Thanks For All Of The Great Questions! Follow Me At @Astro_Jeanette On Twitter and @Jeanette.Epps

Thanks for all of the great questions! Follow me at @Astro_Jeanette on Twitter and @Jeanette.Epps on Instagram, and follow the International Space Station on Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram as I prepare for my mission next year.
More Posts from Nasa and Others

Ever wanted to look back in time? This week, we’re launching a kind of time machine – a telescope so powerful it will help us see back some of the first stars and galaxies made after the Big Bang.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the largest and most advanced telescope we’ve ever put in space. With revolutionary technology, it will study 13.5 billion years of cosmic history and help humanity understand our place in the stars.
Tomorrow, Dec. 25, at 7:20 a.m. ET (12:20 UTC), the Webb Telescope is set to launch from French Guiana, beginning a 29-day journey to a spot a million miles away.
How to Watch:
In English:
Dec. 25
Live coverage starts at 6:00 a.m. ET/11:00 UTC
Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, Twitch
In Spanish:
Dec. 25
Live coverage starts at 6:30 a.m. ET/11:30 UTC
Facebook, YouTube, Twitter
Once Webb launches, the journey has only just begun. The telescope will begin a 2-week-long process of unfolding itself in space before settling in to explore the universe in ways we’ve never seen before.
Follow along on Twitter, Facebook and Instagram and with #UnfoldTheUniverse.
What’s Up for November 2016
What’s Up for November: Venus at sunset, Jupiter at dawn, your last evening glimpse of Saturn until spring, and more meteors!

Through November 3, catch glimpses of a gibbous Venus, a crescent moon and ringed Saturn in the southwest sky just after sunset.

Wake up before sunrise every day this month to see Jupiter just above Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo, shining in the east-southeast sky.
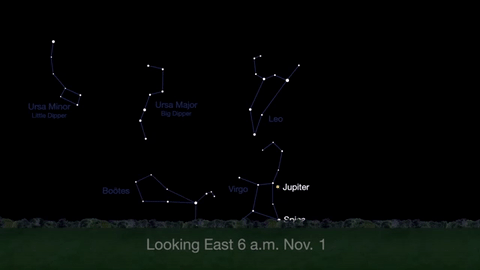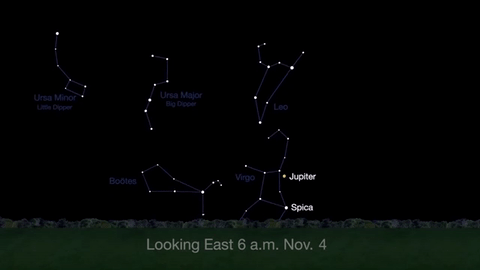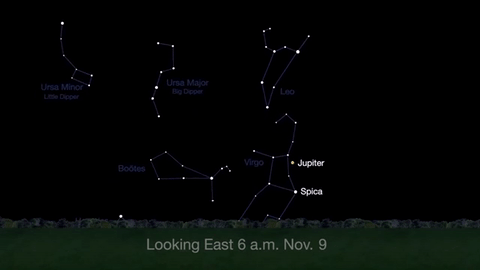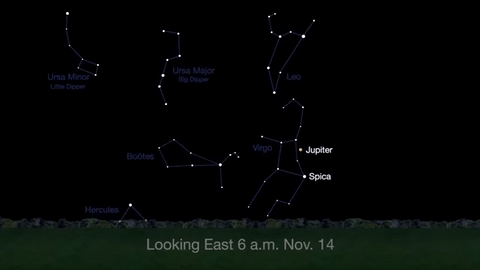
Just before dawn on November 23-24, see the waning crescent moon just above Jupiter.
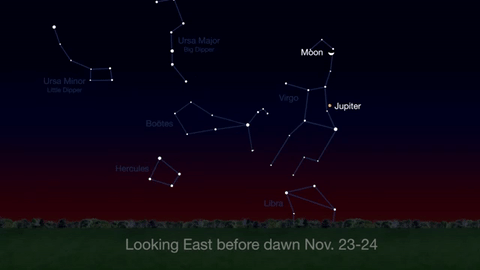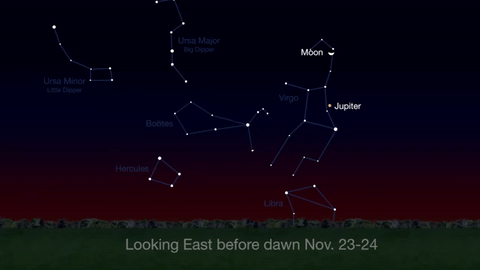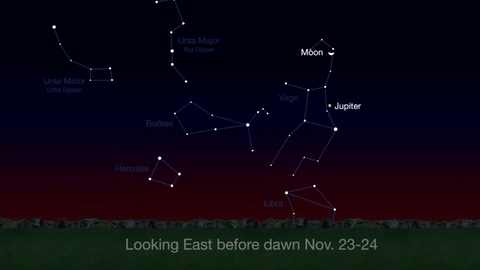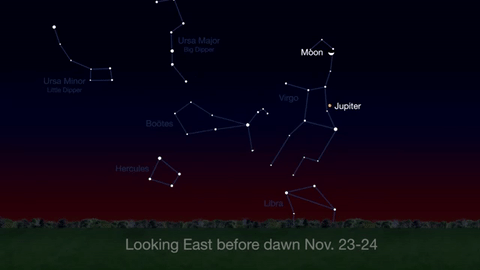
November is a great time to see the constellation Ceres as it glides past Cetus, the Whale and you will be able to see the dwarf planet move relative to the background stars, but you’ll need a telescope for this one.
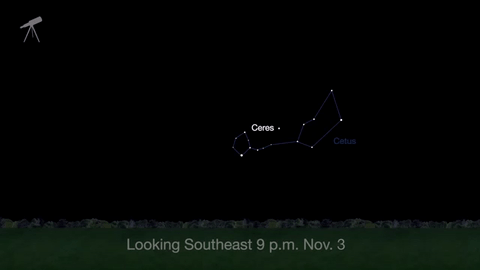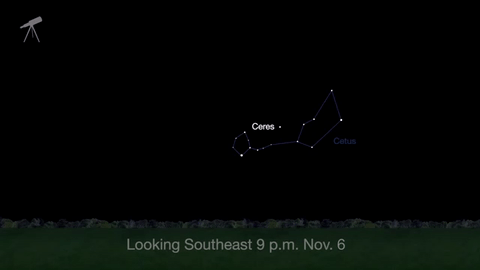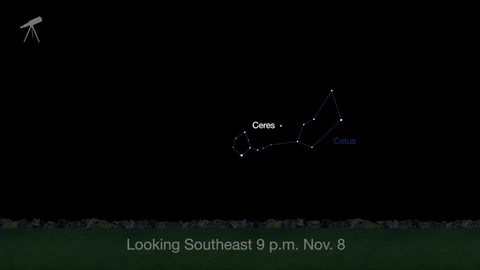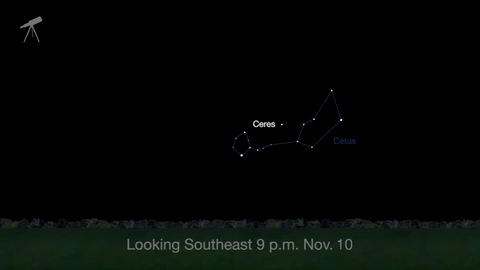
This month, just like last month, there will be three meteor showers--the Northern Tuarids, the Leonids and the November Orionids.

Watch the full November “What’s Up" video for more:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
What's next for NASA? A quick look at some of the big things coming up:
1. We will add to our existing robotic fleet at the Red Planet with the InSight Mars lander set to study the planet's interior.

This terrestrial planet explorer will address one of the most fundamental issues of planetary and solar system science - understanding the processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system (including Earth) more than four billion years ago.
2. The Mars 2020 rover will look for signs of past microbial life, gather samples for potential future return to Earth.

The Mars 2020 mission takes the next step by not only seeking signs of habitable conditions on the Red Planet in the ancient past, but also searching for signs of past microbial life itself. The Mars 2020 rover introduces a drill that can collect core samples of the most promising rocks and soils and set them aside in a "cache" on the surface of Mars.
3. The James Webb Space Telescope will be the premier observatory of the next decade, studying the history of our Universe in infrared.

Webb will study every phase in the history of our Universe, ranging from the first luminous glows after the Big Bang, to the formation of solar systems capable of supporting life on planets like Earth, to the evolution of our own solar system.
4. The Parker Solar Probe will "touch the Sun," traveling closer to the surface than any spacecraft before.

This spacecraft, about the size of a small car, will travel directly into the sun's atmosphere about 4 million miles from our star's surface. Parker Solar Probe and its four suites of instruments – studying magnetic and electric fields, energetic particles, and the solar wind – will be protected from the Sun’s enormous heat by a 4.5-inch-thick carbon-composite heat shield.
5. Our OSIRIS-REx spacecraft arrives at the near-Earth asteroid Bennu in August 2018, and will return a sample for study in 2023.

This mission will help scientists investigate how planets formed and how life began, as well as improve our understanding of asteroids that could impact Earth.
6. Launching in 2018, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will search for planets around 200,000 bright, nearby stars.

The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is the next step in the search for planets outside of our solar system (exoplanets), including those that could support life. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits.
7. A mission to Jupiter's ocean-bearing moon Europa is being planned for launch in the 2020s.

The mission will place a spacecraft in orbit around Jupiter in order to perform a detailed investigation of Europa -- a world that shows strong evidence for an ocean of liquid water beneath its icy crust and which could host conditions favorable for life.
8. We will launch our first integrated test flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, known as Exploration Mission-1.

The Space Launch System rocket will launch with Orion atop it. During Exploration Mission-1, Orion will venture thousands of miles beyond the moon during an approximately three week mission.
9. We are looking at what a flexible deep space gateway near the Moon could be.

We’ve issued a draft announcement seeking U.S. industry-led studies for an advanced solar electric propulsion (SEP) vehicle capability. The studies will help define required capabilities and reduce risk for the 50 kilowatt-class SEP needed for the agency’s near-term exploration goals.
10. Want to know more? Read the full story.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Celebrating Thanksgiving in Space!

Part of the appeal of Thanksgiving is how easily we settle into the familiar: cherished foods, friends and family, and favorite activities like football, puzzles or board games. As anyone who has spent Thanksgiving with someone else’s traditions knows, those familiar things can take on seemingly unusual forms. That’s especially true when you’re 200 miles up in space.
Holidays in space weren’t very common early in the program, but as astronauts start the 20th year of continuous habitation they will also be celebrating the 20th consecutive Thanksgiving in orbit. As it turns out, everything’s the same, but different.
Food
Early in the space program, astronauts didn’t have much choice about their meals. A turkey dinner with all the trimmings was as much a pipe dream in the early 1960s as space travel had been a few decades earlier. Food had to be able to stay fresh, or at least edible, from the time it was packed until the end of the mission, which might be several weeks. It couldn’t be bulky or heavy, but it had to contain all the nutrition an astronaut would need. It had to be easily contained, so crumbs or droplets wouldn’t escape the container and get into the spacecraft instrumentation. For the first flights, that meant a lot of food in tubes or in small bite-sized pieces.

Examples of food from the Mercury program
Chores first, then dinner
Maybe you rake leaves to start the day or straighten up the house for guests. Perhaps you’re the cook. Just like you, astronauts sometimes have to earn their Thanksgiving dinner. In 1974, two members of the Skylab 4 crew started their day with a six-and-a-half hour spacewalk, replacing film canisters mounted outside the spacecraft and deploying an experiment package.
After the spacewalk, the crew could at least “sit down” for a meal together that included food they didn’t have to eat directly from a bag, tube or pouch. In the spacecraft’s “ward room”, a station held three trays of food selected for the astronauts. The trays themselves kept the food warm.

A food tray similar to the ones astronauts used aboard Skylab, showing food, utensils and clean wipes. The tray itself warmed the food.

The ward room aboard Skylab showing the warming trays in use. The Skylab 4 crew ate Thanksgiving dinner there in 1974.
Fresh food
It can’t be all mashed potatoes and pie. There have to be some greens. NASA has that covered with VEGGIE, the ongoing experiment to raise food crops aboard the space station. Though the current crop won’t necessarily be on the Thanksgiving menu, astronauts have already harvested and eaten “space lettuce”. Researchers hope to be growing peppers aboard the space station in 2020.

Astronaut Kjell Lindgren enjoys lettuce grown and harvested aboard the International Space Station.
Football
Space station crews have been able to watch football on Thanksgiving thanks to live feeds from Mission Control. Unfortunately their choices of activities can be limited by their location. That long walk around the neighborhood to shake off the turkey coma? Not happening.

Football in space. It’s a thing.
Be Prepared for the Unplanned
No matter how you plan, there’s a chance something’s going to go wrong, perhaps badly. It happened aboard the Space Shuttle on Thanksgiving 1989. Flight Director Wayne Hale tells of plumbing problem that left Commander Fred Gregory indisposed and vacuum-suctioned to a particular seat aboard the spacecraft.

This is not the seat from which the mission commander flies the Space Shuttle.
Hungry for More?
If you can’t get enough of space food, tune into this episode of “Houston, We Have a Podcast” and explore the delicious science of astronaut mealtime.
And whether you’re eating like a king or one of our astronauts currently living and working in space, we wish everybody a happy and safe Thanksgiving!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Pluto Continues to Amaze

This dwarf planet sure knows how to get a BIG reaction because we’re stunned by the latest images from our New Horizons spacecraft!
Back on July 14, the spacecraft completed it’s historic Pluto flyby, and is now in an intensive downlink phase. During this time, New Horizons will send us some of the best data and images we’ve seen!
These latest images were taken just 15 minutes after New Horizons’ closest approach to Pluto. The spacecraft looked back toward the sun and captured this near-sunset view. Icy mountains, flat plains and the horizon can all be seen in detail.

When we take a closer look, these features truly begin to stand out. Mountains up to 11,000 feet high are met by flat icy plains that extend out to Pluto’s horizon. There, more than a dozen layers of haze in the dwarf planet’s atmosphere can be seen. It’s almost as if we’re flying over the surface with the New Horizons spacecraft.
Speaking of flyover, this new animation of Pluto has been created from images returned from the spacecraft this month. This view shows us what it might be like to take an aerial tour through Pluto’s thin atmosphere and soar above the surface.
These images and videos are not only stunning, but also provide us with important information about the dwarf planet. So far, scientists can tell that the weather changes from day to day on Pluto. These images, combined with others that have been downloaded, provide evidence for a remarkably Earth-like “hydrological” cycle on Pluto.
For updates on the data and images received by the New Horizons spacecraft, check our blog: https://blogs.nasa.gov/pluto/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Black Marble: NASA View Illuminates Earth at Night
When the sun goes down, the lights on Earth shine bright. A new look using our satellite data captures the lights coming from our neighborhoods, vehicles, buildings, factories, fishing vessels and other human activity brightening the night.

Our scientists have just released the first new global map of Earth at night since 2012. This nighttime view of our home planet, dubbed the Black Marble, provides researchers with a unique perspective of human activities around the globe.
By studying Earth at night, researchers can investigate how and why cities expand, monitor light intensity to estimate energy use and economic activity, and aid in disaster response in near-real time.

The data on Earth at night comes from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument on the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite, jointly managed by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
VIIRS captures visible and infrared light, allowing researchers to glimpse the Earth as it looks to astronauts peering out of the International Space Station. The new map is a composite of data collected in 2016, and it took several months of processing to filter out clouds, moonlight, airglow, and other interfering features to create the global image. In the coming months our scientists will release daily nighttime lights data at even finer resolutions for the first time.

The East Coast sparkles with population hubs, suburbs circling cities and major roadways. The I-95 corridor includes the most densely populated region of the United States – the stretch from Washington, DC to Boston.
To get images like these from the satellite data, our scientists had to filter out moonlight, aerosols and other sources of extraneous light – the goal is to eventually be able to detect the lights from a single building or fishing boat.

Daytime satellite images, like this one from Landsat 8, can show us the forests, deserts, mountains, waterways and built-up cities. Add a nighttime view, and scientists can study when and how people are using these limited resources – like the lights tracing the Nile River leading to the metropolis of Cairo, Egypt.

Lights aren’t confined to land. With the global nighttime view, the ocean is dotted with fishing fleets, including boats that try to attract their catch with bright lights.

What lights illuminate your neighborhood? Download a high-resolution version of the Black Marble HERE, and find out more about our new night lights data HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
NASA Sees Our Ocean in Color. How About You?
Take a deep breath. Feel the oxygen in your lungs. We have the ocean to thank for that! Over long time scales, between 50 and 70 percent of our planet's oxygen is produced by microscopic organisms living in the ocean.

Today is World Oceans Day! And as our planet’s climate continues to change, we want to understand how one of our biggest ecosystems is changing with it. Wondering how you can celebrate with NASA? We’ve got downloadable coloring pages and online coloring interactives to show how we study the ocean. Read on.
From Space to Sea

Download ocean missions coloring page here Download Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich coloring page here
We use planes, boats, Earth-observing satellites and much more to study the ocean and partner with organizations all over the world. Here are a few examples:
From Sea
The Export Processes in the Ocean from Remote Sensing (EXPORTS) is one way we study the ocean from the sea to study changes in the ocean’s carbon cycle. In May, scientists and crew conducted research on three ships in the Northern Atlantic Ocean. They hope to create models to better understand climate change patterns.
From Space
Launched last year, the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft began a five-and-a-half-year prime mission to collect the most accurate data yet on global sea level and how our oceans are rising in response to climate change. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is just one of many satellites monitoring the ocean from space. Together with other Earth-observing spacecraft, the mission will also collect precise data of atmospheric temperature and humidity to help improve weather forecasts and climate models.
Finding Eddies

Download Eddies Coloring Page The ocean is full of eddies – swirling water masses that look like hurricanes in the atmosphere. Eddies are often hot spots for biological activity that plays an important role in absorbing carbon. . We find eddies by looking for small changes in the height of the ocean surface, using multiple satellites continuously orbiting Earth. We also look at eddies up close, using ships and planes to study their role in the carbon cycle.
Monitoring Aerosols and Clouds

Clouds coloring interactive here
Aerosols coloring interactive here
Tiny particles in the air called aerosols interact with clouds. These interactions are some of the most poorly understood components of Earth's climate system. Clouds and aerosols can absorb, scatter or reflect incoming radiation -- heat and light from the Sun -- depending on their type, abundance and locations in the atmosphere. We’re building new instruments to better understand aerosols and contribute to air quality forecasts.
The Ocean in Living Color Download PACE coloring page here

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission will continue and greatly advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as Earth’s carbon cycle and atmospheric aerosols and clouds. It’s set to launch in late 2023 to early 2024. Want to learn more? Click here to see how PACE will collect data and here to see what PACE will see through our coloring interactives. (Make sure to check out the hidden surprises in both!)
Exploring Ocean Worlds on Earth and Beyond
Download Clouds coloring page here

Using our understanding of oceans on Earth, we also study oceans on other planets. Mars, for example, contains water frozen in the ice caps or trapped beneath the soil. But there’s even more water out there. Planets and moons in our solar system and beyond have giant oceans on their surface. Saturn’s moon Enceladus is thought to have a massive ocean under its frozen surface, which sometimes sprays into space through massive fissures in the ice.
Learn more about ocean worlds here: nasa.gov/oceanworlds
Interested in learning more about how NASA studies oceans? Follow @NASAClimate, @NASAOcean and @NASAEarth.
You can also find all the coloring pages and interactives here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Mars Helicopter: 6 Things to Know About Ingenuity

When our Perseverance Mars rover lands on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021, it will bring along the Ingenuity helicopter.
This small-but-mighty craft is a technology demonstration that will attempt the first powered, controlled flight on another planet. Its fuselage is about the size of a tissue box, and it weighs about 4 pounds (1.8 kg) on Earth. It started out six years ago as an implausible prospect and has now passed its Earthbound tests.
Here are six things to know about Ingenuity as it nears Mars:
1. Ingenuity is an experimental flight test.

This Mars helicopter is known as a technology demonstration, which is a project that aims to test a new capability for the first time with a limited scope. Previous technology demonstrations include Sojourner, the first Mars rover, and the Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeStats that flew by Mars.
Ingenuity does not carry any science instruments and is not part of Perseverance’s science mission. The only objective for this helicopter is an engineering one – to demonstrate rotorcraft flight in the thin and challenging Martian atmosphere.
2. Mars won’t make it easy for Ingenuity.

Mars’ atmosphere is around 1% the density of Earth’s. Because of that lack of density, Ingenuity has rotor blades that are much larger and spin faster than a helicopter of Ingenuity’s mass here on our planet. It also must be extremely light to travel to Mars.
The Red Planet also has incredibly cold temperatures, with nights reaching minus 130 degrees Fahrenheit (-90 degrees Celsius) in Jezero Crater, where our rover and helicopter will land. Tests on Earth at the predicted temperatures indicate Ingenuity’s parts should work as designed, but the real test will be on Mars.
3. Ingenuity relies on Perseverance for safe passage to Mars and operations on the Martian surface.

Ingenuity is nestled sideways under Perseverance’s belly with a cover to protect the helicopter from debris during landing. The power system on the Mars 2020 spacecraft periodically charges Ingenuity’s batteries during the journey to the Red Planet.
In the first few months after landing, Perseverance will find a safe place for Ingenuity. Our rover will shed the landing cover, rotate the helicopter so its legs face the ground and gently drop it on the Martian surface.
4. Ingenuity is smart for a small robot.

NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory will not be able to control the helicopter with a joystick due to delays communicating with spacecraft across interplanetary distances. That means Ingenuity will make some of its own decisions based on parameters set by its engineering team on Earth.
During flight, Ingenuity will analyze sensor data and images of the terrain to ensure it stays on a flight path designed by project engineers.
5. The Ingenuity team counts success one step at a time.

Ingenuity’s team has a long list of milestones the helicopter must pass before it can take off and land in the Martian atmosphere.
Surviving the journey to and landing on Mars
Safely deploying onto the Martian surface from Perseverance’s belly
Autonomously keeping warm through those intensely cold Martian nights
Autonomously charging itself with its solar panel
Successfully communicating to and from the helicopter via the Mars Helicopter Base Station on Perseverance
6. If Ingenuity succeeds, future Mars exploration could include an ambitious aerial dimension.

The Mars helicopter intends to demonstrate technologies and first-of-its-kind operations needed for flying on Mars. If successful, these technologies and flight experience on another planet could pave the way for other advanced robotic flying vehicles.
Possible uses of a future helicopter on Mars include:
A unique viewpoint not provided by current orbiters, rovers or landers
High-definition images and reconnaissance for robots or humans
Access to terrain that is difficult for rovers to reach
Could even carry light but vital payloads from one site to another
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Around the World 100,000 Times
The International Space Station is a microgravity laboratory in which an international crew of six people live and work while traveling at a speed of five miles per second (or 17,500 miles per hour), orbiting Earth every 90 minutes.
Monday, May 16, marks the International Space Station’s 100,000th orbit!

That’s more than 2,643,342,240 miles traveled! Which is also like 10 round trips to Mars, OR nearly the distance to Neptune!

The space station has been in orbit for over 17 years, and during that time, over 1,922 research investigations have been performed. More than 1,200 scientific results publications have been produced as a result.
Important studies like the VEGGIE experiment, which is working to grow plants in microgravity, and the Twin’s Study, which is studying the impacts of microgravity on the human body, are helping us on our journey to Mars. Using this unique orbiting laboratory as a place to conduct research is helping us learn important things for future deep space missions.

There have even been 222 different people that have visited the space station. This includes the current crew that is working and living on orbit.
Did you know that the space station is the third brightest object in the sky? If you know when and where to look up, you can spot it on your own! Find out when and where to look up HERE.
On Snapchat? Watch today’s Live Story to discover more about the orbiting laboratory and get a tour of the station! You can also add ‘nasa’ on Snapchat to get a regular dose of space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Any advice for young girls going into the sciences?
-
 john-erby liked this · 3 years ago
john-erby liked this · 3 years ago -
 2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago
2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago -
 nousernameuser reblogged this · 4 years ago
nousernameuser reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 komandante liked this · 5 years ago
komandante liked this · 5 years ago -
 mandylee70 liked this · 5 years ago
mandylee70 liked this · 5 years ago -
 sennakm-blog liked this · 6 years ago
sennakm-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 alexisthomps17 liked this · 6 years ago
alexisthomps17 liked this · 6 years ago -
 david03wolfe liked this · 7 years ago
david03wolfe liked this · 7 years ago -
 bigwideblue74 liked this · 7 years ago
bigwideblue74 liked this · 7 years ago -
 oldam reblogged this · 7 years ago
oldam reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 kundankuldeep liked this · 7 years ago
kundankuldeep liked this · 7 years ago -
 kundankuldeep reblogged this · 7 years ago
kundankuldeep reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mitcaelhowell liked this · 7 years ago
mitcaelhowell liked this · 7 years ago -
 indifferent-but-i-care-too-much liked this · 7 years ago
indifferent-but-i-care-too-much liked this · 7 years ago -
 dirtycreekwater liked this · 7 years ago
dirtycreekwater liked this · 7 years ago -
 majesticicecream liked this · 7 years ago
majesticicecream liked this · 7 years ago -
 serenfire liked this · 7 years ago
serenfire liked this · 7 years ago -
 cheesybutgrate liked this · 7 years ago
cheesybutgrate liked this · 7 years ago -
 cumbercrush liked this · 7 years ago
cumbercrush liked this · 7 years ago -
 rightumokay liked this · 7 years ago
rightumokay liked this · 7 years ago -
 dahlinglikeleft reblogged this · 7 years ago
dahlinglikeleft reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 aslanzounder liked this · 7 years ago
aslanzounder liked this · 7 years ago -
 charmedghosts liked this · 7 years ago
charmedghosts liked this · 7 years ago -
 cappuccino-33-blog liked this · 7 years ago
cappuccino-33-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 liviamarly liked this · 7 years ago
liviamarly liked this · 7 years ago -
 hellospaceship-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago
hellospaceship-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago -
 stupendousfartavenue liked this · 7 years ago
stupendousfartavenue liked this · 7 years ago -
 leaharley liked this · 7 years ago
leaharley liked this · 7 years ago -
 oldam liked this · 7 years ago
oldam liked this · 7 years ago -
 oldam reblogged this · 7 years ago
oldam reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 caulfveld liked this · 7 years ago
caulfveld liked this · 7 years ago -
 letslauraantunez liked this · 7 years ago
letslauraantunez liked this · 7 years ago -
 jchapa13 liked this · 7 years ago
jchapa13 liked this · 7 years ago -
 us2626-blog liked this · 7 years ago
us2626-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 fransenteppichfussel-blog liked this · 7 years ago
fransenteppichfussel-blog liked this · 7 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts