Watch A Launch From Your Own Backyard
Watch a Launch From Your Own Backyard
On Monday, Oct. 17, we’re launching cargo to the International Space Station, and if you live on the east coast, there’s a chance you can catch a glimpse!

The above map shows the areas on the east coast where launch may be visible, depending on cloud conditions.
Liftoff is currently scheduled for 7:40 p.m. EDT from our Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
The launch of Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft will carry around 5,100 pounds of supplies and research materials to the crew on the space station.
Not in the launch viewing area? No worries! Full launch coverage will be available starting at 6:45 p.m. EDT HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
What’s in Store for 2017 at NASA?
With 2016 behind us, we take the time to not only reflect on what we’ve accomplished, but also take a look to what’s ahead for the next year.
Here are a few things to look forward to in 2017…
New Telescope in Town
This year marked big progress on our James Webb Space Telescope and there are still a number of large milestones before the telescope is launched in 2018. Once launched, JWST will be the premier observatory of the next decade. It will study every phase in the history of our Universe, ranging from the first luminous glows after the Big Bang, to the formation of solar systems capable of supporting life on planets like Earth, to the evolution of our own solar system.

In 2017, the telescope will be shipped to our Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas where end-to-end optical testing in a simulated cryo-temperature and vacuum space environment will occur.
Epic Final Year at Saturn
After more than 12 years studying Saturn, its rings and moons, our Cassini spacecraft is in its final year of its epic voyage. The conclusion of the historic scientific odyssey is planned for September 2017, but not before the spacecraft completes a daring two-part endgame.

Cassini’s final phase – called the Grand Finale – begins in earnest in April 2017. During this time, Cassini will make the closest-ever observations of Saturn, mapping the planet’s magnetic and gravity fields with exquisite precision and returning ultra-close views of the atmosphere.
Delivering Supplies to Space
Our ambitious commercial space program has enabled a successful partnership with two American companies to resupply the International Space Station.

The companies are successfully resupplying the space station, and more missions to deliver scientific investigations and cargo are planned for 2017.
Launching Two Earth Missions
New Earth science missions got underway in 2016 to enable studies that will unravel the complexities of our planet from the highest reaches of Earth’s atmosphere to its core. In 2017, we will launch two Earth-observing instruments to the International Space Station as part of our ongoing use of the orbiting space laboratory to study our changing planet.

The Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment III (SAGE III) will give us a new way to monitor Earth’s protective ozone layer and document its ongoing recovery. The Lightning Imaging Sensor (LIS) will measure both in-cloud and cloud-to-ground lightning over much of the planet, data that will help improve our understanding of lightning’s connections to weather and related phenomena.
Commercial Crew
Our Commercial Crew Program is working with American aerospace industry as companies develop and operate a new generation of spacecraft and launch systems capable of carrying crews to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station.

In 2017, astronauts will train for commercial flights and launch pad 39A will be completed at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Work is wrapping up on a new structure built specifically for the needs of astronauts climbing into Boeing's CST-100 Starliner as it stands atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida. In 2017, the 200-foot-tall Crew Access Tower and Crew Access Arm will see installation and testing of emergency evacuation systems.

SpaceX has also overhauled the historic Launch Pad 39A at Kennedy and built new support structures for the company's line of Falcon rockets. The Crew Access Arm, currently under construction, will be connected in mid-2017 to provide a bridge from the fixed service structure to the Crew Dragon spacecraft so astronauts can board before launch
Orion Progress
Our Orion spacecraft is being built to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before. Orion will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.

In 2017, computers in the Orion crew module for the spacecraft’s first mission with our Space Launch System rocket will be turned on for the first time to verify the spacecraft can route power and send commands. While the Orion outfitting and assembly process for the first mission of the spacecraft atop the SLS rocket continues in 2017, construction will also begin on the vehicle for the first Orion flight with astronauts that will fly as early as 2021.
Cutting Edge Technology
Our Space Technology office is dedicated to pushing the technological envelope, taking on challenges not only to further space agency missions near Earth, but also to sustain future deep space exploration activities.

In 2016, the office focused on and made significant progress in advancing technologies and capabilities that will continue into 2017.
Advances in Aeronautics
Our rich aeronautical research heritage added to its history of technical innovation in 2016 with advancements that will help make airplanes use less fuel, release fewer emissions and fly more quietly…and that includes working to return supersonic flight to the commercial marketplace.

We took steps in 2016 to resume designing, building and flying several experimental aircraft, or X-planes, as a means to demonstrate key green technologies and help accelerate their use by industry. In 2017, this research will continue to grow and develop.
Thanks for joining us in 2016, we look forward to sharing our progress with you in the coming year.
Happy New Year!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Hubble Space Telescope
You’ve probably heard of our Hubble Space Telescope, but have you had the chance to actually take a look at the amazing images it has captured for us over the years? Since Hubble launched in April 1990, it has made more than 1.2 million observations, some to locations more than 13.4 billion light years from Earth!
Hubble can see astronomical objects with an angular size of 0.05 arc seconds, which is like seeing a pair of fireflies in Tokyo from your home in Maryland…yea, that’s pretty far! This accuracy allows us to see images like this one of Little Gem Nebula, roughly 6,000 light-years away from us.

Images from Hubble are regularly released to the public, and are some of the most breathtaking views in the Universe. Images like this one of Lagoon Nebula, in the constellation of Sagittarius, not only make for amazing desktop screen-savers, but provide us with valuable scientific information about distant stars and galaxies, as well as the planets in our solar system.

We recently celebrated Hubble’s 25th Anniversary, and look forward to many more years of discovery and captivating images.
Why Isn’t Every Year the Warmest Year on Record?
This just in: 2022 effectively tied for the fifth warmest year since 1880, when our record starts. Here at NASA, we work with our partners at NOAA to track temperatures across Earth’s entire surface, to keep a global record of how our planet is changing.
Overall, Earth is getting hotter.

The warming comes directly from human activities – specifically, the release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels. We started burning fossil fuels in earnest during the Industrial Revolution. Activities like driving cars and operating factories continue to release greenhouse gases into our atmosphere, where they trap heat in the atmosphere.

So…if we’re causing Earth to warm, why isn’t every year the hottest year on record?
As 2022 shows, the current global warming isn’t uniform. Every single year isn’t necessarily warmer than every previous year, but it is generally warmer than most of the preceding years. There’s a warming trend.
Earth is a really complex system, with various climate patterns, solar activity, and events like volcanic eruptions that can tip things slightly warmer or cooler.
Climate Patterns
While 2021 and 2022 continued a global trend of warming, they were both a little cooler than 2020, largely because of a natural phenomenon known as La Niña.
La Niña is one third of a climate phenomenon called El Niño Southern Oscillation, also known as ENSO, which can have significant effects around the globe. During La Niña years, ocean temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean cool off slightly. La Niña’s twin, El Niño brings warmer temperatures to the central and eastern Pacific. Neutral years bring ocean temperatures in the region closer to the average.

El Niño and La Niña affect more than ocean temperatures – they can bring changes to rainfall patterns, hurricane frequency, and global average temperature.
We’ve been in a La Niña mode the last three, which has slightly cooled global temperatures. That’s one big reason 2021 and 2022 were cooler than 2020 – which was an El Niño year.
Overall warming is still happening. Current El Niño years are warmer than previous El Niño years, and the same goes for La Niña years. In fact, enough overall warming has occurred that most current La Niña years are warmer than most previous El Niño years. This year was the warmest La Niña year on record.

Solar Activity
Our Sun cycles through periods of more and less activity, on a schedule of about every 11 years. Here on Earth, we might receive slightly less energy — heat — from the Sun during quieter periods and slightly more during active periods.

At NASA, we work with NOAA to track the solar cycle. We kicked off a new one – Solar Cycle 25 – after solar minimum in December 2019. Since then, solar activity has been slightly ramping up.
Because we closely track solar activity, we know that over the past several decades, solar activity hasn't been on the rise, while greenhouse gases have. More importantly, the "fingerprints" we see on the climate, including temperature changes in the upper atmosphere, don't fit the what we'd expect from solar-caused warming. Rather they look like what we expect from increased greenhouse warming, verifying a prediction made decades ago by NASA.
Volcanic Eruptions
Throughout history, volcanoes have driven major shifts in Earth’s climate. Large eruptions can release water vapor — a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide — which traps additional warmth within our atmosphere.
On the flip side, eruptions that loft lots of ash and soot into the atmosphere can temporarily cool the climate slightly, by reflecting some sunlight back into space.
Like solar activity, we can monitor volcanic eruptions and tease out their effect on variations in our global temperature.

At the End of the Day, It’s Us
Our satellites, airborne missions, and measurements from the ground give us a comprehensive picture of what’s happening on Earth every day. We also have computer models that can skillfully recreate Earth’s climate.
By combining the two, we can see what would happen to global temperature if all the changes were caused by natural forces, like volcanic eruptions or ENSO. By looking at the fingerprints each of these climate drivers leave in our models, it’s perfectly clear: The current global warming we’re experiencing is caused by humans.
For more information about climate change, visit climate.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Everything You Need to Know About the Aug. 21 Eclipse
On Aug. 21, all of North America will experience a solar eclipse.

If skies are clear, eclipse-watchers will be able to see a partial solar eclipse over several hours, and some people – within the narrow path of totality – will see a total solar eclipse for a few moments.
How to Watch
It’s never safe to look at the Sun, and an eclipse is no exception. During a partial eclipse (or on any regular day) you must use special solar filters or an indirect viewing method to watch the Sun.

If you have solar viewing glasses, check to make sure they’re safe and undamaged before using them to look at the Sun. Make sure you put them on before looking up at the Sun, and look away before removing them. Eclipse glasses can be used over your regular eyeglasses, but they should never be used when looking through telescopes, binoculars, camera viewfinders, or any other optical device.
If you don’t have eclipse glasses, you can still watch the eclipse indirectly! You can make a pinhole projector out of a box, or use any other object with tiny holes – like a piece of cardstock with a hole, or your outstretched, interlaced fingers – to project an image of the partially eclipsed Sun onto the ground.

Of course, if it’s cloudy (or you’d just rather stay inside), you can watch the whole thing online with us at nasa.gov/eclipselive. Tune in starting at noon ET.
If you’re in the path of totality, there will be a few brief moments when it is safe to look directly at the eclipse. Only once the Moon has completely covered the Sun and there is no light shining through is it safe to look at the eclipse. Make sure you put your eclipse glasses back on or return to indirect viewing before the first flash of sunlight appears around the Moon’s edge.

Why do eclipses happen?
A solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, casting its shadow down on Earth’s surface. The path of totality – where the Moon completely covers the Sun – is traced out by the Moon’s inner shadow, the umbra. People within the Moon’s outer shadow, the penumbra, can see a partial eclipse.

The Moon’s orbit around Earth is tilted by about five degrees, meaning that its shadow usually doesn’t fall on Earth. Only when the Moon lines up exactly between the Sun and Earth do we see an eclipse.

Though the Sun is about 400 times wider than the Moon, it is also about 400 times farther away, making their apparent sizes match up almost exactly. This is what allows the Moon to block out the Sun’s bright face, while revealing the comparatively faint, pearly-white corona.
The Science of Eclipses
Eclipses are a beautiful sight to see, and they’re also helpful for our scientists, so we’re funding eleven ground-based science investigations to learn more about the Sun and Earth.

Total solar eclipses reveal the innermost regions of the Sun’s atmosphere, the corona. Though it’s thought to house the processes that kick-start much of the space weather that can influence Earth, as well as heating the whole corona to extraordinarily high temperatures, we can’t study this region at any other time. This is because coronagraphs – the instruments we use to study the Sun’s atmosphere by creating artificial eclipses – must cover up much of the corona, as well as the Sun’s face in order to produce clear images.

Eclipses also give us the chance to study Earth’s atmosphere under uncommon conditions: the sudden loss of solar radiation from within the Moon’s shadow. We’ll be studying the responses of both Earth’s ionosphere – the region of charged particles in the upper atmosphere – and the lower atmosphere.
Learn all about the Aug. 21 eclipse at eclipse2017.nasa.gov, and follow @NASASun on Twitter and NASA Sun Science on Facebook for more. Watch the eclipse through the eyes of NASA at nasa.gov/eclipselive starting at 12 PM ET on Aug. 21.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

It's Launch Day!
Final preparations are underway for today's 5:55 p.m. EDT launch of the eleventh SpaceX cargo resupply mission to the International Space Station from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SpaceX Dragon spacecraft will liftoff into orbit atop the Falcon 9 rocket carrying about 6,000 pounds of crew supplies, equipment and scientific research to crewmembers living aboard the station. The flight will deliver investigations and facilities that study neutron stars, osteoporosis, solar panels, tools for Earth-observation, and more. Watch live coverage starting today at 5:15pm ET at http://www.nasa.gov/live
Learn more about the mission and launch at http://www.nasa.gov/spacex
Image credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
10 Out of this World NASA Spinoff Technologies
What is a spinoff? Great question! A NASA spinoff is a technology, originally developed to meet our mission needs that has been transferred to the public and now provides benefits as a commercial product or service. Basically, we create awesome stuff and then share it with the world. Here’s a list of just a few NASA spinoff technologies (in no particular order):
1. Enriched Baby Food

While developing life support for Mars missions, NASA-funded researchers discovered a natural source for an omega-3 fatty acid that plays a key role in infant development. The ingredient has since been infused in more than 99% of infant formula on the market and is helping babies worldwide develop healthy brains, eyes and hearts.
2. Digital Camera Sensors

Whether you take pictures and videos with a DSLR camera, phone or even a GoPro, you’re using NASA technology. The CMOS active pixel sensor in most digital image-capturing devices was invented when we needed to miniaturize cameras for interplanetary missions.
3. Airplane Wing Designs

Did you know that we’re with you when you fly? Key aerodynamic advances made by our researchers - such as the up-turned ends of wings, called “winglets” - are ubiquitous among modern aircraft and have saved many billions of dollars in fuel costs.
4. Precision GPS

Uncorrected GPS data can be off by as much as 15 meters thanks to data errors, drift in satellite clocks and interference from Earth’s atmosphere. One of our software packages developed in the 1990s dials in these locations to within centimeters, enabling highly accurate GPS readings anywhere on the planet. One of our most important contributions to modern society, precise GPS is used in everything from personal devices and commercial airplanes to self-driving tractors.
5. Memory Foam

Possibly the most widely recognized spinoff, memory foam was invented by our researchers looking for ways to keep its test pilots and astronauts comfortable as they experienced extreme acceleration. Today, memory foam cushions beds, chairs, couches, car and motorcycle seats, shoes and even football helmets.
6. International Search and Rescue System

We pioneered the technology now used internationally for search and rescue operations. When pilots, sailors or other travelers and adventurers are stranded, they can activate a personal locator bacon that uses overhead satellites to relay their call for help and precise location to authorities.
7. Improvements to Truck Aerodynamics

Nearly every truck on the road has been shaped by NASA - literally. Agency research in vehicle aerodynamic design led to the curves and contours that help modern big rigs cut through the air with less drag. Our contributions to truck design have greatly reduced fuel consumption, perhaps by as much as 6,800 gallons per year for an average vehicle.
8. Shock Absorbers for Buildings and Bridges

Shock absorbers originally designed to survive the extreme conditions of space shuttle launches are now bracing hundreds of buildings and bridges in earthquake-prone regions all over the world. None of which have suffered even minor damage during an earthquake.
9. Advanced Water Filtration

We have recently discovered sources of water on the moon and Mars, but even so space is still practically a desert for human explorers, and every drop possible must be recycled and reused. A nanofiber filer devised to purify water in orbit is currently at work on Earth. From devices that supply water to remote villages, to a water bottle that lets hikers and adventurers stay hydrated using streams and lakes, our technology is being utilized.
10. Invisible Braces

A company working with NASA invented the translucent ceramic that became the first invisible dental braces, which would go on to become one of the best-selling orthodontic products of all time.
So, now that you know a few of the spinoff technologies that we helped develop, you can look for them throughout your day. Visit our page to learn about more spinoff technologies: https://spinoff.nasa.gov
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Tornado Recovery Underway at Michoud Assembly Facility
Teams at our Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans worked overnight and are continuing Wednesday with assessment and recovery efforts following a tornado strike at the facility Tuesday at 11:25 a.m. CST. All 3,500 employees at the facility have been accounted for, with five sustaining minor injuries.
Teams worked through the night on temporary repairs to secure the perimeter fencing and provide access for the essential personnel through the main gate. Approximately 40 to 50 percent of the buildings at Michoud have some kind of damage; about five buildings have some form of severe damage.

Approximately 200 parked cars were damaged, and there was damage to roads and other areas near Michoud.

“The entire NASA family pulls together during good times and bad, and the teams at the Michoud Assembly Facility are working diligently to recover from the severe weather that swept through New Orleans Tuesday and damaged the facility,” said acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. “We are thankful for the safety of all the NASA employees and workers of onsite tenant organizations, and we are inspired by the resilience of Michoud as we continue to assess the facility’s status.”

Teams will reassess the condition of the Vertical Assembly Center (VAC), as the initial examination revealed some electrical damage to its substation. The VAC is used to weld all major pieces of hardware for the core stage of the Space Launch System. The most recently welded part was removed from the facility last week.

The team has prioritized completing the assessment at the site’s main manufacturing building for the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft flight hardware so power can be restored in phases and temporary protection put in place to shield hardware from any further inclement weather.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
uhmm, can you tell me what exactly a black hole is? or what iy does? thanks, just really confused and curious on how it actually works.
Protecting our Home Planet 🌎

Did you ever wonder how we spots asteroids that may be getting too close to Earth for comfort? Wonder no more. Our Planetary Defense Coordination Office does just that. Thanks to a variety of ground and space based telescopes, we’re able to detect potentially hazardous objects so we can prepare for the unlikely threat against our planet.
What is a near-Earth object?

Near-Earth objects (NEOs) are asteroids and comets that orbit the Sun, but their orbits bring them into Earth’s neighborhood – within 30 million miles of Earth’s orbit.
These objects are relatively unchanged remnant debris from the solar system’s formation some 4.6 billion years ago. Most of the rocky asteroids originally formed in the warmer inner solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, while comets, composed mostly of water ice with embedded dust particles, formed in the cold outer solar system.
Who searches for near-Earth objects?

Our Near-Earth Object (NEO) Observations Program finds, tracks and monitors near-Earth asteroids and comets. Astronomers supported by the program use telescopes to follow up the discoveries to make additional measurements, as do many observatories all over the world. The Center for Near-Earth Object Studies, based at our Jet Propulsion Laboratory, also uses these data to calculate high-precision orbits for all known near-Earth objects and predict future close approaches by them to Earth, as well as the potential for any future impacts.
How do we calculate the orbit of a near-Earth object?

Scientists determine the orbit of an asteroid by comparing measurements of its position as it moves across the sky to the predictions of a computer model of its orbit around the Sun. The more observations that are used and the longer the period over which those observations are made, the more accurate the calculated orbit and the predictions that can be made from it.
How many near-Earth objects have been discovered so far?
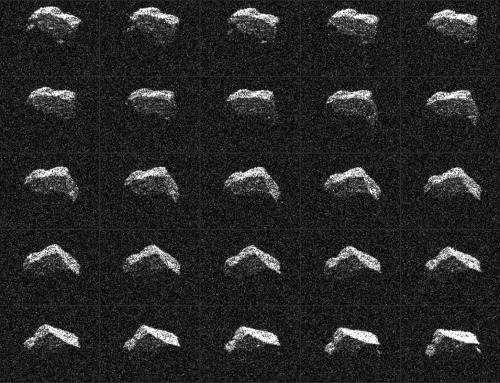
At the start of 2019, the number of discovered NEOs totaled more than 19,000, and it has since surpassed 20,000. An average of 30 new discoveries are added each week. More than 95 percent of these objects were discovered by NASA-funded surveys since 1998, when we initially established its NEO Observations Program and began tracking and cataloguing them.
Currently the risk of an asteroid striking Earth is exceedingly low, but we are constantly monitoring our cosmic neighborhood. Have more questions? Visit our Planetary Defense page to explore how we keep track of near-Earth objects.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Hello there 👋
Welcome to Mindful Monday. It’s good to see you 🧘
For our second week, we’ve got an offer of mindfulness y’all can’t POSSIBLY refuse: join us as we tour the rings of Saturn with NASA! Turn on, tune in, and space out to relaxing music and stunning ultra-high-definition visuals of our cosmic neighborhood 🌌
Sounds good, right? Of course, it does. You can watch even more Space Out episodes on NASA+, a new, no-cost, ad-free streaming service.
Why not give it a try? Just a few minutes this Monday morning can make all the difference to your entire week, as @nasa helps to bring mindfulness from the stars and straight to you.
🧘WATCH: Space Out with NASA: Rings of Saturn 12/04 at 1pm EST🧘
-
 rlbarkerii liked this · 3 years ago
rlbarkerii liked this · 3 years ago -
 gerten-blog1 liked this · 6 years ago
gerten-blog1 liked this · 6 years ago -
 kaydenspacebeam liked this · 7 years ago
kaydenspacebeam liked this · 7 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts