Solar System: 10 Things To Know This Week
Solar System: 10 Things to Know This Week
Planets Outside Our Solar System
Let the planet-hunting begin!
Our Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), which will scan the skies to look for planets beyond our solar system—known as exoplanets—is now in Florida to begin preparations for launch in April. Below, 10 Things to know about the many, many unknown planets out there awaiting our discovery.
1—Exo-what?

We call planets in our solar system, well, planets, but the many planets we’re starting to discover outside of our solar system are called exoplanets. Basically, they’re planets that orbit another star.
2—All eyes on TRAPPIST-1.

Remember the major 2016 announcement that we had discovered seven planets 40 light-years away, orbiting a star called TRAPPIST-1? Those are all exoplanets. (Here’s a refresher.)
3—Add 95 new ones to that.

Just last month, our Kepler telescope discovered 95 new exoplanets beyond our solar system (on top of the thousands of exoplanets Kepler has discovered so far). The total known planet count beyond our solar system is now more than 3,700. The planets range in size from mostly rocky super-Earths and fluffy mini-Neptunes, to Jupiter-like giants. They include a new planet orbiting a very bright star—the brightest star ever discovered by Kepler to have a transiting planet.
4—Here comes TESS.

How many more exoplanets are out there waiting to be discovered? TESS will monitor more than 200,000 of the nearest and brightest stars in search of transit events—periodic dips in a star’s brightness caused by planets passing in front—and is expected to find thousands of exoplanets.
5—With a sidekick, too.

Our upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, will provide important follow-up observations of some of the most promising TESS-discovered exoplanets. It will also allow scientists to study their atmospheres and, in some special cases, search for signs that these planets could support life.
6—Prepped for launch.

TESS is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station nearby our Kennedy Space Center in Florida, no earlier than April 16, pending range approval.
7—A groundbreaking find.

In 1995, 51 Pegasi b (also called "Dimidium") was the first exoplanet discovered orbiting a star like our Sun. This find confirmed that planets like the ones in our solar system could exist elsewhere in the universe.
8—Trillions await.

A recent statistical estimate places, on average, at least one planet around every star in the galaxy. That means there could be a trillion planets in our galaxy alone, many of them in the range of Earth’s size.
9—Signs of life.

Of course, our ultimate science goal is to find unmistakable signs of current life. How soon can that happen? It depends on two unknowns: the prevalence of life in the galaxy and a bit of luck. Read more about the search for life.
10—Want to explore the galaxy?

No need to be an astronaut. Take a trip outside our solar system with help from our Exoplanet Travel Bureau.
Read the full version of this week’s ‘10 Things to Know’ article HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Is your health affected from being in outer space?
NASA’s 60th Anniversary: Trailblazing Technology
Technology drives exploration. For 60 years, we have advanced technology to meet the rigorous needs of our missions. From GPS navigation to water filtration systems, our technologies developed for space improve your daily life on Earth. We continue to innovate and explore. Since we opened for business on Oct. 1, 1958, our history tells a story of exploration, innovation and discoveries. The next 60 years, that story continues. Learn more: https://www.nasa.gov/60
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What’s Up in December 2020 – Skywatching Tips from NASA!
Catch the Geminids meteor shower as the peak coincides with darker skies during a new Moon. Plus, Jupiter and Saturn appear closer than in decades, and the winter solstice arrives. Check this out for when and where to observe! Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
How will Cygnus Spacecraft Dock to Space Station?
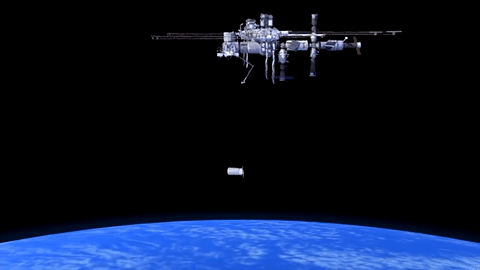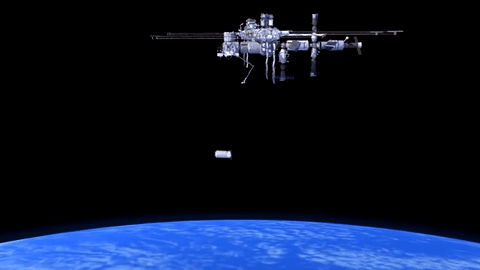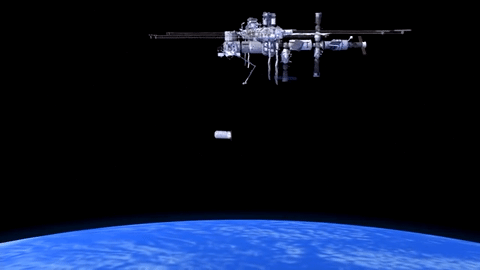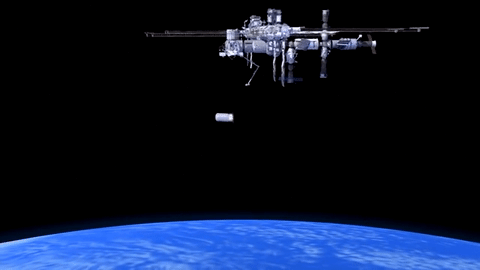
Orbital ATK’s Cygnus CRS-6 spacecraft launched to the International Space Station on March 22.
Cygnus will carry almost 7,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
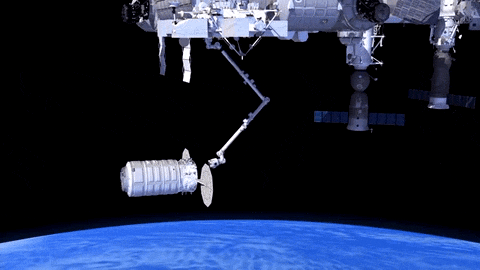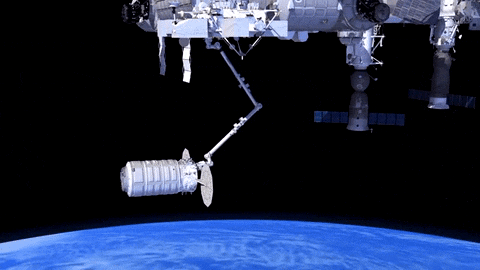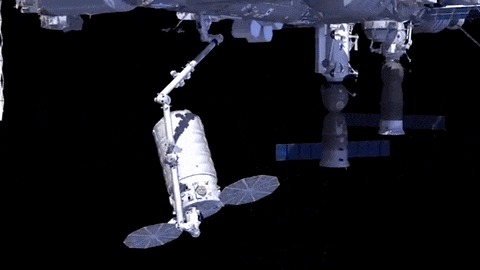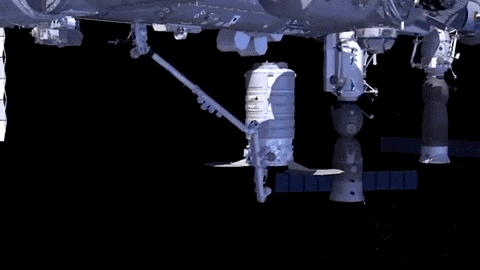
After launch in Florida, the spacecraft will arrive to the station on Saturday, March 26. Upon arrival, NASA astronaut and Expedition 46 Commander Tim Kopra will capture Cygnus at about 6:40 a.m. using the space station's Canadarm2 robotic arm to take hold of the spacecraft. Astronaut Tim Peake of ESA (European Space Agency) will support Kopra in a backup position.
Installation (when Cygnus is connected to space station) is expected to begin at 9:25 a.m. NASA TV coverage for installation resumes at 9:15 a.m.

After the Cygnus spacecraft is berthed (connected) to the space station, the contents will be emptied and brought inside for use. Any trash that is on the space station, can be put inside the empty Cygnus before it is undocked from station and sent to burn up in Earth’s atmosphere.
Watch Capture
You can watch the capture of Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft online. Stream live coverage starting at 5:30 a.m. EDT on Saturday, March 26. Capture is scheduled for 6:40 a.m.
Tune in again at 9:15 a.m. to watch #Cygnus installation to the station.
Watch online: nasa.gov/nasatv
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, let us break it down for you. Here are a few things to know this week:
1. Juno Eyes on Jupiter

After a journey of more than five years, the Juno spacecraft is ready for its detailed look at Jupiter—arrival date: July 4. Using Eyes on the Solar System and data from the Juno flight team, you can take a virtual ride onboard the spacecraft in the "Eyes on Juno" simulation.
2. Taking a Spacecraft for a Spin

Preparations for the launch of the OSIRIS-REx asteroid mission are spinning up, literally. Here, the spacecraft can be seen rotating on a spin table during a weight and center of gravity verification test at our Kennedy Space Center. Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 8. This spacecraft will travel to a near-Earth asteroid called Bennu and bring a small sample back to Earth for study.
3. Long-Range (Or at Least Long-Distance) Weather Report
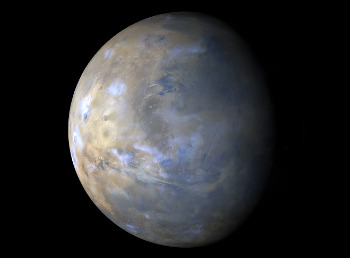
Our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter acquires a global view of the red planet and its weather every day. Last week, dust storms continued along the south polar ice cap edge. Northern portions of Sirenum, Solis, and Noachis also experienced some local dust-lifting activity. A large dust storm propagated eastward over the plains of Arcadia at the beginning of the week, but subsided just a few days later over Acidalia.
4. Hello from the Dark Side

The New Horizons spacecraft took this stunning image of Pluto only a few minutes after closest approach in July 2015, with the sun on the other side of Pluto. Sunlight filters through Pluto's complex atmospheric haze layers. Looking back at Pluto with images like this gives New Horizons scientists information about Pluto's hazes and surface properties that they can't get from images taken on approach.
5. A Titanic Encounter

On June 7, our Cassini orbiter will fly very close by Saturn's giant, haze-shrouded moon Titan. Among the targets of its observations will be the edge of the vortex that swirls in Titan's thick atmosphere near its south pole.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Say hello to the Eskimo Nebula 👋
This nebula began forming about 10,000 years ago when a dying star started flinging material into space. When Sun-like stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, they become unstable and blast their outer layers of gas away into space (bad news for any planets in the area). This Hubble Space Telescope image shows a snapshot of the unworldly process.
Streams of high-energy ultraviolet radiation cause the expelled material to glow, creating a beautiful planetary nebula — a term chosen for the similarity in appearance to the round disk of a planet when viewed through a small telescope.
The Eskimo Nebula got its nickname because it resembles a face surrounded by a fur parka. The “parka” is a disk of material embellished by a ring of comet-shaped objects with their tails streaming away from the central, dying star. In the middle of the nebula is a bubble of material that is being blown outward by the star’s intense “wind” of high-speed material.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
On Monday, August 21, 2017, our nation will be treated to a total eclipse of the Sun. The eclipse will be visible – weather permitting – across all of North America. The entire continent will experience at least a partial eclipse lasting two to three hours. Halfway through the event, anyone within a 60 to 70 mile-wide path from Oregon to South Carolina will experience a total eclipse. During those brief moments when the moon completely blocks the Sun's bright face for 2+ minutes, day will turn into night, making visible the otherwise hidden solar corona, the Sun's outer atmosphere. Bright stars and planets will become visible as well. This is truly one of nature's most awesome sights. The eclipse provides a unique opportunity to study the Sun, Earth, Moon and their interaction because of the eclipse's long path over land coast to coast.
Scientists will be able to take ground-based and airborne observations over a period of about 90 minutes to complement the wealth of data provided by NASA assets.
Watch this and other eclipse videos on our YouTube channel: https://youtu.be/8jaxiha8-rY?list=PL_8hVmWnP_O2oVpjXjd_5De4EalioxAUi
To learn all about the 2017 Total Eclipse: https://eclipse2017.nasa.gov/
Music credit: Ascending Lanterns by Philip Hochstrate
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
🔎 Lava Lake Discovery
🌋 Raikoke Volcano Eruption
🔥 Uptick in Amazon Fire Activity
2019 brought many memorable events on Planet Earth, and NASA satellites and astronauts captured a lot of the action! From new discoveries to tracking natural events and capturing amazing scenery, here are a few highlights from around the globe.
Read more about the images in this video, here.
@paleskeletonuniversitypizza: How does it feel to experience weightlessness for the first time?
Which do you think you'll miss more after your first trip? Space when you're back on Earth or Earth when you're up in Space?
I think that I will miss space when I’m back on Earth. One astronaut when she returned said that gravity sucks, so I’m looking forward to finding out what that’s like.
-
 bizarere liked this · 3 months ago
bizarere liked this · 3 months ago -
 greatgayteensologothbasketball liked this · 3 years ago
greatgayteensologothbasketball liked this · 3 years ago -
 massagemental40-blog liked this · 3 years ago
massagemental40-blog liked this · 3 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts