Part Of A Color Study For The Next Painting I Plan To Start This Week.

Part of a color study for the next painting I plan to start this week.
More Posts from Exobiotica and Others

I've decided to start posting sketches more often, as they comprise over 90% of my artistic time. This is the Greater Parvasalia. It travels in large groups, is about the size of a hamster, and is generally non-aggressive. More details as they are developed.

Grandulus
Trifasciatus grandulus
I should preface the description of this creature by giving a short statement about the natural history of its home planet. Early in its evolutionary history, life on this world did not split into such rigidly defined taxa as it did on Earth. For example, the majority of multicellular earth-life is divided into autotrophic creatures (plants) which are immobile, and the highly mobile heterotrophs (animals). On grandulus’s planet, the peculiar biochemistry allows for a much higher rate of horizontal gene transfer and endocytosis. This means that instead of a taxonomic “tree of life” like on Earth, their evolutionary history looks more like a web. In short, this allows for a wide array of photosynthetic, yet mobile creatures. The grandulus is one of these. It moves around slowly with its sticky appendages and positions itself in a spot with maximum sunlight to unfold its inflatable photosynthetic organ from its posterior shell. It also feeds on the internal fluids of metaflora, as well as decaying organic matter. Its many species range in size from that of a quarter to the size of a hippo.



Curiosity
A massive predator on the ocean floor lures in its next naive dinner guest. The smaller creatures that surround it have been waiting for this moment.
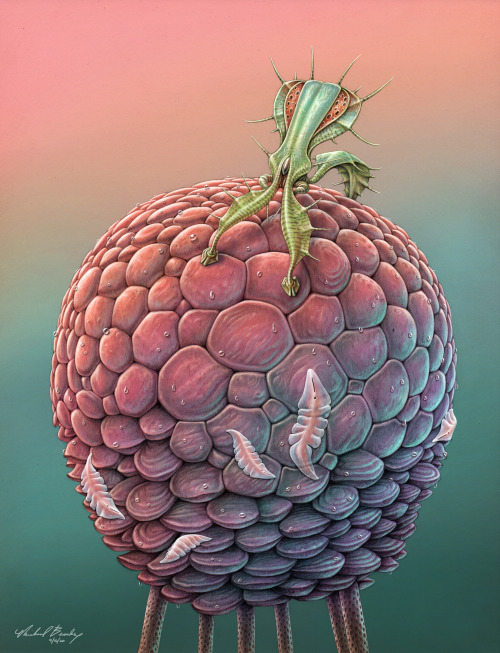

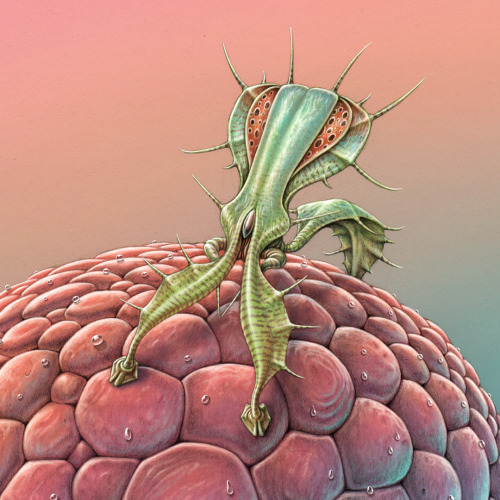
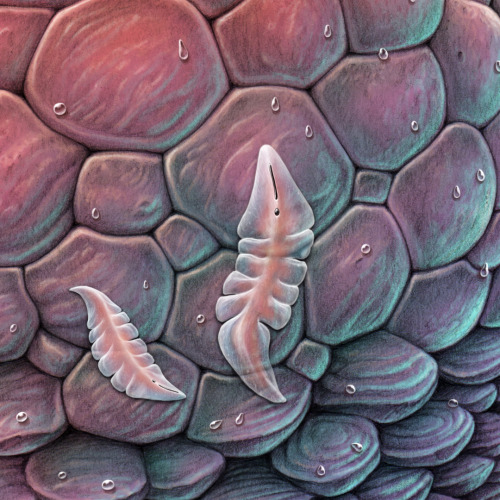
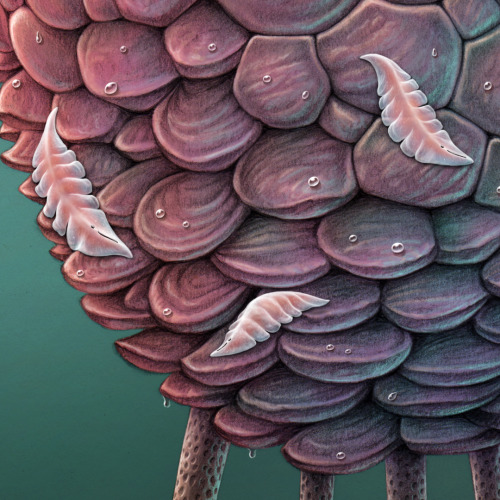
Guardian
On Veteris, it is common for creatures to obtain energy from multiple sources. The large round, multifaceted autotroph angles its plates to face the light at any given time of day. It also feeds on decomposing organic matter it obtains by moving slowly on its long spindly legs. Conversely, the spiny guardian on top originally evolved to hunt the semi-transparent flat creatures that feed on the autotroph, but came to rely on them exclusively. Over many generations, individuals that allowed some prey items to live and reproduce eventually outlasted the more aggressive hunters, and now their style of subsistence is closer to farming. The guardians now protect the entire micro-system – each large round walker and its flock of parasites is topped by a spiny guardian who has the dual task of defending against predators as well as keeping the herd numbers in check. A round walker without a guardian slowly succumbs to parasite overpopulation. Occasionally huge numbers of walkers congregate in vast gently-swaying miniature forests, each crowned by a flamboyant spiny guardian defending its small world.






First Light
Dawn breaks in the desert, revealing a scurrying frenzy of creatures returning to shelter after the night’s mischief. Tallest among them, the Cycloptic Night-Seeker surveys the scene looking for any last morsel of food before the day’s solar onslaught forces its retreat into shadow. The Testapallidus at its feet may prove an ideal treat, unless the sand-swimming Armored Loricatus captures it first. Though the Testapallidus’ hard dorsal shell protects it from most threats, the Night-Seeker possesses a keen intellect, curious disposition, and two formidable front appendages that are as dextrous as they are sharp. Usually too quick for the large hunter, a trio of gregarious Desert Sentinels are more concerned with ambush predators such as the Loricatus, and one inflates its signaling air sacs in alarm. Already, members of the desert’s daytime cast are making an appearance. Luteos have positioned themselves at the top of the ridge to greet the first slanted rays. Relying on photosynthesis for a large portion of their metabolism, they tilt their bodies to follow the sun throughout the day. In a short time, more heat-tolerant daylight denizens will take the stage and play out their part in the everyday drama of the high desert.






World Eater
In the murky ponds on the floor of the Glow Forest lives a surprisingly diverse community adapted to the near total darkness. Decaying organic material releases methane gas which is harnessed by towers of colonial microorganisms. Upon this bedrock of the food chain, a plethora of creatures creep and crawl about their daily lives while trying to avoid the pond’s top predator - a massive leviathan blindly devouring everything in its path.






Codependence
Natural selection breeds competition, but it can also lead to sophisticated cooperation. The Glass Colligatio is what is known as a composite organism—a creature comprised of members of multiple species that share critical biological processes between them. The larger swimmer provides mobility, while its multi-legged symbiont feeds more efficiently than it could alone. Through the interspecies junction—a specialized dual orifice connecting the creatures—they share nutrients and oxygen, each specializing in what it does best while providing for the needs of the whole.
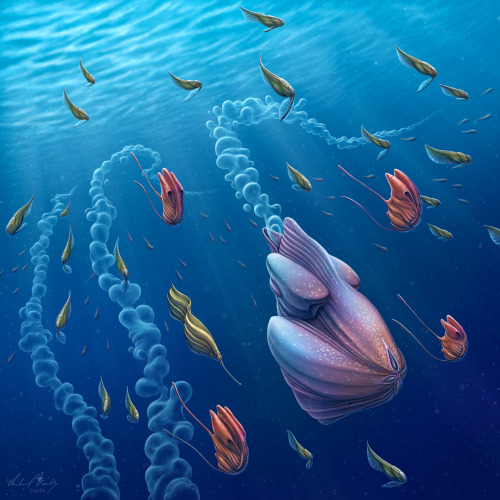
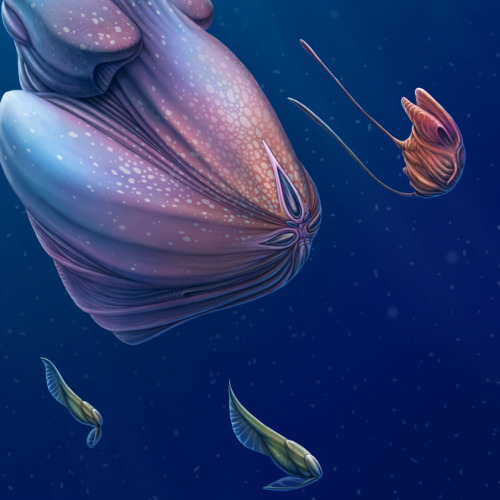
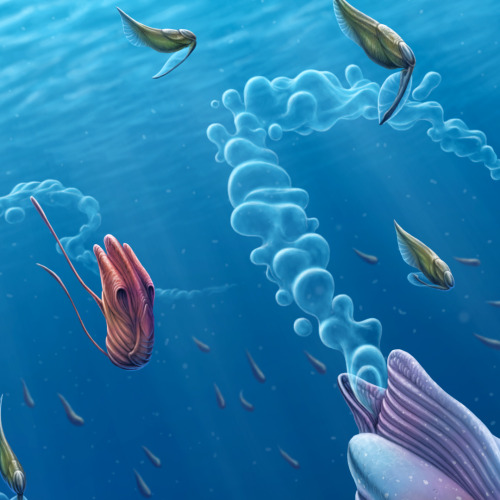
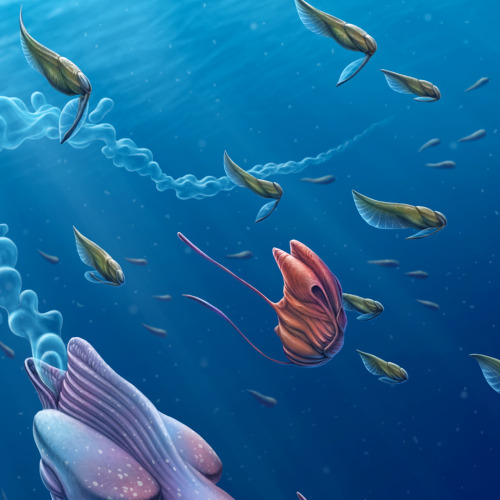



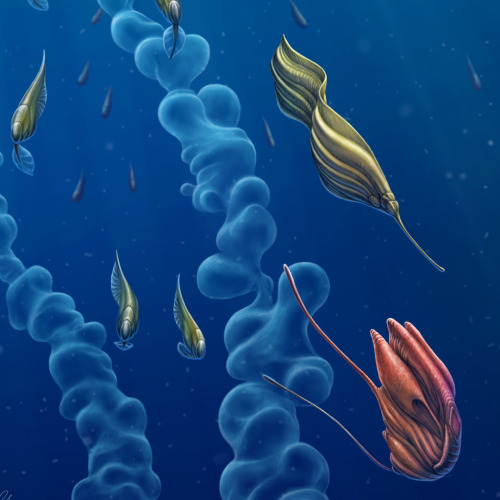

Back to the Depths
An entourage of opportunistic creatures accompanies the deep-sea behemoths during their brief ascent to the surface. Releasing their gelatinous strings of embryos here in the sunlight has a significant benefit - there's far more visibility. The swarm of followers are here in search of a quick meal in the form of the gelatin, which is full of valuable protiens and nutrients. After the feast however, the recipients of this apparent windfall become unwitting hosts for the behemoth's multitudinous offspring, which were embedded in the gel. Adapted to develop inside a wide variety of pelagic creatures, the young grow internally - and sometimes even on the surface of - their hosts until such time as they detach and sink back into the darkness. For most host species, this seems to be a mutually-beneficial symbiosis. At the beginning they receive a large and valuable meal, and usually incur very little detriment due to their temporary parasites. The young behemoths will hide in the dark depths for many years until attaining the size necessary to return to the light and repeat the ancient cycle again.




Here is a nocturnal view of a habitat in which the inhabitants have evolved extreme forms of bioluminescence. The vertical glowing blobs are the reproductive bulb form of a species with a complex life cycle (to be elucidated in following artworks). The groove-backed, ravenous creatures at the bottom are of the same species as the glowing blobs, but at a different life stage. At center is a rather placid, slow-moving consumer of the bulbs- one who has incorporated its own form of bioluminescence into its respiratory apparatus as a means of camouflage. Names and descriptions will come as soon as possible.
-
 ara6gir liked this · 10 months ago
ara6gir liked this · 10 months ago -
 hyddedraws liked this · 10 months ago
hyddedraws liked this · 10 months ago -
 haru-dipthong liked this · 1 year ago
haru-dipthong liked this · 1 year ago -
 wtrotsky-blog liked this · 1 year ago
wtrotsky-blog liked this · 1 year ago -
 bluntfiend161 liked this · 2 years ago
bluntfiend161 liked this · 2 years ago -
 spiffyspidr liked this · 2 years ago
spiffyspidr liked this · 2 years ago -
 mrbgs101 liked this · 2 years ago
mrbgs101 liked this · 2 years ago -
 walkingmybird liked this · 2 years ago
walkingmybird liked this · 2 years ago -
 lastoutter liked this · 2 years ago
lastoutter liked this · 2 years ago -
 shitou456 liked this · 3 years ago
shitou456 liked this · 3 years ago -
 crusty liked this · 3 years ago
crusty liked this · 3 years ago -
 omegaxenonaut liked this · 3 years ago
omegaxenonaut liked this · 3 years ago -
 dozen-times-vanished liked this · 3 years ago
dozen-times-vanished liked this · 3 years ago -
 squirrel-stars liked this · 3 years ago
squirrel-stars liked this · 3 years ago -
 annoyingalchemist liked this · 3 years ago
annoyingalchemist liked this · 3 years ago -
 ferncube liked this · 3 years ago
ferncube liked this · 3 years ago -
 spiderlingbriary reblogged this · 3 years ago
spiderlingbriary reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 spiderlingbriary liked this · 3 years ago
spiderlingbriary liked this · 3 years ago -
 emzawheezy liked this · 3 years ago
emzawheezy liked this · 3 years ago -
 red-red-spout liked this · 4 years ago
red-red-spout liked this · 4 years ago -
 craebe liked this · 4 years ago
craebe liked this · 4 years ago -
 captaincoombs liked this · 4 years ago
captaincoombs liked this · 4 years ago -
 salmonofwisdom liked this · 4 years ago
salmonofwisdom liked this · 4 years ago -
 penumbra51302 liked this · 4 years ago
penumbra51302 liked this · 4 years ago -
 squanderedpotentials liked this · 4 years ago
squanderedpotentials liked this · 4 years ago -
 metalzoic liked this · 4 years ago
metalzoic liked this · 4 years ago -
 disgruntledseagull liked this · 4 years ago
disgruntledseagull liked this · 4 years ago -
 mengerstragedy reblogged this · 4 years ago
mengerstragedy reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 natesart liked this · 5 years ago
natesart liked this · 5 years ago -
 lordgrimoire liked this · 5 years ago
lordgrimoire liked this · 5 years ago -
 nosleeptillyuggoth reblogged this · 5 years ago
nosleeptillyuggoth reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mengerstragedy liked this · 5 years ago
mengerstragedy liked this · 5 years ago -
 vanjets reblogged this · 5 years ago
vanjets reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 vanjets liked this · 5 years ago
vanjets liked this · 5 years ago -
 aramis-dagaz liked this · 5 years ago
aramis-dagaz liked this · 5 years ago -
 funky-insanitear liked this · 5 years ago
funky-insanitear liked this · 5 years ago -
 creaturedeityendless liked this · 6 years ago
creaturedeityendless liked this · 6 years ago -
 opalescent-yams-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
opalescent-yams-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 opalescent-yams-blog liked this · 6 years ago
opalescent-yams-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 zepangborn liked this · 10 years ago
zepangborn liked this · 10 years ago -
 baron-jack liked this · 10 years ago
baron-jack liked this · 10 years ago -
 contemporaryuser reblogged this · 10 years ago
contemporaryuser reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 allthestrings liked this · 10 years ago
allthestrings liked this · 10 years ago



