What Specific Area Of Space Research Most Excites You? Could Be Something Being Explored Currently, Or
What specific area of space research most excites you? Could be something being explored currently, or something you would like to see work done on in the future.
My twin sister worked on genetics in graduate school, and she continues to research ideas in genetics. She comes up with a lot of great ideas for what we can study in space, especially now since genetics is a focus on the space station. I’m looking forward to continuing with the genetics experiments and seeing what we learn.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
How had your background in the US Air Force as a flight test engineer prepare you for the challenges and demands of being an astronaut?
What does actually launching into space feel like?
5 Space Software Codes We Can Use on Earth
We’ve made some amazingly advanced software for our space missions, from launching rockets to the International Space Station to landing rovers on Mars. But a lot of that software can be applied to other situations here on the ground. We’ve got hundreds of downloadable programs in the NASA Software Catalog available for public use—and they’re all free.
We’ve rounded up five interesting software programs to get your search started.
1. Take a walk on Mars from your living room
Want to walk around Mars from the comfort of your living room? OnSight can help with that. Our engineers and scientists created this mixed reality software to immerse themselves in a visualization of the terrain around the Curiosity rover, so users feel like they are really walking on the Red Planet. The software can be adapted to visualize other locations, which means it could also help us explore places on Earth, like caves and lava fields. No wonder it was awarded NASA’s 2018 Software of the Year!
2. Enhancing images from space and the doctor’s office

It’s hard to take a perfect picture from space. That’s why our scientists created the Hierarchical Image Segmentation software program – to help us enhance and analyze images taken of Earth from space by the Landsat and Terra missions. But, that isn’t all it can do. Doctors have used the software to analyze medical images, such as X-rays, ultrasounds and mammography images, to reveal important details previously unseen by the human eye.
3. Video game tech helps our engineers build spaceflight hardware

Installing sensitive spaceflight hardware is hardly a time for fun and games. Except when it comes to the Distributed Observer Network, or DON 3.1. This software combines innovative NASA tools with commercial video game technology to train our employees for stressful tasks – like maneuvering important, delicate tools through tight spots when building instruments or spacecraft. DON can be used in many other industries, particularly for overcoming the challenges that face virtual teams collaborating on complex problems.
4. Software helps protect Earth from space junk

Those of us on the ground may imagine space as a peaceful place to float among the stars, but in reality, Earth’s atmosphere is filled with junk. This space debris can cause damage to spacecraft and satellites, including the International Space Station. That’s where the Orbital Debris Engineering Model software program comes in. Thanks to this NASA software, we can study the risks of debris impact to help us protect our orbiting equipment and – more importantly – our planet. Communication companies could use this software to prevent debris damage when launching satellites, saving them a lot of time and money.
5. From exploration missions to your office, this software keeps projects on track

Do you manage complex projects at work? There are a lot of steps and moving pieces in play when it comes to getting a spacecraft from the launchpad into space. Used during the space shuttle missions, the Schedule Test and Assessment Tool 5.0 add-on works with Microsoft Project to automate project data to help us stay on track. It’s one of the more popular programs in our software catalog because it provides quick, clear assessment info that can help with decision making.
These are just a few examples of the software NASA has free and available for the public. To browse the new 2019-2020 catalog online, visit https://software.nasa.gov/.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Gelatin in space! Looks a bit like a tadpole when it is floating around, but I promise it was a tasty treat for us on the Space Station. The food lab prepared drink bags with gelatin mix inside, and I made gelatin for the crew. It is very tempting to play with your food when it floats.
Why Sequencing DNA in Space is a Big Deal
... And How You Can Talk to the Scientists Who Made It Happen

Less than one month ago, DNA had never been sequenced in space. As of today, more than one billion base pairs of DNA have been sequenced aboard the International Space Station, Earth’s only orbiting laboratory. The ability to sequence the DNA of living organisms in space opens a whole new world of scientific and medical possibilities. Scientists consider it a game changer.

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins, who has a background in genomics, conducted the sequencing on the space station as part of the Biomolecule Sequencer investigation. A small, commercial, off-the-shelf device called MinION (min-EYE-ON), manufactured by Oxford Nanopore Technologies in the UK, was used to sequence the DNA of bacteria, a virus and rodents. Human DNA was not sequenced, and there are no immediate plans to sequence human DNA in space.

(Image Credit: Oxford Nanopore Technologies)
The MinION is about the size of a candy bar, and plugs into a laptop or tablet via USB connection, which also provides power to the device. The tiny, plug and play sequencer is diminutive compared to the large microwave-sized sequencers used on Earth, and uses much less power. Unlike other terrestrial instruments whose sequencing run times can take days, this device’s data is available in near real time; analysis can begin within 10-15 minutes from the application of the sample.

Having real-time analysis capabilities aboard the space station could allow crews to identify microbes, diagnose infectious disease and collect genomic and genetic data concerning crew health, without having to wait long periods of time to return samples to Earth and await ground-based analysis.
The first DNA sequencing was conducted on Aug. 26, and on Sept. 14, Rubins and the team of scientists back at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston hit the one-billionth-base-pairs-of-DNA-sequenced mark.

Have more questions about how the Biomolecule Sequencer works, or how it could benefit Earth or further space exploration? Ask the team of scientists behind the investigation, who will be available for questions during a Reddit Ask Me Anything on /r/science on Wednesday, Sept. 28 at 2 p.m. EDT.
The participants are:
Dr. Aaron Burton, NASA Johnson Space Center, Planetary Scientist and Principal Investigator
Dr. Sarah Castro-Wallace, NASA Johnson Space Center, Microbiologist and Project Manager
Dr. David J. Smith, NASA Ames Research Center, Microbiologist
Dr. Mark Lupisella, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Systems Engineer
Dr. Jason P. Dworkin, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Astrobiologist
Dr. Christopher E. Mason, Weill Cornell Medicine Dept. of Physiology and Biophysics, Associate Professor
Celebrating Women’s Equality Day Across NASA

August 26 is celebrated in the United States as Women’s Equality Day. On this day in 1920, the Nineteenth Amendment was signed into law and American women were granted the constitutional right to vote. The suffragists who fought hard for a woman’s right to vote opened up doors for trailblazers who have helped shape our story of spaceflight, research and discovery. On Women’s Equality Day, we celebrate women at NASA who have broken barriers, challenged stereotypes and paved the way for future generations. This list is by no means exhaustive.
Rocket Girls and the Advent of the Space Age

In the earliest days of space exploration, most calculations for early space missions were done by “human computers,” and most of these computers were women. These women's calculations helped the U.S. launch its first satellite, Explorer 1. This image from 1953, five years before the launch of Explorer 1, shows some of those women on the campus of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
These women were trailblazers at a time when most technical fields were dominated by white men. Janez Lawson (seen in this photo), was the first African American hired into a technical position at JPL. Having graduated from UCLA with a bachelor's degree in chemical engineering, she later went on to have a successful career as a chemical engineer.
Katherine Johnson: A Champion for Women’s Equality

Mathematician Katherine Johnson, whose life story was told in the book and film "Hidden Figures," is 101 years old today! Coincidentally, Johnson’s birthday falls on August 26: which is appropriate, considering all the ways that she has stood for women’s equality at NASA and the country as a whole.
Johnson began her career in 1953 at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), the agency that preceded NASA, one of a number of African-American women hired to work as "human computers.” Johnson became known for her training in geometry, her leadership and her inquisitive nature; she was the only woman at the time to be pulled from the computing pool to work with engineers on other programs.
Johnson was responsible for calculating the trajectory of the 1961 flight of Alan Shepard, the first American in space, as well as verifying the calculations made by electronic computers of John Glenn’s 1962 launch to orbit and the 1969 Apollo 11 trajectory to the moon. She was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the nation's highest civilian honor, by President Barack Obama on Nov. 24, 2015.
JoAnn Morgan: Rocket Fuel in Her Blood

JoAnn Morgan was an engineer at Kennedy Space Center at a time when the launch room was crowded with men. In spite of working for all of the Mercury, Gemini and Apollo programs, and being promoted to a senior engineer, Morgan was still not permitted in the firing room at liftoff — until Apollo 11, when her supervisor advocated for her because of her superior communication skills. Because of this, Morgan was the instrumentation controller — and the only woman — in the launch room for the Apollo 11 liftoff.
Morgan’s career at NASA spanned over 45 years, and she continued to break ceiling after ceiling for women involved with the space program. She excelled in many other roles, including deputy of Expendable Launch Vehicles, director of Payload Projects Management and director of Safety and Mission Assurance. She was one of the last two people who verified the space shuttle was ready to launch and the first woman at KSC to serve in an executive position, associate director of the center.
Oceola (Ocie) Hall: An Advocate for NASA Women

Oceola Hall worked in NASA’s Office of Diversity and Equal Opportunity for over 25 years. She was NASA’s first agency-wide Federal Women’s program manager, from 1974 – 1978. Hall advanced opportunities for NASA women in science, engineering and administrative occupations. She was instrumental in initiating education programs for women, including the Simmons College Strategic Leadership for Women Program.
Hall’s outstanding leadership abilities and vast knowledge of equal employment laws culminated in her tenure as deputy associate administrator for Equal Opportunity Programs, a position she held for five years. Hall was one among the first African-American women to be appointed to the senior executive service of NASA. This photo was taken at Marshall during a Federal Women’s Week Luncheon on November 11, 1977 where Hall served as guest speaker.
Hall was known for saying, “You have to earn your wings every day.”
Sally Ride: Setting the Stage for Women in Space

The Astronaut Class of 1978, otherwise known as the “Thirty-Five New Guys,” was NASA’s first new group of astronauts since 1969. This class was notable for many reasons, including having the first African-American and first Asian-American astronauts and the first women.
Among the first women astronauts selected was Sally Ride. On June 18, 1983, Ride became the first American woman in space, when she launched with her four crewmates aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger on mission STS-7. On that day, Ride made history and paved the way for future explorers.
When those first six women joined the astronaut corps in 1978, they made up nearly 10 percent of the active astronaut corps. In the 40 years since that selection, NASA selected its first astronaut candidate class with equal numbers of women and men, and women now comprise 34 percent of the active astronauts at NASA.
Charlie Blackwell-Thompson: First Female Launch Director

As a part of our Artemis missions to return humans to the Moon and prepare for journeys to Mars, the Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket will carry the Orion spacecraft on an important flight test. Veteran spaceflight engineer Charlie Blackwell-Thompson will helm the launch team at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Her selection as launch director means she will be the first woman to oversee a NASA liftoff and launch team.
"A couple of firsts here all make me smile," Blackwell-Thompson said. "First launch director for the world's most powerful rocket — that's humbling. And I am honored to be the first female launch director at Kennedy Space Center. So many amazing women that have contributed to human space flight, and they blazed the trail for all of us.”
The Future of Women at NASA

In this image, NASA astronauts Anne McClain and Christina Koch pose for a portrait inside the Kibo laboratory module on the International Space Station. Both Expedition 59 flight engineers are members of NASA's 2013 class of astronauts.
As we move forward as a space agency, embarking on future missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond, we reflect on the women who blazed the trail and broke glass ceilings. Without their perseverance and determination, we would not be where we are today.
Follow Women@NASA for more stories like this one and make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
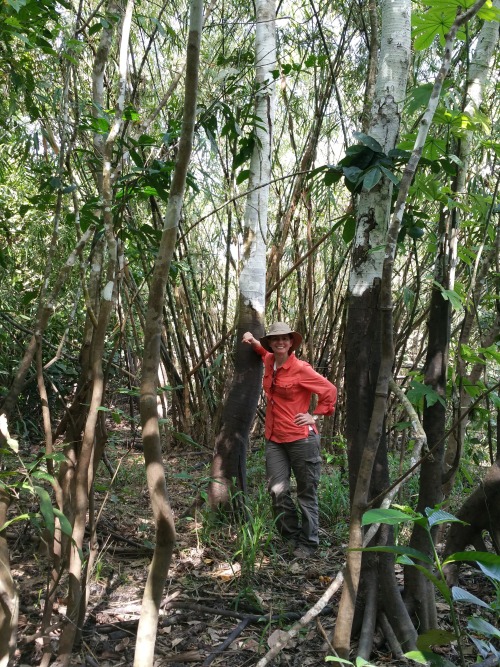

NASA Spotlight: Carbon Cycle and Ecosystems Earth Scientist Erika Podest
Dr. Erika Podest is a scientist with the Carbon Cycle and Ecosystems Group in our Jet Propulsion Laboratory’s Earth Science Division and Visiting Associate Researcher in the Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) at UCLA. Her research entails using satellite images to study Earth’s ecosystems specifically related to wetlands and boreal forests and how they are being affected by climate change.
Erika took time from studying our home planet to answer questions about her life and career! Get to know our Earth Scientist:
What inspires/motivates you?
I am inspired by the beauty of nature, its perfection and by the peace it brings me. My motivation is to make a positive impact on our planet by better understanding it and caring for it.
What first sparked your interest in Earth science?
I was born and raised in Panama, which is a country with an exuberant nature. Since I can remember, I was always surrounded by nature because my father was an adventurer who loved the outdoors and always took me with him to go exploring or simply to enjoy a nice relaxing day outside. This led me to develop a deep sense of appreciation, respect, and curiosity for nature, which sparked my interest to learn about it and pursue a career in Earth Science.
What got you interested in the study of Earth from space?

Early in my college years I was training for my private pilot’s license and during my solo flights I would take pictures of features on the surface from the plane. I was always amazed at the details the pictures showed of the landscape that were not obvious from the ground. This was the first step towards discovering that there was a field for studying Earth from above, called remote sensing and consequently my Masters and Ph.D. were focused in this field.
What technology, discovery, or policy do you think has the most potential to decrease humans’ environmental impact (e.g. wind turbines, carbon taxes, clean meat)?
I don’t think it is a matter of any one technology, discovery or policy. It is a combination of everything. Having an impact on climate change involves every level and direction, from the bottom up at the individual, grassroots and community level to the top down at the policy level. As individuals, I think it is important to educate ourselves about climate change (I suggest climate.nasa.gov). We all have the power to make a positive change by speaking up and making informed decisions about our consumptive habits.
What’s a fact about the role of wetlands and boreal forests in the global ecosystem that you think would surprise people?

Wetlands provide a vital role in carbon storage. Even though they cover about 5-8% of the Earth’s land surface, studies indicate that they contain a disproportionate amount of our planet’s total soil carbon, about 20-30%. In addition, they are like the arteries and veins of the landscape, acting as water sources and purifiers and helping in flood control. They also protect our shores and harbor large amounts of biodiversity.
Boreal forests are found in the uppermost northern hemisphere (Alaska, most of Canada, Russia, Scandinavia and northern Asia) and account for about 30% of the world’s forest cover. These forests lock up enormous amounts of carbon and help slow the increasing buildup of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere. In their peak growth phase during the northern spring and summer, the worldwide levels of carbon dioxide fall and the worldwide levels of oxygen rise.
Can you describe a typical day on a research trip?

It depends on the research trip. For example, one of my more recent ones was to the Peruvian Amazon where we went upriver on a boat for three weeks on a major tributary of the Amazon River called the Ucuyali River. I was with a team of eight researchers and we were studying the wetland ecosystems of the Pacaya-Samiria Natural Reserve, which entailed making vegetation measurements and assessing inundation extent to validate our scientific findings from satellite observations. We camped for most of the trip and a typical day entailed waking up at around 5:00 am with a symphony of sounds that emerged from the forest, including monkeys. We had breakfast and set off from base camp into the forest (~1 hour walk) to work an 8-9 hour day with a short lunch break (we had packed lunches) at noon. At the end of the day I’d be drenched in sweat, sunscreen, insect repellent, and dust and I’d bathe with water from the river, which was as brown as a milk chocolate bar. It was the most refreshing and cleansing feeling! The day would close with dinner followed with a discussion of the measurements to be collected the following day. Lights were out by 7:30 pm (which seemed like midnight) and I’d re-emerge myself into my tent in the dark tropical night surrounded by the sounds of the forest, until the next morning.
What are some of the most important lessons you’ve learned in life?
That it is important to be patient, humble and thankful.
Do you have any secret skills, talents, or hobbies?
Great question! I do not have any secrete skills or talents but I do have a couple of hobbies. I play the piano, though I am still a novice. I love windsurfing. It is an amazing feeling to skim over the water at fast speeds (I’m also an adrenaline junkie). Finally, I am fascinated by magic card tricks and whenever I have some free time I like to learn a new trick.
What do you enjoy the most about your job?
I enjoy constantly learning about our natural world and how it works. I also really enjoy communicating my work to students and to the general public. I find it especially rewarding when I can educate people and motivate students to consider careers in science.
Erika, thank you for your time and everything you do to keep our home planet safe!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
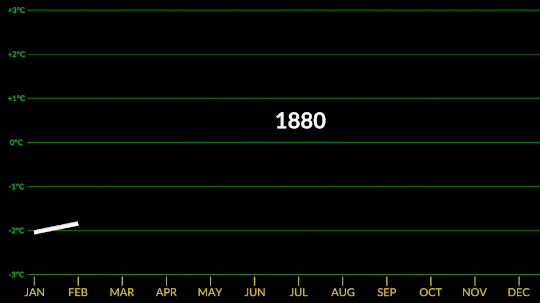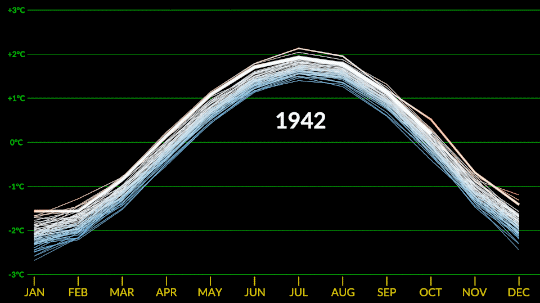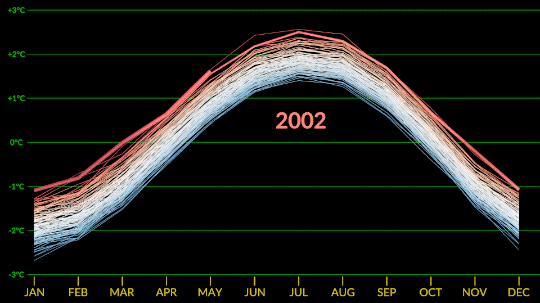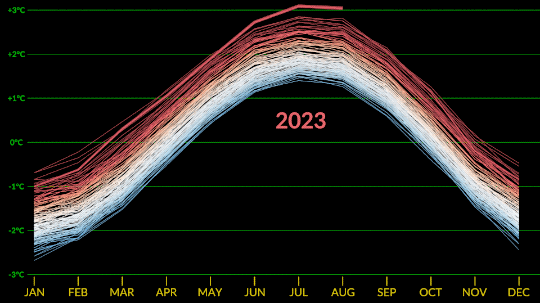
Confirmed: Summer 2023 Hottest in NASA’s Record
All three months of summer 2023 broke records. July 2023 was the hottest month ever recorded, and the hottest July. June 2023 was the hottest June, and August 2023 was the hottest August.
NASA’s temperature record, GISTEMP, starts in 1880, when consistent, modern recordkeeping became possible. Our record uses millions of measurements of surface temperature from weather stations, ships and ocean buoys, and Antarctic research stations. Other agencies and organizations who keep similar global temperature records find the same pattern of long-term warming.
Global temperatures are rising from increased emissions of greenhouse gasses, like carbon dioxide and methane. Over the last 200 years, humans have raised atmospheric CO2 by nearly 50%, primarily through the burning of fossil fuels.
Drivers of climate change, both natural and human-caused, leave distinct fingerprints. Through observations and modeling, NASA researchers confirm that the current warming is the result of human activities, particularly increased greenhouse gas emissions.
Solar System: 5 Things to Know This Week
From Mars to the asteroid belt to Saturn, our hardworking space robots are exploring the solar system. These mechanical emissaries orbit distant worlds or rove across alien landscapes, going places that are too remote or too dangerous for people (for now).
We often show off the pictures that these spacecraft send home, but this week we’re turning that around: here are some of the best pictures of the space robots, taken by other robots (or themselves), in deep space.
1. So Selfless with the Selfies

The Mars Curiosity rover makes breathtaking panoramas of the Martian landscape — and looks good doing it. This mission is famous for the remarkable self portraits of its robotic geologist in action. See more Martian selfies HERE. You can also try this draggable 360 panorama HERE. Find out how the rover team makes these images HERE.
2. Two Spaceships Passing in the Moonlight

In a feat of timing on Jan. 14, 2014, our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter caught a snapshot of LADEE, another robotic spacecraft that was orbiting the moon at the time. LADEE zoomed past at a distance of only about five miles below.
3. Bon Voyage, Galileo

The history-making Galileo mission to Jupiter set sail from the cargo bay of another spacecraft, Space Shuttle Atlantis, on Oct. 18, 1989. Get ready for Juno, which is the next spacecraft to arrive at Jupiter in July.
4. Cometary Close-Up

Using a camera on the Philae lander, the Rosetta spacecraft snapped an extraordinary self portrait at comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko from a distance of about 10 miles. The image captures the side of Rosetta and one of its 14-meter-long solar wings, with the comet in the background. Learn more about Rosetta HERE.
5. Man and Machine

This snapshot captures a remarkable moment in the history of exploration: the one and only time a human met up in space with a robotic forerunner on location. The Surveyor 3 lander helped pave the way for the astronaut footsteps that came a few years later. See the story of Apollo 12 and this unique encounter HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Curiosity Rover: Five Years on Mars
The evening of August 5, 2012…five years ago…our Mars Curiosity rover landed on the Red Planet.

Arriving at Mars at 10:32 p.m. PDT (morning of Aug 6 EDT), this rover would prove to be the most technologically advanced rover ever built.

Curiosity used a series of complicated landing maneuvers never before attempted.

The specialized landing sequence, which employed a giant parachute, a jet-controlled descent vehicle and a daring “sky crane” maneuver similar to rappelling was devised because testing and landing techniques used during previous rover missions could not safely accommodate the much larger and heavier rover.
Curiosity’s mission: To determine whether the Red Planet ever was, or is, habitable to microbial life.

The car-size rover is equipped with 17 cameras, a robotic arm, specialized instruments and an on-board laboratory.

Let’s explore Curiosity’s top 5 discoveries since she landed on Mars five years ago…
1. Gale Crater had conditions suitable for life about 3.5 billion years ago

In 2013, Curiosity’s analysis of a rock sample showed that ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Scientists identified sulfur, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and carbon – some of the key chemical ingredients for life – in the powder Curiosity drilled out of a sedimentary rock near an ancient stream bed in Gale Crater.

Later, in 2014, Curiosity discovered that these conditions lasted for millions of years, perhaps much longer. This interpretation of Curiosity’s findings in Gale Crater suggests ancient Mars maintained a climate that could have produced long-lasting lakes at many locations on the Red Planet.
2. Organic molecules detected at several locations

In 2014, our Curiosity rover drilled into the Martian surface and detected different organic chemicals in the rock powder. This was the first definitive detection of organics in surface materials of Mars. These Martian organics could either have formed on Mars or been delivered to Mars by meteorites.

Curiosity's findings from analyzing samples of atmosphere and rock powder do not reveal whether Mars has ever harbored living microbes, but the findings do shed light on a chemically active modern Mars and on favorable conditions for life on ancient Mars.
3. Present and active methane in Mars’ atmosphere

Also in 2014, our Curiosity rover measured a tenfold spike in methane, an organic chemical, in the atmosphere around the planet. This temporary increase in methane tells us there must be some relatively localized source.

Researchers used Curiosity’s onboard Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) laboratory a dozen times in a 20-month period to sniff methane in the atmosphere. During two of those months, in late 2013 and early 2014, four measurements averaged seven parts per billion.
4. Radiation could pose health risks for humans

Measurements taken by our Curiosity rover since launch have provided us with the information needed to design systems to protect human explorers from radiation exposure on deep-space expeditions in the future. Curiosity’s Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD) was the first instrument to measure the radiation environment during a Mars cruise mission from inside a spacecraft that is similar to potential human exploration spacecraft.

The findings indicate radiation exposure for human explorers could exceed our career limit for astronauts if current propulsion systems are used. These measurements are being used to better understand how radiation travels through deep space and how it is affected and changed by the spacecraft structure itself. This, along with research on the International Space Station are helping us develop countermeasures to the impacts of radiation on the human body.
5. A thicker atmosphere and more water in Mars past

In 2015, Curiosity discovered evidence that has led scientists to conclude that ancient Mars was once a warmer, wetter place than it is today.
To produce this more temperate climate, several researchers have suggested that the planet was once shrouded in a much thicker carbon dioxide atmosphere. You may be asking…Where did all the carbon go?

The solar wind stripped away much of Mars’ ancient atmosphere and is still removing tons of it every day. That said, 3.8 billion years ago, Mars might have had a moderately dense atmosphere, with a surface pressure equal to or less than that found on Earth.
Our Curiosity rover continues to explore the Red Planet today. On average, the rover travels about 30 meters per hour and is currently on the lower slope of Mount Sharp.

Get regular updates on the Curiosity mission by following @MarsCuriosity on Twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 strstruckcomiccsanimeoperator liked this · 3 years ago
strstruckcomiccsanimeoperator liked this · 3 years ago -
 streawberige liked this · 3 years ago
streawberige liked this · 3 years ago -
 john-erby liked this · 3 years ago
john-erby liked this · 3 years ago -
 lightwood-miau liked this · 3 years ago
lightwood-miau liked this · 3 years ago -
 thechaoticgooddoctor liked this · 3 years ago
thechaoticgooddoctor liked this · 3 years ago -
 toc1n0 liked this · 3 years ago
toc1n0 liked this · 3 years ago -
 fandomstalker27 liked this · 3 years ago
fandomstalker27 liked this · 3 years ago -
 barbedwireandfences liked this · 3 years ago
barbedwireandfences liked this · 3 years ago -
 hisokasbungeec-g-um liked this · 3 years ago
hisokasbungeec-g-um liked this · 3 years ago -
 my23456 liked this · 3 years ago
my23456 liked this · 3 years ago -
 newspapergatory liked this · 3 years ago
newspapergatory liked this · 3 years ago -
 toodeepintofandoms liked this · 3 years ago
toodeepintofandoms liked this · 3 years ago -
 souless6 liked this · 3 years ago
souless6 liked this · 3 years ago -
 2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago
2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago -
 ydueyeeggsist liked this · 3 years ago
ydueyeeggsist liked this · 3 years ago -
 partyynextdoorr liked this · 3 years ago
partyynextdoorr liked this · 3 years ago -
 the-lav liked this · 3 years ago
the-lav liked this · 3 years ago -
 maximumskeletonpeanutpickle liked this · 3 years ago
maximumskeletonpeanutpickle liked this · 3 years ago -
 raven-crows-world liked this · 3 years ago
raven-crows-world liked this · 3 years ago -
 doccywhomst liked this · 3 years ago
doccywhomst liked this · 3 years ago -
 certainoperatorghostmonger liked this · 3 years ago
certainoperatorghostmonger liked this · 3 years ago -
 thebctman liked this · 3 years ago
thebctman liked this · 3 years ago -
 bloblikesbleh liked this · 3 years ago
bloblikesbleh liked this · 3 years ago -
 imnotrevealingmyname liked this · 4 years ago
imnotrevealingmyname liked this · 4 years ago -
 chaiipanikam liked this · 4 years ago
chaiipanikam liked this · 4 years ago -
 the-shooting-star liked this · 4 years ago
the-shooting-star liked this · 4 years ago -
 junkthoughtsposts liked this · 4 years ago
junkthoughtsposts liked this · 4 years ago -
 thecosmos25 liked this · 4 years ago
thecosmos25 liked this · 4 years ago -
 miniatureillustrationforanime liked this · 4 years ago
miniatureillustrationforanime liked this · 4 years ago -
 klingons-and-dragons liked this · 4 years ago
klingons-and-dragons liked this · 4 years ago -
 cosmofrog liked this · 5 years ago
cosmofrog liked this · 5 years ago -
 policebox5issherlocked liked this · 7 years ago
policebox5issherlocked liked this · 7 years ago -
 fridakahloblvd liked this · 7 years ago
fridakahloblvd liked this · 7 years ago -
 121yo-u liked this · 7 years ago
121yo-u liked this · 7 years ago -
 neginegiiyahoi liked this · 7 years ago
neginegiiyahoi liked this · 7 years ago -
 justfandomblogstuff liked this · 7 years ago
justfandomblogstuff liked this · 7 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts