What Was Your First Thought When You First Saw Earth From Space? And What Realizations Did You Have?
What was your first thought when you first saw earth from space? And what realizations did you have?
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Discover NASA Technology in Your Life
Have you ever wondered how space exploration impacts you? “Spinoffs” are products and services developed from NASA technology or improved through NASA partnerships. These innovations—first created to help explore space and study Earth—are responsible for billions of dollars in both revenue and saved costs, tens of thousands of jobs created, and for changing the world around us.
Our NASA Home & City interactive web platform allows you to explore some of the spinoff technologies you can find in your everyday life, demonstrating the wider benefits of America’s investments in its space program.

Here are the seven most unexpected items you can find in your homes and cities which were “spun off” from technologies to enable the study and exploration of space.
1. Wireless Headsets
“That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” On July 20, 1969, millions were glued to their television sets when NASA astronaut Neil Armstrong offered these famous words via live broadcast, upon becoming the first man to ever step foot on the Moon. This historic transmission was delivered from Armstrong’s headset to the headsets of Mission Control personnel at NASA, and then on to the world.
Improved by the technology that carried Neil Armstrong’s words, more compact and comfortable headsets were developed for airline pilots in the 1960s and '70s. Today those advancements continue to evolve in all forms of communications and telephone equipment. Mobile headsets provide greater efficiency and flexibility for everyone from professionals to video gamers.

2. Water Quality Monitoring
On the International Space Station very little goes to waste. This includes water, which is recovered from every possible source, cleaned and recycled.
Following our development of a simplified bacteria test for water quality on the space station, one engineer created a foundation to distribute test kits suitable for use in rural communities around the world. Water contamination is still a major problem in many places, and the test helps local communities and governments obtain and share water quality data using a smartphone app.
3. Skin Cream
We know that on Earth, gravity is a constant. For astronauts in orbit, however, it’s a different story—and according to a scientist at NASA's Johnson Space Center, studying what happens to bodies in microgravity “can lead to significant new discoveries in human biology for the benefit of humankind.”
As our researchers experimented with replicating microgravity conditions in the lab, they invented a bioreactor that could help simulate conditions that human cells experience in a space-like environment. This allowed them to perform tissue-growth experiments on the ground and in space, and eventually, to consider the question of how to protect human cells from the toxic effects of long-duration space missions.
Now, thanks to this NASA-patented bioreactor, one company uses agents from human cells that produce collagen to enrich its skin cream products. Lab tests have shown the rejuvenating cream to increase skin moisture content by 76 percent and reduce darkness and wrinkles by more than 50 percent.

4. Acoustic Guitars
From its start, NASA has innovated in all branches of aeronautics, which has led to numerous advances in helicopters, including ways to limit vibrations as they fly and advanced composites to build tougher, safer vehicles.
An industrious helicopter manufacturer that built up its expertise with NASA contracts later used the same special vibration analysis equipment to enhance the sound of acoustic guitars. The company also built the body out of a fiberglass composite used for rotor blades. The resulting instruments are stronger and less expensive to produce than those of traditional rosewood and produce a rich, full sound.

5. Tiny [Mobile] Homes
While the International Space Station is the largest spacecraft ever flown—it's about the size of a football field—living and working space for astronauts is still at a premium. NASA created a studio called the Habitability Design Center to experiment with the interior design of spacecraft to maximize usable space and make scientific research as efficient and effective as possible.
An architect who helped NASA design the interior of the International Space Station launched a company specializing in compact trailers for camping and exploration. Suitable for a full hookup campsite or going completely off-grid, the company's flagship trailer can accommodate two adults and two children for sleeping and can be customized with a range of features including a shower, refrigerator, toilet, and more. And it all fits into a unit light enough to be towed by a four-cylinder car.

6. Blue Light Blocking Ski Goggles
Skiers and snowboarders face extremely bright sunlight, especially when it's reflected off the white snow. That can make it hard to see, and not just because of glare. The blue in sunlight makes it more difficult to discern colors at the edge of the visible light spectrum, like reds. A NASA-designed filter used in snow goggles helps block up to 95 percent of blue light, making it easier for people on the slopes to see the terrain clearly.

7. Implants for the Hearing Impaired
Hearing aids, which make sound louder, can only do so much for those who were born or have become deaf. Cochlear implants work in a completely different way, converting sound into digital signals that can be processed by the brain. And the technology traces back in part to a NASA space shuttle engineer who used skills in electronics instrumentation and his own experiences with hearing loss to develop an early version of the life-changing device.

These are just a few examples of thousands of NASA Spinoff and dual-purpose technologies benefiting the world around us.
Trace space back to you and visit NASA Home and City today!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Stars, Sea, and Smoke from the ISS: Tournament Earth 2021
We started Tournament Earth with 32 photos taken by astronauts from the Interantional Space Station and now we are down to 8. All of the #1 seeds are gone. Two #8 seeds are dominating their groups. Who will win? Let's take a closer look at the competitors still in the game. Then remember to vote for your favorites. The champion will be announced on April 13, 2021.
Stars in Motion vs. Cleveland Volcano
This matchup pits smoke against stars, but both have interesting stories.

The International Space Station (ISS) is constantly in motion. For astronaut photographers on board, that motion has consequences. For one, it makes it challenging to take photos. The same motion makes it possible to shoot spectacular photos like the one above. The image is compiled from a series of photographs taken by astronaut Don Pettit while he was onboard the ISS in April 2012. This composite was made from more than 72 individual long-exposure photographs taken over several minutes as the ISS traveled over the Caribbean Sea, across South America, and over the South Atlantic Ocean.

Astronaut Jeff Williams was the first to witness activity at the Cleveland Volcano on May 3, 2006. The Cleveland Volcano is one of the most active in the Aleutian Islands, which extend west-southwest from the Alaska mainland. It is a stratovolcano composed of alternating layers of hardened lava, compacted volcanic ash, and volcanic rocks. The event proved to be short-lived; two hours later, the plume had completely detached from the volcano. The ash cloud height could have been as high as 6,000 meters (20,000 feet) above sea level.
Stargazing from the ISS vs. Cruising Past the Aurora Borealis
This is the most stellar matchup of the tournament, literally. Two beloved star pictures face off in what will be one of the most difficult choices of the tournament.

An astronaut took this broad, short-lens photograph of Earth’s night lights while looking out over the remote reaches of the central equatorial Pacific Ocean. The ISS was passing over the island nation of Kiribati at the time, about 2600 kilometers (1,600 miles) south of Hawaii. Scientists identified the pattern of stars in the photo as our Milky Way galaxy (looking toward its center). The dark patches are dense dust clouds in an inner spiral arm of our galaxy; such clouds can block our view of stars toward the center. The curvature of the Earth crosses the center of the image and is illuminated by a variety of airglow layers in orange, green, and red.

Commonly known as the northern lights, these colorful ribbons of light appear to dance in the sky over the planet’s high latitudes, attracting sky chasers and photographers. Astronaut Randy “Komrade” Bresnik shot this photograph on September 15, 2017, as the space station passed over Ontario, Canada. Curtains of green—the most familiar color of auroras—dominate the light show, with hints of purple and red.
Rolling Through the Appalachians vs. Castellanus Cloud Tower

The Susquehanna River cuts through the folds of the Valley-and-Ridge province of the Appalachian Mountains in this photograph taken from the International Space Station by astronaut Christina Koch. The Valley-and-Ridge province is a section of the larger Appalachian Mountain Belt between the Appalachian Plateau and the Blue Ridge physiographic provinces. The northeast-southwest trending ridges are composed of Early Paleozoic sedimentary rocks. The valleys between them were made of softer rocks (limestone and shales) that were more susceptible to erosion; they are now occupied by farms.

An astronaut aboard the International Space Station took this photograph of a massive vertical cloud formation—known to meteorologists as cumulus castellanus—above Andros Island. The cloud name castellanus comes from the similarity to the crenellated towers or turrets of medieval castles. These clouds develop due to strong vertical air movement typically associated with thunderstorms.
Lake Van, Turkey vs. Typhoon Maysak from the Space Station

While orbiting on the International Space Station, astronaut Kate Rubins shot this photograph of part of Lake Van in Turkey, the largest soda or alkaline lake on Earth. Generally, soda lakes are distinguished by high concentrations of carbonate species. Lake Van is an endorheic lake—it has no outlet, so its water disappears by evaporation—with a pH of 10 and high salinity levels.

This photograph of super typhoon Maysak was taken by European Space Agency astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti as the International Space Station passed near the storm on March 31, 2015. The category 4 typhoon was headed for a possible landfall in the Philippines by the end of the week. It was unusual for the western Pacific to see such a strong storm so early in the year.
See all of the images and vote HERE. Follow @NASAEarth on social media for updates.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

“We saw to the edge of all there is—
So brutal and alive it seemed to comprehend us back.”
-Tracy K. Smith, US Poet Laureate
Some pictures are worth a thousand words and some a thousand thoughts. On Jan. 31, astronaut Christina Koch shared this emotional view and quote from the International Space Station. Enjoy.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up - January 2018
What’s Up For January?
Quadrantid meteors, a West Coast-favoring total lunar eclipse and time to start watching Mars!

This month the new year's first meteor shower fizzles, Mars meets Jupiter in the morning sky and the U.S. will enjoy a total lunar eclipse!

Most meteor showers radiate from recognizable constellations. Like the Leonids, Geminids and Orionids.

But the Quadrantids are meteors that appear to radiate from the location of the former Quadrans Muralis constellation, an area that's now part of the constellation Bootes.

The Quadrantids' peak lasts for just a few hours, and sadly, this year their timing coincides with a very bright, nearly full moon that will wash out most of the meteors.

You can look in any direction to see all the meteor showers. When you see one of these meteors, hold a shoestring along the path it followed. The shoestring will lead you back to the constellation containing the meteor’s origin.

On the morning of January 6th, look in the south-southeast sky 45 minutes before sunrise to see Jupiter and fainter Mars almost as close as last month's Jupiter and Venus close pairing.

Mars is only one-sixth the apparent diameter of Jupiter, but the two offer a great binocular and telescopic view with a pretty color contrast. They remain in each other's neighborhood from January 5th through the 8th.

Finally, to end the month, a great total lunar eclipse favors the western U.S., Alaska, and Hawaii and British Columbia on January 31st. Australia and the Pacific Ocean are well placed to see a major portion of the eclipse--if not all of it.

Watch the full What’s Up for January Video:
There are so many sights to see in the sky. To stay informed, subscribe to our What’s Up video series on Facebook. Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Are We Alone? How NASA Is Trying to Answer This Question.
One of the greatest mysteries that life on Earth holds is, “Are we alone?”

At NASA, we are working hard to answer this question. We’re scouring the universe, hunting down planets that could potentially support life. Thanks to ground-based and space-based telescopes, including Kepler and TESS, we’ve found more than 4,000 planets outside our solar system, which are called exoplanets. Our search for new planets is ongoing — but we’re also trying to identify which of the 4,000 already discovered could be habitable.

Unfortunately, we can’t see any of these planets up close. The closest exoplanet to our solar system orbits the closest star to Earth, Proxima Centauri, which is just over 4 light years away. With today’s technology, it would take a spacecraft 75,000 years to reach this planet, known as Proxima Centauri b.
How do we investigate a planet that we can’t see in detail and can’t get to? How do we figure out if it could support life?
This is where computer models come into play. First we take the information that we DO know about a far-off planet: its size, mass and distance from its star. Scientists can infer these things by watching the light from a star dip as a planet crosses in front of it, or by measuring the gravitational tugging on a star as a planet circles it.
We put these scant physical details into equations that comprise up to a million lines of computer code. The code instructs our Discover supercomputer to use our rules of nature to simulate global climate systems. Discover is made of thousands of computers packed in racks the size of vending machines that hum in a deafening chorus of data crunching. Day and night, they spit out 7 quadrillion calculations per second — and from those calculations, we paint a picture of an alien world.

While modeling work can’t tell us if any exoplanet is habitable or not, it can tell us whether a planet is in the range of candidates to follow up with more intensive observations.

One major goal of simulating climates is to identify the most promising planets to turn to with future technology, like the James Webb Space Telescope, so that scientists can use limited and expensive telescope time most efficiently.

Additionally, these simulations are helping scientists create a catalog of potential chemical signatures that they might detect in the atmospheres of distant worlds. Having such a database to draw from will help them quickly determine the type of planet they’re looking at and decide whether to keep observing or turn their telescopes elsewhere.
Learn more about exoplanet exploration, here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How does flying feel?
What’s Up for April 2016?

Jupiter, Mars, the Lyrid meteor shower and 2016’s best views of Mercury are all visible in the sky this month.

Jupiter, where our Juno mission will begin orbiting on July 4, continues to shine almost as brightly this month as last. And eagle-eyed telescope viewers will see a transit, a shadow transit, an occultation and an eclipse of Jupiter’s moons- all in one night: April 6-7.

Io transits first, crossing the planet beginning at 9:52 p.m. EDT. It’s shadow can be seen less than an hour later.

Next Jupiter occults, or eclipses, Europa as Europa slips behind the giant planet at 10:48 p.m. EDT. At 3 a.m. Europa reappears from its eclipse, dramatically leaving the shadow of Jupiter.

Ganymede transits the planet beginning at 1:01 EDT April 7.
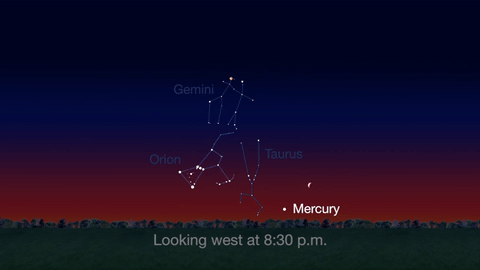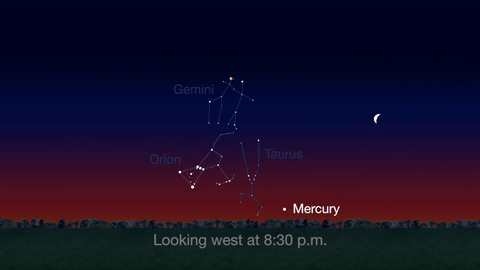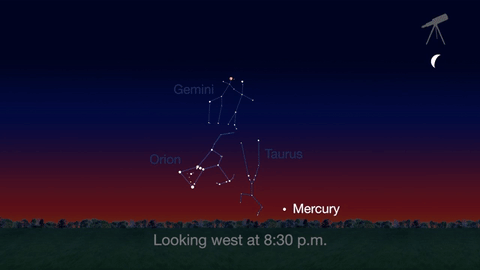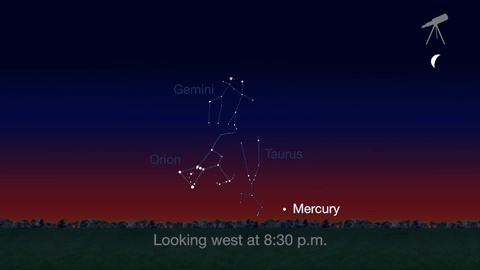
Check out the other planets in April, too! Mercury is always a challenging object to view, but this month you can spot it after sunset about 10 degrees above the horizon. Through a telescope you can see its phase. It will appear like a tiny crescent moon, with about 1/3 of its disk illuminated.

Mars is finally visible before midnight this month. It rises in the southeast at about 10 p.m. by the end of April. The best observing of Mars will be when it is highest in the sky. This means a few hours before dawn. Its brightness and apparent size increase dramatically this month. By month’s end, Mars appears nearly twice as bright as at the beginning of the month.

About mid-month you’ll see Mars near its rival in the sky: the similar-colored red supergiant star Antares. The name “Antares” means “equal to or rival of Mars”.
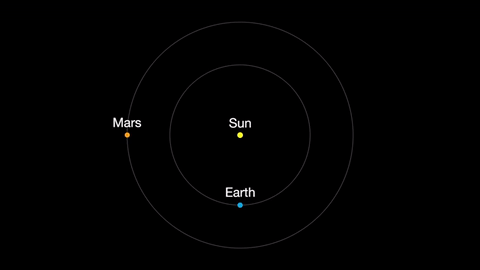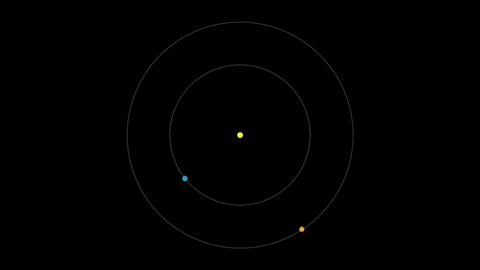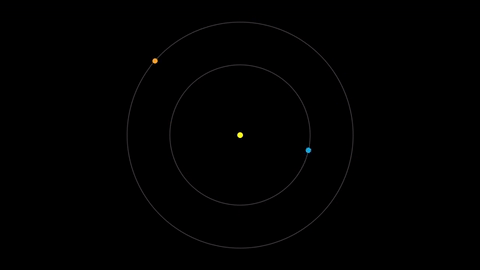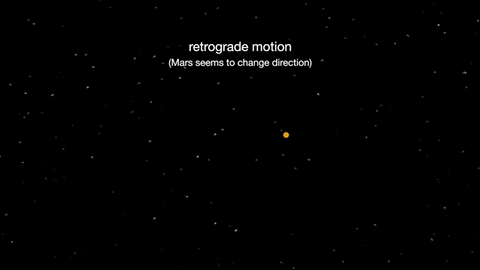
Earth moves almost twice as fast as Mars does, so it often passes Mars in their race around the sun. This causes “retrograde motion”: an illusion we see from our viewpoint on Earth.
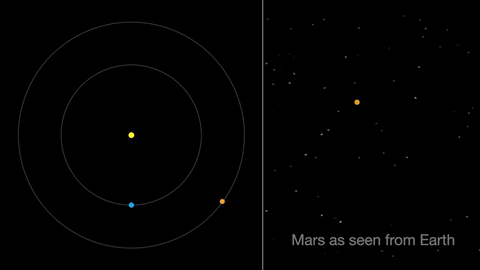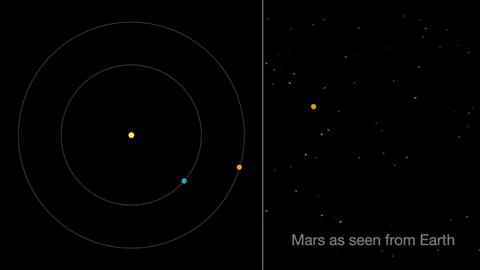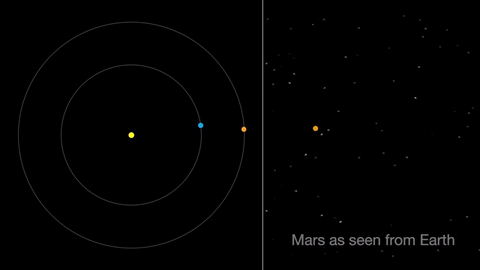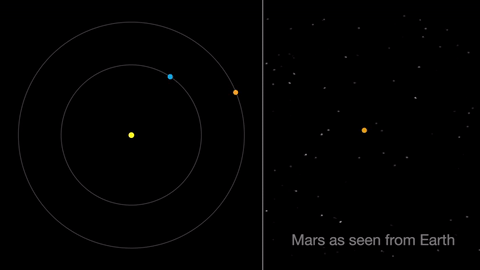
Retrograde motion happens as Earth catches up to Mars, causing Mars to appear slow to slow its eastward motion against the stars. After a few days, when Earth has overtaken Mars, the Red Planet seems to move westward. Eventually, Earth moves far enough around its orbit that Mars appears to be moving eastward again.
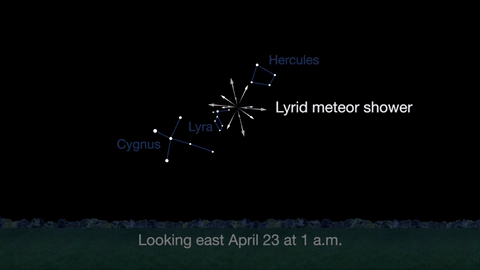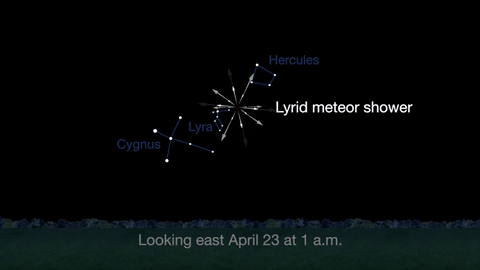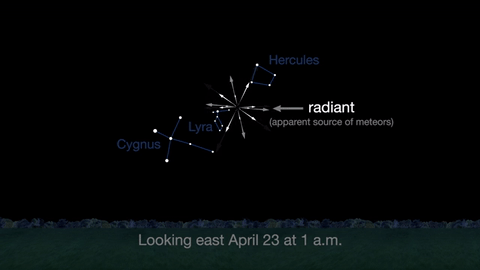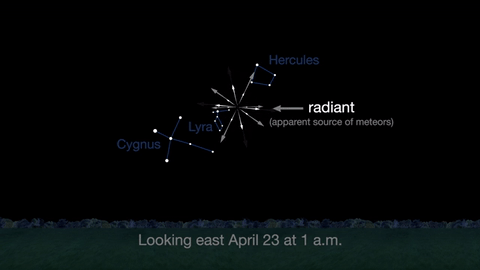
April features one meteor shower, the Lyrids. This year the Lyrids are marred by the full moon. The best time to view will be just before dawn on April 23, when the constellation Lyra is overhead and the moon will be near to setting.
With all of these great things to spot in the sky this month, be sure to get outside and look up!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How did your perspective on Earth & humanity change from space?

And that’s a wrap!! Thank you for all the wonderful questions in this Tumblr Answer Time, and we hope you learned a little something about what it takes to launch humans to space.
You can follow all of our latest Space Station news on Twitter, Instagram and Facebook.
Exercising in Space
Are you hoping to get to the gym more often in 2016? While you work out on Earth, here are a few ways that astronauts stay fit on the International Space Station.

Exercise is an important part of the daily routine for astronauts aboard the International Space Station to prevent bone and muscle loss, and to maintain cardiovascular health. On average, astronauts exercise two hours per day. The equipment they use in space is different than what we use on Earth.
Lifting 200 pounds on Earth may be a lot of work, but in microgravity a 200 pound dumbbell would not weigh anything. Therefore, free weights do not serve as a good strength training tool for the astronauts in space. That means exercise equipment needs to be specifically designed for use in space so astronauts will receive the workout needed.
What Equipment Do They Use in Space?
Advanced Resistive Exercise Device (ARED)

The ARED hardware uses adjustable resistance piston-driven vacuum cylinders along with a flywheel system to simulate free-weight exercises in normal gravity. It’s primary goal is to maintain muscle strength and bone mass in astronauts during long periods in space.
Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS)

CEVIS is very similar to a mechanical bicycle. It’s bolted to the floor, and astronauts snap their shoes on to the pedals. A seat belt can be used to hold them in position, and they can change the resistance for varying levels of difficulty.
Russian Treadmill (BD-2)

BD-2 is the treadmill that is found in the Russian segment of the space station. It allows crew members to walk and run with a speed from 2.4 to 20 km/hr.
Combined Operational Load Bearing External Resistance Treadmill (COLBERT)

COLBERT is the second generation U.S. treadmill on the space station. It features data collection devices that will allow scientists and doctors to evaluate how effective the exercise is in reducing the amount of bone and muscle density loss due to microgravity exposure. It allows crew members to walk and run with a speed from 4.8 to 20 km/hr.
Why is it called COLBERT?

The treadmill’s name was selected after comedian Stephen Colbert took interest in our online naming poll for Node 3 of space station. He urged his viewers to submit the name “Colbert.” Although we ended up choosing the suggested name “Tranquillity” for the node, we designated its new treadmill “COLBERT” in honor of the name that received the most entries.
VELO Ergomoeter Bike (VB-3)

VB-3 is used for aerobic training, medical tests and pedaling regimes. It is located in the Russian segment of the space station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 watch reblogged this · 1 year ago
watch reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 asadwasteofcarbon reblogged this · 3 years ago
asadwasteofcarbon reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ohhobaby liked this · 4 years ago
ohhobaby liked this · 4 years ago -
 unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago
unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago -
 call-me-schmidt reblogged this · 5 years ago
call-me-schmidt reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 santoshkumardwivedi liked this · 5 years ago
santoshkumardwivedi liked this · 5 years ago -
 adt-space reblogged this · 5 years ago
adt-space reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 smol-bean-dragon-hoard liked this · 5 years ago
smol-bean-dragon-hoard liked this · 5 years ago -
 saturnspaceshark liked this · 5 years ago
saturnspaceshark liked this · 5 years ago -
 chloesmom2011 liked this · 5 years ago
chloesmom2011 liked this · 5 years ago -
 justanoldfashiontumblog liked this · 5 years ago
justanoldfashiontumblog liked this · 5 years ago -
 nasatranscription reblogged this · 5 years ago
nasatranscription reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 liliumnnavona liked this · 5 years ago
liliumnnavona liked this · 5 years ago -
 iinthepalemoonlight liked this · 5 years ago
iinthepalemoonlight liked this · 5 years ago -
 immano liked this · 5 years ago
immano liked this · 5 years ago -
 diabaliful reblogged this · 5 years ago
diabaliful reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 androidsghost liked this · 5 years ago
androidsghost liked this · 5 years ago -
 mysticmachineman-blog liked this · 5 years ago
mysticmachineman-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 whitecatnatalie liked this · 5 years ago
whitecatnatalie liked this · 5 years ago -
 walkingmassofdisarray reblogged this · 5 years ago
walkingmassofdisarray reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 iconiclavinia liked this · 5 years ago
iconiclavinia liked this · 5 years ago -
 natscapegalore liked this · 5 years ago
natscapegalore liked this · 5 years ago -
 tgyberg liked this · 5 years ago
tgyberg liked this · 5 years ago -
 littlemissrand liked this · 5 years ago
littlemissrand liked this · 5 years ago -
 dredgen-bazinga liked this · 5 years ago
dredgen-bazinga liked this · 5 years ago -
 lemonbluesky reblogged this · 5 years ago
lemonbluesky reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 death-titan liked this · 5 years ago
death-titan liked this · 5 years ago -
 vulcanperihelion liked this · 5 years ago
vulcanperihelion liked this · 5 years ago -
 cursed-nurse reblogged this · 5 years ago
cursed-nurse reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 panesdulces reblogged this · 5 years ago
panesdulces reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 witchpuddin liked this · 5 years ago
witchpuddin liked this · 5 years ago -
 ohhobaby reblogged this · 5 years ago
ohhobaby reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 womanofmassdestruction liked this · 5 years ago
womanofmassdestruction liked this · 5 years ago -
 positivityheart reblogged this · 5 years ago
positivityheart reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lila-flowerpetal897 reblogged this · 5 years ago
lila-flowerpetal897 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lila-flowerpetal897 reblogged this · 5 years ago
lila-flowerpetal897 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lila-flowerpetal897 liked this · 5 years ago
lila-flowerpetal897 liked this · 5 years ago -
 yungsassss liked this · 5 years ago
yungsassss liked this · 5 years ago -
 latenightdyke liked this · 5 years ago
latenightdyke liked this · 5 years ago -
 luciferspoison liked this · 5 years ago
luciferspoison liked this · 5 years ago -
 chocolateismynemesis reblogged this · 5 years ago
chocolateismynemesis reblogged this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts