Top 10 Things To Know For The Return Of Our Launch America Mission With SpaceX
Top 10 Things to Know for the Return of our Launch America Mission With SpaceX

History was made May 30 when NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley launched from American soil in a commercially built and operated American crew spacecraft on its way to the International Space Station.
Pictured above is the SpaceX Dragon Endeavour spacecraft that lifted off on the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida and docked with the space station on May 31. Now, Behnken and Hurley are ready to return home in Endeavour for a splashdown off the coast of Florida, closing out a mission designed to test SpaceX’s human spaceflight system, including launch, docking, splashdown, and recovery operations. Undocking is targeted for 7:34 p.m. ET on August 1, with splashdown back to Earth slated for 2:42 p.m. on August 2. Watch our continuous live coverage HERE.
1. Where will Behnken and Hurley splash down?

Image: SpaceX’s Crew Dragon is guided by four parachutes as it splashes down in the Atlantic on March 8, 2019, after the uncrewed spacecraft's return from the International Space Station on the Demo-1 mission.
Together with SpaceX, we are capable of supporting seven splashdown sites off the coast of Florida. The seven potential splashdown sites for the Dragon Endeavor are off the coasts of Pensacola, Tampa, Tallahassee, Panama City, Cape Canaveral, Daytona, and Jacksonville.
2. How will a splashdown location be chosen?
Splashdown locations are selected using defined priorities, starting with selecting a station departure date and time with the maximum number of return opportunities in geographically diverse locations to protect for weather changes. Teams also prioritize locations which require the shortest amount of time between undocking and splashdown based on orbital mechanics, and splashdown opportunities that occur in daylight hours.
Check out the Departure and Splashdown Criteria Fact Sheet for an in-depth look at selecting return locations, decision points during return, and detailed weather criteria.
3. How long will it take for Behnken and Hurley to return to Earth?

Return time for Behnken and Hurley will vary depending on the undock and splashdown opportunities chosen, with the primary opportunity taking between six and 30 hours.
4. What does the return look like? What are the major milestones?

Crew Dragon’s return home will start with undocking from the International Space Station. At the time of undock, Dragon Endeavour and its trunk weigh approximately 27,600 pounds. We will provide live coverage of the return from undocking all the way through splashdown.
There will be two very small engine burns immediately after hooks holding Crew Dragon in place retract to actually separate the spacecraft from the station. Once flying free, Dragon Endeavour will autonomously execute four departure burns to move the spaceship away from the space station and begin the flight home. Several hours later, one departure phasing burn, lasting about six minutes, puts Crew Dragon on the proper orbital path to line it up with the splashdown zone.
Shortly before the final deorbit burn, Crew Dragon will separate from its trunk, which will burn up in Earth’s atmosphere. The spacecraft then executes the deorbit burn, which commits Crew Dragon to return and places it on an orbit with the proper trajectory for splashdown. After trunk separation and the deorbit burn are complete, the Crew Dragon capsule weighs approximately 21,200 pounds.
5. How fast will Dragon Endeavour be going when it re-enters the Earth’s atmosphere? How hot will it get?
Crew Dragon will be traveling at orbital velocity prior to re-entry, moving at approximately 17,500 miles per hour. The maximum temperature it will experience on re-entry is approximately 3,500 degrees Fahrenheit. The re-entry creates a communications blackout between the spacecraft and Earth that is expected to last approximately six minutes.
6. When do the parachutes deploy?

Image: SpaceX’s final test of Crew Dragon’s Mark 3 parachute system on Friday, May 1, 2020, that will be used during the Demo-2 splashdwon mission.
Dragon Endeavour has two sets of parachutes will that deploy once back inside Earth’s atmosphere to slow down prior to splashdown. Two drogue parachutes will deploy at about 18,000 feet in altitude while Crew Dragon is moving approximately 350 miles per hour. Four main parachutes will deploy at about 6,000 feet in altitude while Crew Dragon is moving approximately 119 miles per hour.
7. Who recovers the crew and the Dragon Endeavour capsule from the water? What vehicles and personnel are involved?

Image: SpaceX’s Crew Dragon is loaded onto the company’s recovery ship, Go Searcher, in the Atlantic Ocean, about 200 miles off Florida’s east coast, on March 8, after returning from the International Space Station on the Demo-1 mission.Credits: SpaceX
For splashdown at any of the seven potential sites, SpaceX personnel will be on location to recover the capsule from the water. Two recovery ships, the Go Searcher and the Go Navigator, split locations between the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida. On either ship will be more than 40 personnel from SpaceX and NASA, made up of spacecraft engineers, trained water recovery experts, medical professionals, the ship’s crew, NASA cargo experts, and others to assist in the recovery.
8. How long after splashdown until Behnken and Hurley are out of the capsule?

Image: NASA astronaut Doug Hurley, along with teams from NASA and SpaceX, rehearse crew extraction from SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, on August 13, 2019. Credits: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Immediately after splashdown has occurred, two fast boats with SpaceX personnel deploy from the main recovery ship. The first boat checks capsule integrity and tests the area around the Crew Dragon for the presence of any hypergolic propellant vapors. Once cleared, the personnel on the boats begin preparing the spaceship for recovery by the ship. The second fast boat is responsible for safing and recovering Crew Dragon’s parachutes, which have at this point detached from the capsule and are in the water.
At this point the main recovery vessel can move in and begin to hoist the Crew Dragon capsule onto the main deck. Once the capsule is on the recovery vessel, it is moved to a stable location for the hatch to be opened for waiting medical professionals to conduct initial checks and assist Behnken and Hurley out of Dragon Endeavour.
This entire process is expected to take approximately 45 to 60 minutes, depending on spacecraft and sea state conditions.
9. Where do Behnken and Hurley go after they are out of the capsule?
Immediately after exiting the Crew Dragon capsule, Behnken and Hurley will be assisted into a medical area on the recovery ship for initial assessment. This is similar to procedures when welcoming long-duration crew members returning home on Soyuz in Kazakhstan.
After initial medical checks, Behnken and Hurley will be returned to shore either by traveling on the primary recovery ship or by helicopter. Helicopter returns from the recovery ship are the baseline for all splashdown zones except for the Cape Canaveral splashdown site, with travel times ranging from approximately 10 minutes to 80 minutes. The distance from shore will be variable depending on the splashdown location, ranging from approximately 22 nautical miles to 175 nautical miles.
Once returned to shore, both crew members will immediately board a waiting NASA plane to fly back to Ellington field in Houston.
10. What happens next?

Image: NASA astronauts Shannon Walker, Victor Glover Jr. and Mike Hopkins and Japan’s Soichi Noguchi train in a SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule. Credit: SpaceX
Meanwhile, Dragon Endeavour will be returned back to the SpaceX Dragon Lair in Florida for inspection and processing. Teams will examine the data and performance of the spacecraft throughout the test flight to complete the certification of the system to fly operational missions for our Commercial Crew and International Space Station Programs. The certification process is expected to take about six weeks. Following successful certification, the first operational mission will launch with Crew Dragon commander Michael Hopkins, pilot Victor Glover, and mission specialist Shannon Walker – all of NASA – along with Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) mission specialist Soichi Noguchi will launch on the Crew-1 mission from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The four crew members will spend six months on the space station.
The launch is targeted for no earlier than late-September.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
5 Space Software Codes We Can Use on Earth
We’ve made some amazingly advanced software for our space missions, from launching rockets to the International Space Station to landing rovers on Mars. But a lot of that software can be applied to other situations here on the ground. We’ve got hundreds of downloadable programs in the NASA Software Catalog available for public use—and they’re all free.
We’ve rounded up five interesting software programs to get your search started.
1. Take a walk on Mars from your living room
Want to walk around Mars from the comfort of your living room? OnSight can help with that. Our engineers and scientists created this mixed reality software to immerse themselves in a visualization of the terrain around the Curiosity rover, so users feel like they are really walking on the Red Planet. The software can be adapted to visualize other locations, which means it could also help us explore places on Earth, like caves and lava fields. No wonder it was awarded NASA’s 2018 Software of the Year!
2. Enhancing images from space and the doctor’s office

It’s hard to take a perfect picture from space. That’s why our scientists created the Hierarchical Image Segmentation software program – to help us enhance and analyze images taken of Earth from space by the Landsat and Terra missions. But, that isn’t all it can do. Doctors have used the software to analyze medical images, such as X-rays, ultrasounds and mammography images, to reveal important details previously unseen by the human eye.
3. Video game tech helps our engineers build spaceflight hardware

Installing sensitive spaceflight hardware is hardly a time for fun and games. Except when it comes to the Distributed Observer Network, or DON 3.1. This software combines innovative NASA tools with commercial video game technology to train our employees for stressful tasks – like maneuvering important, delicate tools through tight spots when building instruments or spacecraft. DON can be used in many other industries, particularly for overcoming the challenges that face virtual teams collaborating on complex problems.
4. Software helps protect Earth from space junk

Those of us on the ground may imagine space as a peaceful place to float among the stars, but in reality, Earth’s atmosphere is filled with junk. This space debris can cause damage to spacecraft and satellites, including the International Space Station. That’s where the Orbital Debris Engineering Model software program comes in. Thanks to this NASA software, we can study the risks of debris impact to help us protect our orbiting equipment and – more importantly – our planet. Communication companies could use this software to prevent debris damage when launching satellites, saving them a lot of time and money.
5. From exploration missions to your office, this software keeps projects on track

Do you manage complex projects at work? There are a lot of steps and moving pieces in play when it comes to getting a spacecraft from the launchpad into space. Used during the space shuttle missions, the Schedule Test and Assessment Tool 5.0 add-on works with Microsoft Project to automate project data to help us stay on track. It’s one of the more popular programs in our software catalog because it provides quick, clear assessment info that can help with decision making.
These are just a few examples of the software NASA has free and available for the public. To browse the new 2019-2020 catalog online, visit https://software.nasa.gov/.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Happy New Year From NASA! The year 2021 was one for the books, so what will 2022 bring? No matter what, remember: You are made of star stuff. Sparkly, glorious star stuff.
What's this image? Click here. Credit: ESA/Hubble and NASA, A. Sarajedini Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

Thank you, Tumblr!
That’s it, Tumblr! Losing comm soon. I’m in space, so that happens. Thank you for all your good questions. I enjoyed #AnswerTime with you today!
Keep following my Year In Space here on Tumblr and on Twitter, Facebook and Instagram!
is there a pre-flight personal ritual that you do before piloting a flight?
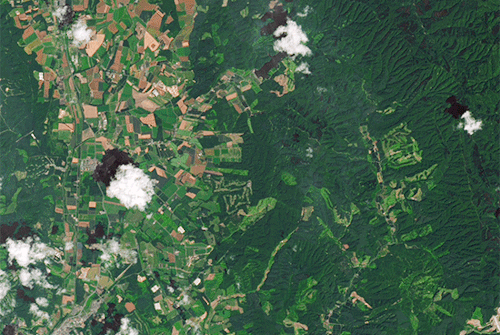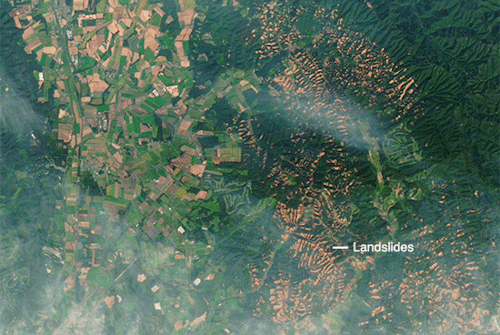
Landslides in Japan
On Sept. 6, 2018, shortly after the remnants of Typhoon Jebi drenched southern Hokkaido, a powerful earthquake rattled the Japanese island. The 6.6-magnitude quake shook the surface enough to unleash hundreds of landslides.
The Landsat 8 satellite acquired imagery of the widespread damage. An image acquired on Sept. 15, 2018, shows mud and debris in a hilly area east of Abira. For comparison, the previous image shows the same area on July 26, 2017.
Read more about this
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
NASA’s View of COVID-19
#COVID19 led to changes in human activities around the globe. We can see some of these changes from space. Some bodies of water have run clearer, emissions of pollutants have temporarily declined, and transportation and shipment of goods have decreased.

Along with our partner agencies – ESA and JAXA – we’re making satellite data available on the COVID-19 Earth Observation Dashboard, where you can explore some of the changes we can see from space.

But it’s not just what we can see. When the pandemic began, NASA engineers sprang into action to build ventilators, oxygen hoods and more to help save lives.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How does the whole sleeping situation work with 0 gravity, or do sleep mid air?
Observing the Ozone Hole from Space: A Science Success Story
Using our unique ability to view Earth from space, we are working together with NOAA to monitor an emerging success story – the shrinking ozone hole over Antarctica.

Thirty years ago, the nations of the world agreed to the landmark ‘Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.’ The Protocol limited the release of ozone-depleting chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) into the atmosphere.

Since the 1960s our scientists have worked with NOAA researchers to study the ozone layer.

We use a combination of satellite, aircraft and balloon measurements of the atmosphere.

The ozone layer acts like a sunscreen for Earth, blocking harmful ultraviolet, or UV, rays emitted by the Sun.

In 1985, scientists first reported a hole forming in the ozone layer over Antarctica. It formed over Antarctica because the Earth’s atmospheric circulation traps air over Antarctica. This air contains chlorine released from the CFCs and thus it rapidly depletes the ozone.

Because colder temperatures speed up the process of CFCs breaking up and releasing chlorine more quickly, the ozone hole fluctuates with temperature. The hole shrinks during the warmer summer months and grows larger during the southern winter. In September 2006, the ozone hole reached a record large extent.

But things have been improving in the 30 years since the Montreal Protocol. Thanks to the agreement, the concentration of CFCs in the atmosphere has been decreasing, and the ozone hole maximum has been smaller since 2006’s record.

That being said, the ozone hole still exists and fluctuates depending on temperature because CFCs have very long lifetimes. So, they still exist in our atmosphere and continue to deplete the ozone layer.
To get a view of what the ozone hole would have looked like if the world had not come to the agreement to limit CFCs, our scientists developed computer models. These show that by 2065, much of Earth would have had almost no ozone layer at all.

Luckily, the Montreal Protocol exists, and we’ve managed to save our protective ozone layer. Looking into the future, our scientists project that by 2065, the ozone hole will have returned to the same size it was thirty years ago.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What are the different fields of Earth Science? Are they related to each other?
Questions coming up from….
@Dee-an-ugh-deactivated20210528: My 4-year-old is already interested in space. How can I nurture her interest the older she gets in a productive way
@marvelpjostarwarsobssessed: What inspired/caused your interest in space?
@Anonymous: Do you like your job?
-
 raqstarnails liked this · 1 year ago
raqstarnails liked this · 1 year ago -
 mona-vainy liked this · 2 years ago
mona-vainy liked this · 2 years ago -
 spaceexplorationgenz liked this · 3 years ago
spaceexplorationgenz liked this · 3 years ago -
 mrclaw61 liked this · 3 years ago
mrclaw61 liked this · 3 years ago -
 powerfrog reblogged this · 4 years ago
powerfrog reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 felp7k liked this · 4 years ago
felp7k liked this · 4 years ago -
 wayward-coffee-raccoon liked this · 4 years ago
wayward-coffee-raccoon liked this · 4 years ago -
 atranz79 liked this · 4 years ago
atranz79 liked this · 4 years ago -
 blotto liked this · 4 years ago
blotto liked this · 4 years ago -
 gayidioot liked this · 4 years ago
gayidioot liked this · 4 years ago -
 lijretta liked this · 4 years ago
lijretta liked this · 4 years ago -
 sue49universe liked this · 4 years ago
sue49universe liked this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago -
 wingspanmatters liked this · 4 years ago
wingspanmatters liked this · 4 years ago -
 lunasnownature liked this · 4 years ago
lunasnownature liked this · 4 years ago -
 voldysgonemodly liked this · 4 years ago
voldysgonemodly liked this · 4 years ago -
 go3dprinting reblogged this · 4 years ago
go3dprinting reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 setwelven liked this · 4 years ago
setwelven liked this · 4 years ago -
 knight-kennedy liked this · 4 years ago
knight-kennedy liked this · 4 years ago -
 saltythexfilesindianjonescop liked this · 4 years ago
saltythexfilesindianjonescop liked this · 4 years ago -
 texboge liked this · 4 years ago
texboge liked this · 4 years ago -
 duudone liked this · 4 years ago
duudone liked this · 4 years ago -
 zuljpr liked this · 4 years ago
zuljpr liked this · 4 years ago -
 pineconeishere liked this · 4 years ago
pineconeishere liked this · 4 years ago -
 oshri liked this · 4 years ago
oshri liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts