper part of the lake.
See more photos of the frozen lakes in Greenland: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/144965/greenland-refrozen
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How Do Cargo Spacecraft Work?

Today is the day that our commercial partner, Orbital ATK, has set for the launch of its fourth contracted mission to the International Space Station. The Cygnus spacecraft will carry more than 7,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory.
How Does it Launch?

This mission is the first Cygnus mission to utilize NASA’s Kennedy Space Center and launch from the Cape Canaveral Air Force base in Cape Canaveral, Florida.
The cargo will be launched inside the Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft using a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
But how does it get there? Is there someone on the ground controlling and directing it to the space station? Surprisingly, no. After launch, the Cygnus spacecraft is automated until it gets near the station. At that point, the robotic controllers use the CanadArm2 to reach out and grapple it (grab), and then berth (connect) it to the station.
What’s Inside?

In order to keep the thousands of pounds of supplies, science and hardware from moving during launch and in flight, the cargo is packed in bags and strapped to the walls.
The new experiments arriving to the space station will challenge and inspire future scientists and explorers. A few of the highlights are:
The Packed Bed Reactor Experiment (PBRE) - This experiment (image below) will study the behavior of gases and liquids when they flow simultaneously through a column filled with fixed porous media. The findings from this will be of interest in many chemical and biological processing systems as well as many geophysical applications.

BASS-M (Burning and Suppression of Solids – Milliken) - This experiment (image below) will evaluate flame retardant and/or resistant textiles as a mode of personal protection from fire-related hazards. Studying this in microgravity will aid in better designs for future textiles and benefit those who wear flame retardant and/or resistant protective apparel such as military personnel and civilian workers in the electrical and energy industries.

Space Automated Bioproduct Lab (SABL) - This equipment is a single locker-sized facility (image below) that will enable a wide variety of fundamental, applied and commercial life sciences research. It will also benefit K-16 education-based investigations aboard the space station. Research will be supported on microorganisms (bacteria, yeast, algae, fungi, viruses, etc.), animal cells and tissues and small plant and animal organisms.

Nodes Satellites – These satellites (image below) will be deployed from the space station to demonstrate new network capabilities critical to the operation of swarms of spacecraft. They will show the ability of multi-spacecraft swarms to receive and distribute ground commands, exchange information periodically and more.

Holiday Surprises - With the upcoming holidays the crew’s family has the opportunity to send Christmas gifts to their family members on the International Space Station.

What About After?
The spacecraft will spend more than a month attached to the space station before it’s detached for re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere in January 2016, disposing of about 3,000 pounds of trash. It will disintegrate while entering the atmosphere.

Want to Watch Launch?
Launch coverage begins at 4:30 p.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 3 on NASA Television. Cygnus is set to lift off on the Atlas V at 5:55 p.m., the beginning of a 30-minute launch window, from Space Launch Complex 41.
In addition to launch coverage, a post-launch briefing will be held approximately two hours after launch. All briefings will air live on NASA TV.
UPDATE: Due to poor weather conditions, today’s launch has been scrubbed and moved to tomorrow at 5:33 p.m. EST. The forecast for tomorrow calls for a 30% chance of acceptable conditions at launch time. Continuous countdown coverage will be available on NASA Television starting at 4:30 p.m.

UPDATE 2: The uncrewed Cygnus cargo ship launched at 4:44 p.m. EST on Sunday, Dec. 6 on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to begin its three-day journey to the orbiting laboratory.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
A Mesmerizing Model of Monster Black Holes
Just about every galaxy the size of our Milky Way (or bigger) has a supermassive black hole at its center. These objects are ginormous — hundreds of thousands to billions of times the mass of the Sun! Now, we know galaxies merge from time to time, so it follows that some of their black holes should combine too. But we haven’t seen a collision like that yet, and we don’t know exactly what it would look like.

A new simulation created on the Blue Waters supercomputer — which can do 13 quadrillion calculations per second, 3 million times faster than the average laptop — is helping scientists understand what kind of light would be produced by the gas around these systems as they spiral toward a merger.
The new simulation shows most of the light produced around these two black holes is UV or X-ray light. We can’t see those wavelengths with our own eyes, but many telescopes can. Models like this could tell the scientists what to look for.
You may have spotted the blank circular region between the two black holes. No, that’s not a third black hole. It’s a spot that wasn’t modeled in this version of the simulation. Future models will include the glowing gas passing between the black holes in that region, but the researchers need more processing power. The current version already required 46 days!

The supermassive black holes have some pretty nifty effects on the light created by the gas in the system. If you view the simulation from the side, you can see that their gravity bends light like a lens. When the black holes are lined up, you even get a double lens!
But what would the view be like from between two black holes? In the 360-degree video above, the system’s gas has been removed and the Gaia star catalog has been added to the background. If you watch the video in the YouTube app on your phone, you can moved the screen around to explore this extreme vista. Learn more about the new simulation here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Sixty Years of Exploration, Innovation, and Discovery!

Exactly sixty years ago today, we opened our doors for the first time. And since then, we have opened up a universe of discovery and innovation.
There are so many achievements to celebrate from the past six decades, there’s no way we can go through all of them. If you want to dive deeper into our history of exploration, check out NASA: 60 Years and Counting.
In the meantime, take a moonwalk down memory lane with us while we remember a few of our most important accomplishments from the past sixty years!

In 1958, President Eisenhower signed the National Aeronautics and Space Act, which effectively created our agency. We officially opened for business on October 1.
To learn more about the start of our space program, watch our video: How It All Began.

Alongside the U.S. Air Force, we implemented the X-15 hypersonic aircraft during the 1950s and 1960s to improve aircraft and spacecraft.
The X-15 is capable of speeds exceeding Mach 6 (4,500 mph) at altitudes of 67 miles, reaching the very edge of space.
Dubbed the “finest and most productive research aircraft ever seen,” the X-15 was officially retired on October 24, 1968. The information collected by the X-15 contributed to the development of the Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, and Space Shuttle programs.
To learn more about how we have revolutionized aeronautics, watch our Leading Edge of Flight video.

On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the moon. The crew of Apollo 11 had the distinction of completing the first return of soil and rock samples from beyond Earth.
Astronaut Gene Cernan, during Apollo 17, was the last person to have walked on the surface of the moon. (For now!)
The Lunar Roving Vehicle was a battery-powered rover that the astronauts used during the last three Apollo missions.
To learn more about other types of technology that we have either invented or improved, watch our video: Trailblazing Technology.

Our long-term Earth-observing satellite program began on July 23, 1972 with the launch of Landsat 1, the first in a long series (Landsat 9 is expected to launch in 2020!) We work directly with the U.S. Geological Survey to use Landsat to monitor and manage resources such as food, water, and forests.
Landsat data is one of many tools that help us observe in immense detail how our planet is changing. From algae blooms to melting glaciers to hurricane flooding, Landsat is there to help us understand our own planet better.
Off the Earth, for the Earth.
To learn more about how we contribute to the Earth sciences, watch our video: Home, Sweet Home.

Space Transportation System-1, or STS-1, was the first orbital spaceflight of our Space Shuttle program.
The first orbiter, Columbia, launched on April 12, 1981. Over the next thirty years, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour would be added to the space shuttle fleet.
Together, they flew 135 missions and carried 355 people into space using the first reusable spacecraft.

On January 16, 1978, we selected a class of 35 new astronauts--including the first women and African-American astronauts.
And on June 18, 1983, Sally Ride became the first American woman to enter space on board Challenger for STS-7.
To learn more about our astronauts, then and now, watch our Humans in Space video.

Everybody loves Hubble! The Hubble Space Telescope was launched into orbit on April 24, 1990, and has been blowing our minds ever since.
Hubble has not only captured stunning views of our distant stars and galaxies, but has also been there for once-in-a-lifetime cosmic events. For example, on January 6, 2010, Hubble captured what appeared to be a head-on collision between two asteroids--something no one has ever seen before.
In this image, Hubble captures the Carina Nebula illuminating a three-light-year tall pillar of gas and dust.
To learn more about how we have contributed to our understanding of the solar system and beyond, watch our video: What’s Out There?

Cooperation to build the International Space Station began in 1993 between the United States, Russia, Japan, and Canada.
The dream was fully realized on November 2, 2000, when Expedition 1 crew members boarded the station, signifying humanity’s permanent presence in space!
Although the orbiting lab was only a couple of modules then, it has grown tremendously since then!
To learn more about what’s happening on the orbiting outpost today, visit the Space Station page.

We have satellites in the sky, humans in orbit, and rovers on Mars. Very soon, we will be returning humankind to the Moon, and using it as a platform to travel to Mars and beyond.
And most importantly, we bring the universe to you.
What are your favorite NASA moments? We were only able to share a few of ours here, but if you want to learn about more important NASA milestones, check out 60 Moments in NASA History or our video, 60 Years in 60 Seconds.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How to Connect with NASA
We're the nation’s space agency, but that doesn’t mean you have to travel to the depths of the universe to stay connected with the awesome stuff we’re doing. There are actually some really easy ways to stay updated on all things space. Check them out:
Apps

We have lots of apps for smartphones and tablets that will make it easier than ever to stay connected to space. Here are a few to pique your interest:
NASA App: Showcases a huge collection of the latest content, including images, videos, mission information, stories, space station sighting opportunities and more! Download: Apple/Android
NASA Spinoff App: This application profiles the best examples of technology that have been transferred from NASA research and missions into commercial products. From life-saving satellite systems to hospital robots, our technologies benefit society. Download: Apple
NASA 3DV App: The 3DV mobile app allows you to examine several of our Deep Space Exploration projects that will take our space program to asteroids, Mars and beyond! Download: Apple/Android
Spacecraft 3D: This augmented reality (AR) application lets you learn about and interact with a variety of spacecraft that are used to explore our solar system, study Earth and observe the universe. Download: Apple/Android
Competitions and Challenges

NASA Solve is an invitation to members of the public to contribute their time and expertise to solving problems and potentially winning prizes as a result of their work. This is a great way for individual members of the public to be a part of the nation’s space program. For a complete list of current challenges and competitions, visit THIS page.
Citizen Science
You don’t have to be a NASA employee to engage in the fun of interpreting scientific data and imagery from our many spacecraft and missions. As part of our Open Government plan, our goal is to promote transparency, participation and collaboration. By expanding the research base and using open innovation, we are all able to benefit from the accumulated findings. You can find data from our missions, research and activities HERE.
Email and Social Media
We have a wide-range of social media accounts here at NASA. Everything from Earth Science to the Mars Curiosity Rover, you can stay updated on many of our missions on many popular social media sites. For a full list of our accounts, visit THIS page.
If you’d like to get space news delivered straight to your inbox, you can sign up for updates and manage preferences HERE.
NASA Socials

What is a NASA Social? We’re glad you asked! These programs provide opportunities for our social media followers to learn and share information about our missions, people and programs. NASA Social includes both special in-person events and social media credentials for individuals who share the news in a significant way. Social events provide the participants with the opportunity to go behind-the-scenes at our facilities and events and speak with scientists engineers, astronauts and managers. Visit THIS page for a list of upcoming NASA Social opportunities.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What sparked your interest in science?
A Tour of Cosmic Temperatures
We often think of space as “cold,” but its temperature can vary enormously depending on where you visit. If the difference between summer and winter on Earth feels extreme, imagine the range of temperatures between the coldest and hottest places in the universe — it’s trillions of degrees! So let’s take a tour of cosmic temperatures … from the coldest spots to the hottest temperatures yet achieved.
First, a little vocabulary: Astronomers use the Kelvin temperature scale, which is represented by the symbol K. Going up by 1 K is the same as going up 1°C, but the scale begins at 0 K, or -273°C, which is also called absolute zero. This is the temperature where the atoms in stuff stop moving. We’ll measure our temperatures in this tour in kelvins, but also convert them to make them more familiar!
We’ll start on the chilly end of the scale with our CAL (Cold Atom Lab) on the International Space Station, which can chill atoms to within one ten billionth of a degree above 0 K, just a fraction above absolute zero.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Just slightly warmer is the Resolve sensor inside XRISM, pronounced “crism,” short for the X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission. This is an international collaboration led by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) with NASA and ESA (European Space Agency). Resolve operates at one twentieth of a degree above 0 K. Why? To measure the heat from individual X-rays striking its 36 pixels!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Resolve and CAL are both colder than the Boomerang Nebula, the coldest known region in the cosmos at just 1 K! This cloud of dust and gas left over from a Sun-like star is about 5,000 light-years from Earth. Scientists are studying why it’s colder than the natural background temperature of deep space.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Let’s talk about some temperatures closer to home. Icy gas giant Neptune is the coldest major planet. It has an average temperature of 72 K at the height in its atmosphere where the pressure is equivalent to sea level on Earth. Explore how that compares to other objects in our solar system!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
How about Earth? According to NOAA, Death Valley set the world’s surface air temperature record on July 10, 1913. This record of 330 K has yet to be broken — but recent heat waves have come close. (If you’re curious about the coldest temperature measured on Earth, that’d be 183.95 K (-128.6°F or -89.2°C) at Vostok Station, Antarctica, on July 21, 1983.)
We monitor Earth's global average temperature to understand how our planet is changing due to human activities. Last year, 2023, was the warmest year on our record, which stretches back to 1880.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
The inside of our planet is even hotter. Earth’s inner core is a solid sphere made of iron and nickel that’s about 759 miles (1,221 kilometers) in radius. It reaches temperatures up to 5,600 K.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We might assume stars would be much hotter than our planet, but the surface of Rigel is only about twice the temperature of Earth’s core at 11,000 K. Rigel is a young, blue star in the constellation Orion, and one of the brightest stars in our night sky.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We study temperatures on large and small scales. The electrons in hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, can be stripped away from their atoms in a process called ionization at a temperature around 158,000 K. When these electrons join back up with ionized atoms, light is produced. Ionization is what makes some clouds of gas and dust, like the Orion Nebula, glow.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We already talked about the temperature on a star’s surface, but the material surrounding a star gets much, much hotter! Our Sun’s surface is about 5,800 K (10,000°F or 5,500°C), but the outermost layer of the solar atmosphere, called the corona, can reach millions of kelvins.
Our Parker Solar Probe became the first spacecraft to fly through the corona in 2021, helping us answer questions like why it is so much hotter than the Sun's surface. This is one of the mysteries of the Sun that solar scientists have been trying to figure out for years.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Looking for a hotter spot? Located about 240 million light-years away, the Perseus galaxy cluster contains thousands of galaxies. It’s surrounded by a vast cloud of gas heated up to tens of millions of kelvins that glows in X-ray light. Our telescopes found a giant wave rolling through this cluster’s hot gas, likely due to a smaller cluster grazing it billions of years ago.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Now things are really starting to heat up! When massive stars — ones with eight times the mass of our Sun or more — run out of fuel, they put on a show. On their way to becoming black holes or neutron stars, these stars will shed their outer layers in a supernova explosion. These layers can reach temperatures of 300 million K!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Jeremy Schnittman
We couldn’t explore cosmic temperatures without talking about black holes. When stuff gets too close to a black hole, it can become part of a hot, orbiting debris disk with a conical corona swirling above it. As the material churns, it heats up and emits light, making it glow. This hot environment, which can reach temperatures of a billion kelvins, helps us find and study black holes even though they don’t emit light themselves.
JAXA’s XRISM telescope, which we mentioned at the start of our tour, uses its supercool Resolve detector to explore the scorching conditions around these intriguing, extreme objects.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/CI Lab
Our universe’s origins are even hotter. Just one second after the big bang, our tiny, baby universe consisted of an extremely hot — around 10 billion K — “soup” of light and particles. It had to cool for a few minutes before the first elements could form. The oldest light we can see, the cosmic microwave background, is from about 380,000 years after the big bang, and shows us the heat left over from these earlier moments.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We’ve ventured far in distance and time … but the final spot on our temperature adventure is back on Earth! Scientists use the Large Hadron Collider at CERN to smash teensy particles together at superspeeds to simulate the conditions of the early universe. In 2012, they generated a plasma that was over 5 trillion K, setting a world record for the highest human-made temperature.
Want this tour as a poster? You can download it here in a vertical or horizontal version!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Explore the wonderful and weird cosmos with NASA Universe on X, Facebook, and Instagram. And make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Solar System: 10 Ways Interns Are Exploring Space With Us
Simulating alien worlds, designing spacecraft with origami and using tiny fossils to understand the lives of ancient organisms are all in a day’s work for interns at NASA.
Here’s how interns are taking our missions and science farther.
1. Connecting Satellites in Space

Becca Foust looks as if she’s literally in space – or, at least, on a sci-fi movie set. She’s surrounded by black, except for the brilliant white comet model suspended behind her. Beneath the socks she donned just for this purpose, the black floor reflects the scene like perfectly still water across a lake as she describes what happens here: “We have five spacecraft simulators that ‘fly’ in a specially designed flat-floor facility,” she says. “The spacecraft simulators use air bearings to lift the robots off the floor, kind of like a reverse air hockey table. The top part of the spacecraft simulators can move up and down and rotate all around in a similar way to real satellites.” It’s here, in this test bed on the Caltech campus, that Foust is testing an algorithm she’s developing to autonomously assemble and disassemble satellites in space. “I like to call it space K’nex, like the toys. We're using a bunch of component satellites and trying to figure out how to bring all of the pieces together and make them fit together in orbit,” she says. A NASA Space Technology Research Fellow, who splits her time between Caltech and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), working with Soon-Jo Chung and Fred Hadaegh, respectively, Foust is currently earning her Ph.D. at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. She says of her fellowship, “I hope my research leads to smarter, more efficient satellite systems for in-space construction and assembly.”
2. Diving Deep on the Science of Alien Oceans

Three years ago, math and science were just subjects Kathy Vega taught her students as part of Teach for America. Vega, whose family emigrated from El Salvador, was the first in her family to go to college. She had always been interested in space and even dreamed about being an astronaut one day, but earned a degree in political science so she could get involved in issues affecting her community. But between teaching and encouraging her family to go into science, It was only a matter of time before she realized just how much she wanted to be in the STEM world herself. Now an intern at NASA JPL and in the middle of earning a second degree, this time in engineering physics, Vega is working on an experiment that will help scientists search for life beyond Earth.
“My project is setting up an experiment to simulate possible ocean compositions that would exist on other worlds,” says Vega. Jupiter’s moon Europa and Saturn’s moon Enceladus, for example, are key targets in the search for life beyond Earth because they show evidence of global oceans and geologic activity. Those factors could allow life to thrive. JPL is already building a spacecraft designed to orbit Europa and planning for another to land on the icy moon’s surface. “Eventually, [this experiment] will help us prepare for the development of landers to go to Europa, Enceladus and another one of Saturn’s moons, Titan, to collect seismic measurements that we can compare to our simulated ones,” says Vega. “I feel as though I'm laying the foundation for these missions.”
3. Unfolding Views on Planets Beyond Our Solar System

“Origami is going to space now? This is amazing!” Chris Esquer-Rosas had been folding – and unfolding – origami since the fourth grade, carefully measuring the intricate patterns and angles produced by the folds and then creating new forms from what he’d learned. “Origami involves a lot of math. A lot of people don't realize that. But what actually goes into it is lots of geometric shapes and angles that you have to account for,” says Esquer-Rosas. Until three years ago, the computer engineering student at San Bernardino College had no idea that his origami hobby would turn into an internship opportunity at NASA JPL. That is, until his long-time friend, fellow origami artist and JPL intern Robert Salazar connected him with the Starshade project. Starshade has been proposed as a way to suppress starlight that would otherwise drown out the light from planets outside our solar system so we can characterize them and even find out if they’re likely to support life. Making that happen requires some heavy origami – unfurling a precisely-designed, sunflower-shaped structure the size of a baseball diamond from a package about half the size of a pitcher’s mound. It’s Esquer-Rosas’ project this summer to make sure Starshade’s “petals” unfurl without a hitch. Says Esquer-Rosas, “[The interns] are on the front lines of testing out the hardware and making sure everything works. I feel as though we're contributing a lot to how this thing is eventually going to deploy in space.”
4. Making Leaps in Extreme Robotics

Wheeled rovers may be the norm on Mars, but Sawyer Elliott thinks a different kind of rolling robot could be the Red Planet explorer of the future. This is Elliott’s second year as a fellow at NASA JPL, researching the use of a cube-shaped robot for maneuvering around extreme environments, like rocky slopes on Mars or places with very little gravity, like asteroids. A graduate student in aerospace engineering at Cornell University, Elliott spent his last stint at JPL developing and testing the feasibility of such a rover. “I started off working solely on the rover and looking at can we make this work in a real-world environment with actual gravity,” says Elliott. “It turns out we could.” So this summer, he’s been improving the controls that get it rolling or even hopping on command. In the future, Elliott hopes to keep his research rolling along as a fellow at JPL or another NASA center. “I'm only getting more and more interested as I go, so I guess that's a good sign,” he says.
5. Starting from the Ground Up

Before the countdown to launch or the assembling of parts or the gathering of mission scientists and engineers, there are people like Joshua Gaston who are helping turn what’s little more than an idea into something more. As an intern with NASA JPL’s project formulation team, Gaston is helping pave the way for a mission concept that aims to send dozens of tiny satellites, called CubeSats, beyond Earth’s gravity to other bodies in the solar system. “This is sort of like step one,” says Gaston. “We have this idea and we need to figure out how to make it happen.” Gaston’s role is to analyze whether various CubeSat models can be outfitted with the needed science instruments and still make weight. Mass is an important consideration in mission planning because it affects everything from the cost to the launch vehicle to the ability to launch at all. Gaston, an aerospace engineering student at Tuskegee University, says of his project, “It seems like a small role, but at the same time, it's kind of big. If you don't know where things are going to go on your spacecraft or you don't know how the spacecraft is going to look, it's hard to even get the proposal selected.”
6. Finding Life on the Rocks

By putting tiny samples of fossils barely visible to the human eye through a chemical process, a team of NASA JPL scientists is revealing details about organisms that left their mark on Earth billions of years ago. Now, they have set their sights on studying the first samples returned from Mars in the future. But searching for signatures of life in such a rare and limited resource means the team will have to get the most science they can out of the smallest sample possible. That’s where Amanda Allen, an intern working with the team in JPL’s Astrobiogeochemistry, or abcLab, comes in. “Using the current, state-of-the-art method, you need a sample that’s 10 times larger than we’re aiming for,” says Allen, an Earth science undergraduate at the University of California, San Diego, who is doing her fifth internship at JPL. “I’m trying to get a different method to work.” Allen, who was involved in theater and costume design before deciding to pursue Earth science, says her “superpower” has always been her ability to find things. “If there’s something cool to find on Mars related to astrobiology, I think I can help with that,” she says.
7. Taking Space Flight Farther

If everything goes as planned and a thruster like the one Camille V. Yoke is working on eventually helps send astronauts to Mars, she’ll probably be first in line to play the Mark Watney role. “I'm a fan of the Mark Watney style of life [in “The Martian”], where you're stranded on a planet somewhere and the only thing between you and death is your own ability to work through problems and engineer things on a shoestring,” says Yoke. A physics major at the University of South Carolina, Yoke is interning with a team that’s developing a next-generation electric thruster designed to accelerate spacecraft more efficiently through the solar system. “Today there was a brief period in which I knew something that nobody else on the planet knew – for 20 minutes before I went and told my boss,” says Yoke. “You feel like you're contributing when you know that you have discovered something new.”
8. Searching for Life Beyond Our Solar System

Without the option to travel thousands or even tens of light-years from Earth in a single lifetime, scientists hoping to discover signs of life on planets outside our solar system, called exoplanets, are instead creating their own right here on Earth. This is Tre’Shunda James’ second summer simulating alien worlds as an intern at NASA JPL. Using an algorithm developed by her mentor, Renyu Hu, James makes small changes to the atmospheric makeup of theoretical worlds and analyzes whether the combination creates a habitable environment. “This model is a theoretical basis that we can apply to many exoplanets that are discovered,” says James, a chemistry and physics major at Occidental College in Los Angeles. “In that way, it's really pushing the field forward in terms of finding out if life could exist on these planets.” James, who recently became a first-time co-author on a scientific paper about the team’s findings, says she feels as though she’s contributing to furthering the search for life beyond Earth while also bringing diversity to her field. “I feel like just being here, exploring this field, is pushing the boundaries, and I'm excited about that.”
9. Spinning Up a Mars Helicopter

Chloeleen Mena’s role on the Mars Helicopter project may be small, but so is the helicopter designed to make the first flight on the Red Planet. Mena, an electrical engineering student at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, started her NASA JPL internship just days after NASA announced that the helicopter, which had been in development at JPL for nearly five years, would be going to the Red Planet aboard the Mars 2020 rover. This summer, Mena is helping test a part needed to deploy the helicopter from the rover once it lands on Mars, as well as writing procedures for future tests. “Even though my tasks are relatively small, it's part of a bigger whole,” she says.
10. Preparing to See the Unseen on Jupiter's Moon Europa

In the 2020s, we’re planning to send a spacecraft to the next frontier in the search for life beyond Earth: Jupiter’s moon Europa. Swathed in ice that’s intersected by deep reddish gashes, Europa has unveiled intriguing clues about what might lie beneath its surface – including a global ocean that could be hospitable to life. Knowing for sure hinges on a radar instrument that will fly aboard the Europa Clipper orbiter to peer below the ice with a sort of X-ray vision and scout locations to set down a potential future lander. To make sure everything works as planned, NASA JPL intern Zachary Luppen is creating software to test key components of the radar instrument. “Whatever we need to do to make sure it operates perfectly during the mission,” says Luppen. In addition to helping things run smoothly, the astronomy and physics major says he hopes to play a role in answering one of humanity’s biggest questions. “Contributing to the mission is great in itself,” says Luppen. “But also just trying to make as many people aware as possible that this science is going on, that it's worth doing and worth finding out, especially if we were to eventually find life on Europa. That changes humanity forever!”
Read the full web version of this week’s ‘Solar System: 10 Things to Know” article HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Solar System: Things to Know This Week

For the first time in almost a decade, we're going back to Jupiter. Our Juno spacecraft arrives at the king of planets on the fourth of July. From a unique polar orbit, Juno will repeatedly dive between the planet and its intense belts of charged particle radiation. Juno's primary goal is to improve our understanding of Jupiter's formation and evolution, which will help us understand the history of our own solar system and provide new insight into how other planetary systems form.
In anticipation, here are a few things you need to know about the Juno mission and the mysterious world it will explore:
1. This is the Big One

The most massive planet in our solar system, with dozens of moons and an enormous magnetic field, Jupiter rules over a kind of miniature solar system.
2. Origin Story

Why study Jupiter in the first place? How does the planet fit into the solar system as a whole? What is it hiding? How will Juno unlock its secrets? A series of brief videos tells the stories of Jupiter and Juno. Watch them HERE.
3. Eyes on Juno
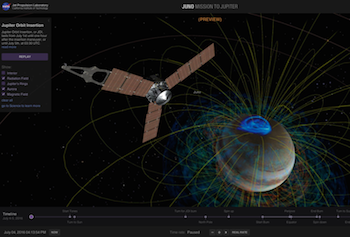
If you really want a hands-on understanding of Juno's flight through the Jupiter system, there's no better tool than the "Eyes on Juno" online simulation. It uses data from the mission to let you realistically see and interact with the spacecraft and its trajectory—in 3D and across both time and space.
4. You’re on JunoCam!

Did you know that you don't have to work for NASA to contribute to the Juno mission? Amateur astronomers and space enthusiasts everywhere are invited to help with JunoCam, the mission's color camera. You can upload your own images of Jupiter, comment on others' images, and vote on which pictures JunoCam will take when it reaches the Jovian system.
5. Ride Along
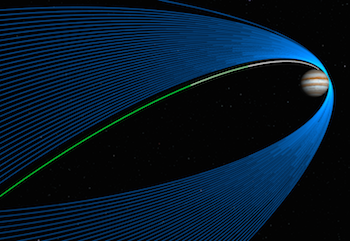
It's easy to follow events from the Juno mission as they unfold. Here are several ways to follow along online:
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Chart-Topping Space Images From 2019 You Won’t Want to Miss
From the first-ever image of a black hole, to astronaut Christina Koch breaking the record for the longest single spaceflight by a woman – 2019 was full of awe-inspiring events!
As we look forward to a new decade, we’ve taken ten of our top Instagram posts and put them here for your viewing pleasure. With eight out of ten being carousels, be sure to click on each title to navigate to the full post.
1. First-Ever Black Hole Image Makes History

In a historic feat by the Event horizon Telescope and National Science Foundation, an image of a black hole and its shadow was captured for the first time. At a whopping 3.4 million likes, this image takes home the gold as our most loved photo of 2019. Several of our missions were part of a large effort to observe this black hole using different wavelengths of light and collect data to understand its environment. Here’s a look at our Chandra X-Ray Observatory’s close-up of the core of the M87 galaxy with the imaged black hole at its center.
2. Hubble Celebrates 29 Years of Dazzling Discoveries


When you wish upon a star… Hubble captures it from afar ✨On April 18, 2019 our Hubble Space Telescope celebrated 29 years of dazzling discoveries, serving as a window to the wonders of worlds light-years away.
Hubble continues to observe the universe in near-ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light. Over the past 29 years, it has captured the farthest views ever taken of the evolving universe, found planet-forming disks around nearby stars and identified the first supermassive black hole in the heart of a neighboring galaxy. Want more? Enjoy the full 10 photo Instagram carousel here.
3. Stars and Stripes in Space for Flag Day


Patriotism was in the air June 14 for Flag Day, and coming in at number three in our most liked Instagram line up is a carousel of our stars and stripes in space! One of the most iconic images from the Apollo 11 missions is of Buzz Aldrin saluting the American flag on the surface of the Moon. But did you know that over the years, five more flags joined the one left by Apollo 11 – and that many other flags have flown onboard our spacecraft? Scroll through the full carousel for flag day here.
4. Spitzer Celebrates its Super Sweet 16!


Since 2003, our Spitzer Space Telescope has been lifting the veil on the wonders of the cosmos, from our own solar system to faraway galaxies, using infrared light! Thanks to Spitzer, we've confirm the presence of seven rocky, Earth-size planets, received weather maps of hot, gaseous exoplanets and discovered a hidden ring around Saturn. In honor of Spitzer's Sweet 16 in space, enjoy 16 jaw-dropping images from its mission here.
5. Earth as Seen Through Our Astronauts’ Eyes Show Perspective Changing Views

“That's here. That's home. That's us.” – Carl Sagan
Seeing Earth from space can alter an astronauts’ cosmic perspective, a mental shift known as the “Overview Effect.” First coined by space writer Frank White in 1987, the Overview Effect is described as a feeling of awe for our home planet and a sense of responsibility for taking care of it. See Earth from the vantage point of our astronauts in a carousel of perspective-changing views here.
6. Astronaut Christina Koch Breaks Record for Longest Single Spaceflight by Woman


Astronaut Christina Koch (@Astro_Christina) set a record Dec. 28, 2019 for the longest single spaceflight by a woman, eclipsing the former record of 288 days set by Peggy Whitson. Her long-duration mission is helping us learn how to keep astronauts healthy for deep space exploration to the Moon and Mars. Congrats to Christina on reaching new heights! Join in the celebration and view few photos she captured from her vantage point aboard the Space Station here.
7. Our Beautiful Planet – The Only Place We Know to Harbor Life – From Space


Earth is special. It’s the only place in the universe that we know contains life.
On July 7, 2019, two million people joined us in celebrating its beauty with a jaw dropping carousel of our home planet, as captured by crew members aboard the International Space Station. Bright blue oceans, glowing city lights and ice-capped mountain peaks come to life in a collection of breathtaking images, found here.
8. A Moon Even Sinatra Couldn’t Help But Sing About

Every 29 days our Moon turns over a new leaf, and on May, 18 we saw a very special one of its faces. Appearing opposite the Sun at 5:11 p.m. EDT, the world looked up to find a Blue Moon! Though the Moon didn’t actually look blue, the site of one is kind of rare. They occur on average about every two-and-a-half years when a season ends up having four full moons instead of three. Click through a carousel of high-definition lunar phases here.
9. The Majesty of Hubble Imagery ... From Your Backyard


On December 23, a new gallery of Hubble Space Telescope images highlighting celestial objects visible to amateur and professional astronomers alike was released. All of the objects are from a collection known as the Caldwell catalog, which includes 109 interesting objects visible in amateur-sized telescopes in both the northern and southern skies. Flip through the jaw-dropping carousel here, and learn more about how you can study the night sky with Hubble here.
10. The Moon Gets Sassy

Nobody:
The Moon: “Y'all on the way yet?” 👀
We're working on it, Moon. Under the Artemis program, we're sending the first woman and the next man to walk on your surface by 2024. Find out how we’re doing it here.

For more pictures like these, follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/nasa/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 dead-or-alive liked this · 3 years ago
dead-or-alive liked this · 3 years ago -
 luvmesumme liked this · 3 years ago
luvmesumme liked this · 3 years ago -
 noziroh liked this · 3 years ago
noziroh liked this · 3 years ago -
 riversmoke reblogged this · 3 years ago
riversmoke reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 riversmoke liked this · 3 years ago
riversmoke liked this · 3 years ago -
 preludejunkydebonairclassed reblogged this · 3 years ago
preludejunkydebonairclassed reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 rachelcatmeow reblogged this · 3 years ago
rachelcatmeow reblogged this · 3 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts