How Has Being In Space Changed Your Perspective Of Life On Earth?
How has being in space changed your perspective of life on Earth?
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Meet the Four Artemis Astronauts Who Will Fly Around the Moon

Today, we revealed the four astronauts who will fly around the Moon during the Artemis II mission, scheduled to launch in 2024. Get to know them:
Christina Koch

Meet the first member of our Artemis II crew: mission specialist Christina Koch. Koch visited the International Space Station in 2019, where she participated in the first all-woman spacewalk with Jessica Meir. She began her NASA career as an electrical engineer at Goddard Space Flight Center.
Jeremy Hansen

Representing the Canadian Space Agency is Jeremy Hansen from London, Ontario. Col. Hansen was a fighter pilot with Canadian Armed Forces before joining the Canadian Space Agency, and currently works with NASA on astronaut training and mission operations. This will be Col. Hansen’s first mission in space.
Victor Glover

Victor Glover is our Artemis II pilot. Glover is part of our 2013 class of NASA astronauts and was the pilot for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission. He’s logged 3,000 flight hours in more than 40 different aircraft.
Reid Wiseman

...and rounding out our Artemis II crew: mission commander Reid Wiseman. Wiseman lived and worked aboard the International Space Station as a flight engineer in 2014. He also commanded the undersea research mission NEEMO21, and most recently served as Chief of the NASA astronauts.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Earth is the ultimate ocean planet (that we know of), but it turns out that our solar system has water in some surprising places, with five ocean-bearing moons and potentially several more worlds with their own oceans.

1. The Original "Alien Ocean"
Our Galileo spacecraft (1989-2003) detected the first evidence of an ocean beyond Earth under the ice of Jupiter's icy moon Europa.

2. Lost Oceans
There are signs that Mars and Venus once had oceans, but something catastrophic may have wiped them out. Earth's natural force field -- our magnetosphere -- acts like shield against the erosive force of the solar wind.

3. Earth, the Original Ocean World
The search for life beyond Earth relies, in large part, on understanding our home planet. Among the newest Earth ocean explorers us the Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS--a constellation of microsatellites that will make detailed measurements of wind speeds over Earth's oceans to help understand hurricanes. The spacecraft have moved into their science operations phase.

4. Sister Ships
It's fitting the first mission to explore an alien ocean is named in honor of fast-sailing clipper ships of old. Our Europa Clipper spacecraft will seek signs of habitability on Jupiter's moon Europa.

5. Game Changer
Scientists expected Saturn's moon Enceladus to be a tiny, solid chunk of ice and rock. But, not long after arriving at Saturn, our Cassini spacecraft made a series of incremental discoveries, eventually confirming that a global subsurface ocean is venting into space, with signs of hydrothermal activity.

6. Why Ocean Worlds Matter
"The question of whether or not life exists beyond Earth, the question of whether or not biology works beyond our home planet, is one of humanity's oldest and yet unanswered questions. And for the first time in the history of humanity, we have the tools and technology and capability to potentially answer this question. And, we know where to go to find it. Jupiter's ocean world Europa." - Kevin Hand, NASA Astrobiologist

7. More Alien Oceans
Scientists think Jupiter's giant moons Ganymede and Callisto also hide oceans beneath their surfaces. Elsewhere in the solar system, scientists hope to look for hidden oceans on far-flung worlds from Ceres in the main asteroid belt to Pluto in the Kuiper Belt.

8. Cold Faithful(s)?
Thanks to our Cassini orbiter we know the tiny moon Enceladus is venting its ocean into space in a towering, beautiful plume. The Hubble Space Telescope also has seen tantalizing hints of plumes on Jupiter's moon Europa. Plumes are useful because they provide samples of ocean chemistry for oceans that could be miles below the surface and difficult for spacecraft to reach. It's like they're giving out free samples!

9. Titanic Seas and Ocean
Saturn's moon Titan not only has liquid hydrocarbon seas on its surface. It also shows signs of a global, subsurface saltwater ocean--making the giant moon a place to possibly look for life as we know it and life as we don't know it ... yet.

10. Oceans Beyond
Several of the thousands of planets discovered beyond our solar system orbit their stars in zones where liquid surface water is possible--including Proxima-b, a rocky planet orbiting the star nearest to our own.
BONUS: Adopt a bit of YOUR Ocean World
We invite everyone to help us celebrate Earth Day 2017 by virtually adopting a piece of Earth as seen from space. Your personalized adoption certificate will feature data from our Earth-observing satellites for a randomly assigned location, much of it ocean (it is 70 percent of the Earth's surface after all!). Print it and share it, then explore other locations with our interactive map and get even more Earth science data from NASA's Worldview website.
Visit go.nasa.gov/adopt to adopt your piece of the planet today!
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
NASA: 2016 Look Ahead

The work we do, and will continue in 2016, helps the United States maintain its world leadership in space exploration and scientific discovery. Here’s an overview of what we have planned for the coming year:
Our Journey to Mars

We’re developing the capabilities needed to send humans to an asteroid by 2025 and Mars in the 2030s. Mars is a rich destination for scientific discovery and robotic and human exploration as we expand our presence into the solar system. Its formation and evolution are comparable to Earth, helping us learn more about our own planet’s history and future.
Work and Research on the International Space Station

The International Space Station is a unique place – a convergence of science, technology and human innovation that demonstrates new technologies and makes research breakthroughs not possible on Earth. In 2016, we will continue our groundbreaking research on the orbiting laboratory.
Returning Human Spaceflight Launches to American Soil

Our Commercial Crew Program is working with the American aerospace industry as companies develop and operate a new generation of spacecraft and launch systems capable of carrying crews to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station. Commercial transportation to and from the station will provide expanded utility, additional research time and broader opportunities of discovery on the orbiting laboratory.
Studying Our Earth Right Now

We use the vantage point of space to increase our understanding of our home planet, improve lives and safeguard our future. In 2016, we will continue to monitor Earth’s vital signs from land, air and space with a fleet of satellites and ambitious airborne and ground-based observation campaigns.
Fostering Groundbreaking Technology Development

Sustained investments in NASA technology advances our space exploration, science and aeronautics capabilities. Our technology development also supports the nation's innovation economy by creating solutions that generate tangible benefits for life on earth. In 2016, we will continue to invest in the future of innovation.
Breakthroughs in Aeronautics

Thanks to our advancements in aeronautics, today’s aviation industry is better equipped than ever to safely and efficiently transport all those passengers to their destinations. In fact, every U.S. aircraft flying today and every U.S. air traffic control tower uses NASA-developed technology in some way. In 2016, we will continue making these breakthroughs in aeronautics.
Discoveries in Our Solar System and Beyond

This year we will continue exploring our solar system and beyond to unravel the mysteries of our universe. We are looking to answer key questions about our home planet, neighboring planets in our solar system and more!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
10 Ways the 2010s Pushed Communication and Navigation into the Future!
We transmit vast amounts of data from space, letting all of our satellites “phone home.” Imagery from far off regions of our solar system, beautiful visions of other galaxies and insights into planet Earth flow through our communications networks.
Our Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) program is dedicated to making sure we precisely track, command and control our spacecraft. All the while, they develop bold new technologies and capabilities for Artemis – our sustainable lunar exploration program that will place the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
As we prepare to say goodbye to the 2010s, let’s take a look at 10 of the biggest milestones in space communications and navigation of the past decade.
1. Continuous global communications? TDRS has you covered.

From 2013 to 2017, we launched three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites, or TDRS for short. These new satellites replenished a fleet that has been around since the early 1980s, allowing us to provide continuous global communications coverage into the next decade. Missions like the International Space Station depend on TDRS for 24/7 coverage, allowing our astronauts to call home day or night.
2. Binge watching on the Moon? Laser communications will make it possible.

Imagine living at the Moon. With the Artemis program, we’re making it happen! However, we can’t live there without decent internet, right? In 2013, we conducted the Lunar Laser Communication Demonstration (LLCD). This was the first high-speed laser communications demonstration from the Moon, transmitting data at a whopping 622 megabits per second, which is comparable to many high-speed fiber-optic connections enjoyed at home on Earth! Our LLCD sent back high-definition video with no buffering.
3. Record Breaking GPS navigation, at your service.
Space communications is just one piece of the SCaN puzzle. We do navigation too! We even break records for it. In 2016, our Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission broke the world record for highest altitude GPS fix at 43,500 miles above Earth. In 2017, they broke it again at 93,200 miles. Earlier this year, they broke it a third time at 116,200 miles from Earth — about halfway to the Moon!
Thanks to MMS, our navigation engineers believe that GPS and similar navigation constellations could play a significant role in the navigation architecture of our planned Gateway spaceship in lunar orbit!
4. Crashing planes as part of the game – of research!

Then there was that one summer we crashed three planes in the name of research! In 2015, our Search and Rescue office tested crash scenarios at Langley Research Center’s Landing and Impact Research Facility to improve the reliability of emergency beacons installed in planes. After the study, we made recommendations on how pilots should install these life-saving beacons, increasing their chances of survival in the event of a crash. The Federal Aviation Administration adopted these recommendations this year!
5. The Deep Space Atomic Clock takes flight.

Missions venturing into deep space want the autonomy to make decisions without waiting for a commands from Earth. That’s why we launched the Deep Space Atomic Clock this past year. This itty-bitty technology demonstration is a small, ultra-stable timekeeping device that could enable autonomous navigation!
6. 50 never looked so good – for our Deep Space Network.

In 2013, our Deep Space Network celebrated its 50th birthday! This is the network that transmitted Neil Armstrong’s famous words, "That's one small step for (a) man, one giant leap for mankind." Some of its more recent accomplishments? Gathering the last bits of data before Cassini dove into Saturn’s upper atmosphere, pulling down the “heart” of Pluto and talking to the Voyager probes as they journeyed into interstellar space!
7. SCaN Testbed becomes an official Hall of Famer.

In 2012, we installed the SCaN Testbed, which looks like a blue box in the above picture, on the space station! We built the testbed out of Software Defined Radios, which can change their functionality and employ artificial intelligence. These radios will help us adapt to the increasingly crowded communications landscape and improve the efficiency of radio technology. The Testbed was so ground-breaking that it was inducted into the Space Technology Hall of Fame in 2019.
8. Moon mission communications system, secured!

Just a few weeks ago, we held a ribbon-cutting for the Near Earth Network’s Launch Communications Segment, which will support Artemis missions as they rocket toward the Moon! During initial, dynamic phases of launch, the segment’s three stations will provide communications between astronauts and mission controllers, giving them the data necessary to ensure crew safety.
9. Deep Space Station antenna introduces “beam waveguide” technology.

On October 1, 2014, in Canberra, Australia, the Deep Space Network’s Deep Space Station 35 (DSS-35) antenna went operational. It was the first of a number of new antennas built to support the growing number of deep space missions! The antenna is different from other antennas that were built before it. Older antennas had a lot of their equipment stored high up on the antenna above the dish. DSS-35 uses “beam waveguide” technology that stores that equipment underground. This makes the weight sitting on the dish much lighter, cuts down on interference and makes the antenna much easier to operate and maintain.
10. Hello, Alaska!

Last — but certainly not least — we expanded our presence in the 49th state, Alaska! While this picture might look like antennas rising from the forests of Endor, the one in the foreground is actually an antenna we installed in 2014 in partnership with the University of Alaska Fairbanks. Because of its proximity to the polar north, this 11-meter beauty is uniquely situated to pull down valuable Earth science data from our polar-orbiting spacecraft, contributing to scientists’ understanding of our changing planet!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
5 Signs You Might Be Ready to Apply to be an Astronaut
Did you hear? Astronaut applications are open! Here are a few signs that might mean you’re ready to apply:
1. You Don’t Mind Having Roommates

When you’re an astronaut, you have to work and live with your crew mates for extended periods of time. It’s important to the mission and your safety that everyone can collaborate and work together.
2. You LOVE Space

If the Milky Way, planets and space travel doesn’t excite you then this might not be the perfect job for you. But if you love galaxies, space station research and deep space exploration, then maybe you should take a look at our application.
3. Adventure Doesn’t Scare You

Being an astronaut means that you get to take part in adventures that most people will never experience. Imagine: sitting on the launch pad in the Orion spacecraft, atop a rocket that’s getting ready to launch. You’ll travel farther into space than any other humans have been and help push the boundaries of technology in the proving ground of deep space lunar orbits, leading the way for future missions to Mars.
4. You Want to be on the Cutting Edge of Science

Not only do astronauts get to travel to space, but they also get to conduct really cool research in microgravity. Did you know that right now they’re growing Zinnia flowers on the International Space Station? This research could help with our future deep space exploration and could teach us a few things about growing plants on Earth. Learn more about all the awesome research on the space station HERE.
5. You’re Not Afraid of Heights

One of the coolest things about being an astronaut, is that you get to go to SPACE! At the very least, you’ll travel to the International Space Station, which is 250 miles above Earth. Or, you could be one of the first astronauts to travel to a distant asteroid or even Mars!
Interested in applying to become an astronaut? You’re in luck, applications open Dec. 14! Learn about some common myths about becoming an astronaut HERE.
Apply to be one of our astronauts HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
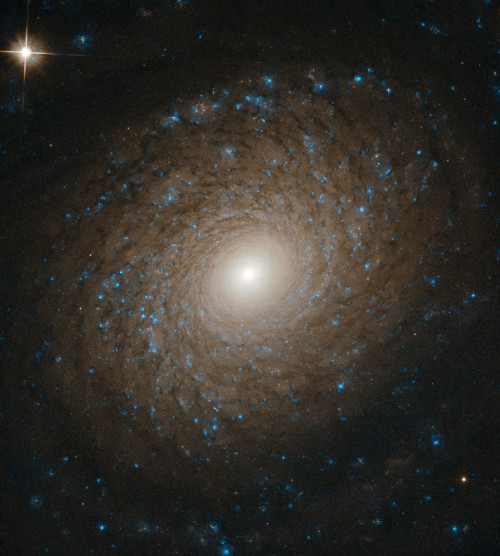

Flawless. Gorgeous. Stellar.
You probably think this post is about you. Well, it could be.
In this image taken by our Hubble Space Telescope, we see a spiral galaxy with arms that widen as they whirl outward from its bright core, slowly fading into the emptiness of space. Click here to learn more about this beautiful galaxy that resides 70 million light-years away.
Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, L. Ho Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.




Ariana Grande got some space at N-A-S-A. Get yours too.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
The 2021 Perseid Meteor Shower Is Here!

Image Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
The Perseids are at their peak this week!
The Perseid meteor shower, one of the biggest meteor showers of the year, will be at its brightest early in the morning on Thursday, August 12, 2021 and Friday, August 13, 2021. Read on for some tips on how to watch the night sky this week – and to find out: what exactly are the Perseids, anyway?

Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Your best chance to spot the Perseids will be between 2 AM and dawn (local time) the morning of August 12 or 13. Find a dark spot, avoid bright lights (yes, that includes your phone) and get acclimated to the night sky.
Your eyes should be at peak viewing capacity after about 30 minutes; with a clear, dark sky, you could see more than 40 Perseids an hour! If you’re not an early bird, you can try and take a look soon after sunset (around 9 PM) on the 12th, though you may not see as many Perseids then.

Credit: NASA/MEO
If it’s too cloudy, or too bright, to go skywatching where you are, just stay indoors and watch the Perseids online!
Our Meteor Watch program will be livestreaming the Perseids from Huntsville, Alabama on Facebook (weather permitting), starting around 11 p.m. EDT on August 11 and continuing through sunrise.
So… why are they called the Perseids?
Because all of a meteor shower’s meteors have similar orbits, they appear to come from the same place in the sky – a point called the radiant.

The radiant for the Perseids, as you might guess from the name, is in the constellation Perseus, found near Aries and Taurus in the night sky.
But they’re not actually coming from Perseus, right?

Credit: NASA/Joel Kowsky
Right! The Perseids are actually fragments of the comet Swift-Tuttle, which orbits within our solar system.
If you want to learn more about the Perseids, visit our Watch the Skies blog or check out our monthly “What’s Up” video series. Happy viewing!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Solar System: Top 5 Things to Know This Week
Here are five things you need to know about our amazing solar system this week:
1. Perpetual Pluto-palooza

The New Horizons spacecraft continues its ongoing download of data and images from the July 14 flyby of the Pluto system. In the latest weekly release, the new images don’t disappoint, showing fine details in an exotic landscape. The New Horizons team has also described a wide range of findings about the dwarf planet’s system in its first science paper. Learn more HERE.
2. Encounter at Enceladus

The Cassini spacecraft has returned the closest images ever showing the north polar region of Saturn’s intriguing ice moon Enceladus. Scientists expected the area to be heavily cratered, but the new high-resolution Cassini images also show a landscape of stark contrasts, crisscrossed by a spidery network of gossamer-thin cracks that slice through the craters. The robotic spacecraft buzzed by the moon during the first of what will be three close encounters this year -- the last of the long mission. Next up: on Oct. 28 Cassini will deep dive right through Enceladus’ famous ice geyser plume! Learn more HERE.
3. We’re Giving You the Whole World, Every Day
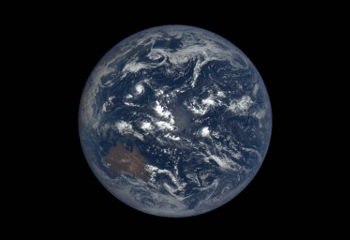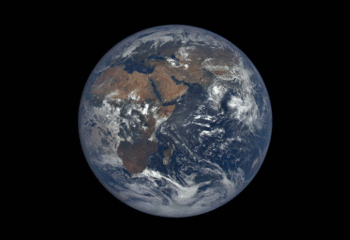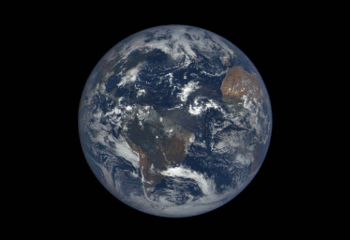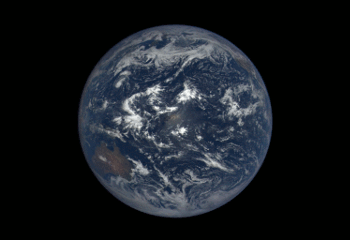
We have worked with NOAA to launch a new website that shows the full, sunlit side of the Earth on a daily basis. The images come from our camera a million miles away aboard the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR). Each daily sequence of images shows the Earth as it rotates, revealing the entire planet over the course of a day. Take a look HERE.
4. Going Big at Jupiter

We have large, new maps of Jupiter, thanks to data from the Wide Field Camera 3 on our Hubble Space Telescope. The big images provide a detailed look at how the giant planet’s features change over time. In fact, the maps are just the first in a planned series of yearly portraits of the solar system’s four outer planets. The views come as we prepare for the Juno mission to arrive at Jupiter in little less than a year.
5. Catch a Falling Star

Meteors aren’t really falling stars, just dust and rock from deep space meeting a fiery end in Earth’s atmosphere -- but they’re a sight to behold if you can catch a glimpse. The Orionid meteors appear every year around this time, when Earth travels through an area of space littered with debris from Halley’s Comet. This year the peak will occur on the night of Wednesday, Oct. 21, into the morning of Thursday, Oct. 22. Find out how to watch HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How long did it take to build the rover??
-
 watch reblogged this · 1 year ago
watch reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 thosblog liked this · 3 years ago
thosblog liked this · 3 years ago -
 panther0302 reblogged this · 3 years ago
panther0302 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 panther0302 liked this · 3 years ago
panther0302 liked this · 3 years ago -
 sagitariane liked this · 5 years ago
sagitariane liked this · 5 years ago -
 3120-7-2 liked this · 5 years ago
3120-7-2 liked this · 5 years ago -
 just-peachy-posts reblogged this · 5 years ago
just-peachy-posts reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 just-peachy-posts liked this · 5 years ago
just-peachy-posts liked this · 5 years ago -
 aelinth reblogged this · 5 years ago
aelinth reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 humminbird reblogged this · 5 years ago
humminbird reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 autisticassassinbird liked this · 5 years ago
autisticassassinbird liked this · 5 years ago -
 pedassinho liked this · 5 years ago
pedassinho liked this · 5 years ago -
 soycrisp liked this · 5 years ago
soycrisp liked this · 5 years ago -
 shailendra65631 reblogged this · 5 years ago
shailendra65631 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 shailendra65631 liked this · 5 years ago
shailendra65631 liked this · 5 years ago -
 habitina liked this · 5 years ago
habitina liked this · 5 years ago -
 cherryobvious liked this · 5 years ago
cherryobvious liked this · 5 years ago -
 endless-nameless-2 reblogged this · 5 years ago
endless-nameless-2 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 readinginzerogravity liked this · 5 years ago
readinginzerogravity liked this · 5 years ago -
 adt-space reblogged this · 5 years ago
adt-space reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 smol-bean-dragon-hoard liked this · 5 years ago
smol-bean-dragon-hoard liked this · 5 years ago -
 solar-cycle liked this · 5 years ago
solar-cycle liked this · 5 years ago -
 spaciegracie07 liked this · 5 years ago
spaciegracie07 liked this · 5 years ago -
 kayk0la liked this · 5 years ago
kayk0la liked this · 5 years ago -
 colibrona reblogged this · 5 years ago
colibrona reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lougiordanoposts liked this · 5 years ago
lougiordanoposts liked this · 5 years ago -
 cityvillagewitch195 liked this · 5 years ago
cityvillagewitch195 liked this · 5 years ago -
 ilikeux liked this · 5 years ago
ilikeux liked this · 5 years ago -
 mariacandela705 liked this · 5 years ago
mariacandela705 liked this · 5 years ago -
 johanneswelwich liked this · 5 years ago
johanneswelwich liked this · 5 years ago -
 whitegloom liked this · 5 years ago
whitegloom liked this · 5 years ago -
 photowenchca liked this · 5 years ago
photowenchca liked this · 5 years ago -
 texboge liked this · 5 years ago
texboge liked this · 5 years ago -
 surendrauikey liked this · 5 years ago
surendrauikey liked this · 5 years ago -
 whitecatnatalie liked this · 5 years ago
whitecatnatalie liked this · 5 years ago -
 t-catherine liked this · 5 years ago
t-catherine liked this · 5 years ago -
 natscapegalore liked this · 5 years ago
natscapegalore liked this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts