Look! A Cosmic Block Party 🥳 In This Hubble Image, You’ll Find 50 Spiral And Dwarf Galaxies Hanging
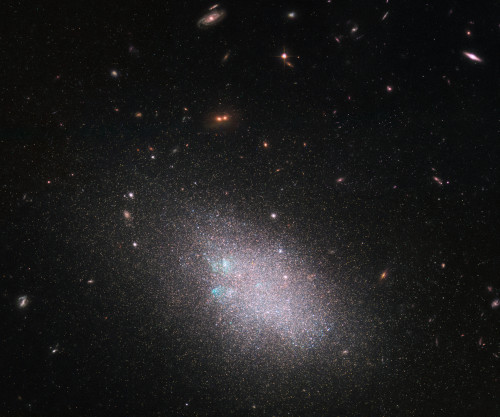

Look! A cosmic block party 🥳 In this Hubble image, you’ll find 50 spiral and dwarf galaxies hanging out in our cosmic neighborhood. The main focal point of stars is actually a dwarf galaxy. Dwarf galaxies often show a hazy structure, an ill-defined shape and an appearance somewhat akin to a swarm or cloud of stars — and UGC 685 is no exception to this. These data were gathered under Hubble’s Legacy ExtraGalactic UV Survey (LEGUS) program, the sharpest and most comprehensive ultraviolet survey of star-forming galaxies in the nearby universe. Image Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA; the LEGUS team, B. Tully, D. Calzetti
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
The Artemis Story: Where We Are Now and Where We’re Going

Using a sustainable architecture and sophisticated hardware unlike any other, the first woman and the next man will set foot on the surface of the Moon by 2024. Artemis I, the first mission of our powerful Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft, is an important step in reaching that goal.
As we close out 2019 and look forward to 2020, here’s where we stand in the Artemis story — and what to expect in 2020.
Cranking Up The Heat on Orion
The Artemis I Orion spacecraft arrived at our Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, on Tuesday, Nov. 26 for in-space environmental testing in preparation for Artemis I.
This four-month test campaign will subject the spacecraft, consisting of its crew module and European-built service module, to the vacuum, extreme temperatures (ranging from -250° to 300° F) and electromagnetic environment it will experience during the three-week journey around the Moon and back. The goal of testing is to confirm the spacecraft’s components and systems work properly under in-space conditions, while gathering data to ensure the spacecraft is fit for all subsequent Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. This is the final critical step before the spacecraft is ready to be joined with the Space Launch System rocket for this first test flight in 2020!
Bringing Everyone Together

On Dec. 9, we welcomed members of the public to our Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans for #Artemis Day and to get an up-close look at the hardware that will help power our Artemis missions. The 43-acre facility has more than enough room for guests and the Artemis I, II, and III rocket hardware! NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine formally unveiled the fully assembled core stage of our SLS rocket for the first Artemis mission to the Moon, then guests toured of the facility to see flight hardware for Artemis II and III. The full-day event — complete with two panel discussions and an exhibit hall — marked a milestone moment as we prepare for an exciting next phase in 2020.
Rolling On and Moving Out

Once engineers and technicians at Michoud complete functional testing on the Artemis I core stage, it will be rolled out of the Michoud factory and loaded onto our Pegasus barge for a very special delivery indeed. About this time last year, our Pegasus barge crew was delivering a test version of the liquid hydrogen tank from Michoud to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville for structural testing. This season, the Pegasus team will be transporting a much larger piece of hardware — the entire core stage — on a slightly shorter journey to the agency’s nearby Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi.
Special Delivery

Why Stennis, you ask? The giant core stage will be locked and loaded into the B2 Test Stand there for the landmark Green Run test series. During the test series, the entire stage, including its extensive avionics and flight software systems, will be tested in full. The series will culminate with a hot fire of all four RS-25 engines and will certify the complex stage “go for launch.” The next time the core stage and its four engines fire as one will be on the launchpad at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Already Working on Artemis II

As Orion and SLS make progress toward the pad for Artemis I, employees at NASA centers and large and small companies across America are hard at work assembling and manufacturing flight hardware for Artemis II and beyond. The second mission of SLS and Orion will be a test flight with astronauts aboard that will go around the Moon before returning home. Our work today will pave the way for a new generation of moonwalkers and Artemis explorers.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Cracking Earth’s Carbon Puzzle
It’s a scientific conundrum with huge implications for our future: How will our planet react to increasing levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?

Carbon – an essential building block for life – does not stay in one place or take only one form. Carbon, both from natural and human-caused sources, moves within and among the atmosphere, ocean and land.

We’ve been a trailblazer in using space-based and airborne sensors to observe and quantify carbon in the atmosphere and throughout the land and ocean, working with many U.S. and international partners.

Our Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) is making unprecedented, accurate global measurements of carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere and providing unique information on associated natural processes.

ABoVE, our multi-year field campaign in Alaska and Canada is investigating how changes in Arctic ecosystems such as boreal forests in a warming climate result in changes to the balance of carbon moving between the atmosphere and land.

This August we’re embarking on an ocean expedition with the National Science Foundation to the northeast Pacific called EXPORTS that will help scientists develop the capability to better predict how carbon in the ocean moves, which could change as Earth’s climate changes.

ECOSTRESS is slated to launch this summer to the International Space Station to make the first-ever measurements of plant water use and vegetation stress on land – providing key insights into how plants link Earth’s global carbon cycle with its water cycle.

Later this year, ECOSTRESS will be joined on the space station by GEDI, which will use a space borne laser to help estimate how much carbon is locked in forests and how that quantity changes over time.

In early 2019, the OCO-3 instrument is scheduled to launch to the space station to complement OCO-2 observations and allow scientists to probe the daily cycle of carbon dioxide exchange processes over much of the Earth.

And still in the early stages of development is the Geostationary Carbon Cycle Observatory (GeoCarb) satellite, planned to launch in the early 2020s. GeoCarb will collect 10 million observations a day of carbon dioxide, methane and carbon monoxide.

Our emphasis on carbon cycle science and the development of new carbon-monitoring tools is expected to remain a top priority for years to come. READ MORE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
We’re Landing a Rover on Mars in 2020…But How Do We Decide Where?
In 2020, we will launch our next Mars rover. It will journey more than 33 million miles to the Red Planet where it will land, explore and search for signs of ancient microbial life. But how do we pinpoint the perfect location to complete this science…when we’re a million miles away on Earth?

We utilize data sent to us by spacecraft on and orbiting Mars. That includes spacecraft that have recorded data in the past.
This week, hundreds of scientists and Mars enthusiasts are gathering to deliberate the four remaining options for where we’re going to land the Mars 2020 rover on the Red Planet.

The landing site for Mars 2020 is of great interest to the planetary community because, among the rover's new science gear for surface exploration, it carries a sample system that will collect rock and soil samples and set them aside in a "cache" on the surface of Mars. A future mission could potentially return these samples to Earth. The next Mars landing, after Mars 2020, could very well be a vehicle which would retrieve these Mars 2020 samples.
Here's an overview of the potential landing sites for our Mars 2020 rover…
Northeast Syrtis

This area was once warmed by volcanic activity. Underground heat sources made hot springs flow and surface ice melt. Microbes could have flourished here in liquid water that was in contact with minerals. The layered terrain there holds a rich record of interactions between water and minerals over successive periods of early Mars history.
Jezero Crater

This area tells a story of the on-again, off-again nature of the wet past of Mars. Water filled and drained away from the crater on at least two occasions. More than 3.5 billion years ago, river channels spilled over the crater wall and created a lake. Scientists see evidence that water carried clay minerals from the surrounding area into the crater after the lake dried up. Conceivably, microbial life could have lived in Jezero during one or more of these wet times. If so, signs of their remains might be found in lakebed sediments.
Columbia Hills

At this site, mineral springs once bubbled up from the rocks. The discovery that hot springs flowed here was a major achievement of the Mars Exploration Rover, Spirit. The rover’s discovery was an especially welcome surprise because Spirit had not found signs of water anywhere else in the 100-mile-wide Gusev Crater. After the rover stopped working in 2010, studies of its older data records showed evidence that past floods may have formed a shallow lake in Gusev.
Midway

Candidate landing sites Jezero and Northeast Syrtis are approximately 37 km apart…which is close enough for regional geologic similarities to be present, but probably too far for the Mars 2020 rover to travel. This midway point allows exploration of areas of both landing sites.

How Will We Select a Site?
The team is gathered this week for the fourth time to discuss these locations. It'll be the final workshop in a series designed to ensure we receive the best and most diverse range of information and opinion from the scientific community before deciding where to send our newest rover.
The Mars 2020 mission is tasked with not only seeking signs of ancient habitable conditions on Mars, but also searching for signs of past microbial life itself. So how do we choose a landing site that will optimize these goals? Since InSight is stationary and needs a flat surface to deploy its instruments, we’re basically looking for a flat, parking lot area on Mars to land the spacecraft.

The first workshop started with about 30 candidate landing sites and was narrowed down to eight locations to evaluate further. At the end of the third workshop in February 2017, there were only three sites on the radar as potential landing locations…
…but in the ensuing months, a proposal came forward for a landing site that is in between Jezero and Northeast Syrtis – The Midway site. Since our goal is to get to the right site that provides the maximum science, this fourth site was viewed as worthy of being included in the discussions.
Now, with four sites remaining, champions for each option will take their turn at the podium, presenting and defending their favorite spot on the Red Planet.

On the final day, after all presentations have concluded, workshop participants will weigh the pros and cons of each site. The results of these deliberations will be provided to the Mars 2020 Team, which will incorporate them into a recommendation to NASA Headquarters. A final selection will be made and will likely be announced by the end of the year.
To get more information about the workshop, visit: https://marsnext.jpl.nasa.gov/workshops/wkshp_2018_10.cfm
Learn more about our Mars 2020 rover HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Hot & Steamy RS-25 Engine Test

Today, we tested the RS-25 engine at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi, and boy was it hot! Besides the fact that it was a hot day, the 6,000 degree operating temperature of the hot fire test didn’t help things. This engine is one of four that will power the core stage of our Space Launch System (SLS) into deep space and to Mars. Today’s test reached 109% power and burned 150,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and 60,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen. When SLS launches with all 4 of its engines, it will be the most powerful rocket in the world!

This engine was previously used to to fly dozens of successful missions on the space shuttle, so you might be asking, “Why are we spending time testing it again if we already know it’s awesome?” Well, it’s actually really important that we test them specifically for use with SLS for a number of reasons, including the fact that we will be operating at 109% power, vs. the 104% power previously used.

If you missed the 535-second, ground rumbling test today -- you’re in luck. We’ve compiled all the cool stuff (fire, steam & loud noises) into a recap video. Check it out here:
The Abyss of Time

Scotland is part of the bedrock of geology, so to speak.
In the late 18th century, Scottish farmer and scientist James Hutton helped found the science of geology. Observing how wind and water weathered rocks and deposited layers of soil at his farm in Berwickshire, Hutton made a conceptual leap into a deeper and expansive view of time. After spending decades observing the processes of erosion and sedimentation, and traveling the Scottish countryside in search of fossils, stream cuts and interesting rock formations, Hutton became convinced that Earth had to be much older than 6,000 years, the common belief in Western civilization at the time.
In 1788, a boat trip to Siccar Point, a rocky promontory in Berwickshire, helped crystallize Hutton’s view. The Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 acquired this image of the area on June 4, 2018, top. A closer view of Siccar Point is below.

At Siccar Point, Hutton was confronted with the juxtaposition of two starkly different types of rock—a gently sloping bed of young red sandstone that was over a near vertical slab of older graywacke that had clearly undergone intensive heating, uplift, buckling, and folding. Hutton argued to his two companions on the boat that the only way to get the two rock formations jammed up against one another at such an odd angle was that an enormous amount of time must have elapsed between when they had been deposited at the bottom of the ocean.
He was right.
Read more: https://go.nasa.gov/2OBnyJ8
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Is the earth really as beautiful as they say from space?
You don't necessarily need fancy equipment to watch one of the sky's most awesome shows: a solar eclipse. With just a few simple supplies, you can make a pinhole camera that allows you to view the event safely and easily. Before you get started, remember: You should never look at the Sun directly without equipment that's specifically designed for solar viewing. Do not use standard binoculars or telescopes to watch the eclipse, as the light could severely damage your eyes. Sunglasses also do NOT count as protection when attempting to look directly at the Sun. Stay safe and still enjoy the Sun's stellar show by creating your very own pinhole camera. It's easy!
See another pinhole camera tutorial at https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/edu/learn/project/how-to-make-a-pinhole-camera/
Watch this and other eclipse videos on our YouTube channel: https://youtu.be/vWMf5rYDgpc?list=PL_8hVmWnP_O2oVpjXjd_5De4EalioxAUi
A pinhole camera is just one of many viewing options. Learn more at https://eclipse2017.nasa.gov/safety
Music credit: Apple of My Eye by Frederik Wiedmann
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
5 Things You Didn’t Know About Astronaut Shane Kimbrough!
After years of training NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough is launching to the International Space Station on Wednesday, so there’s not much left to say, right? Wrong! Here are five secrets about his past that the Texas native and retired Army officer hasn’t told us, until now.
1. Shane went to elementary school in Germany

But his family returned to the U.S. where he attended middle and high school.
2. Life is Smyrna, Georgia

Shane attended middle and high school in the Atlanta suburb of Smyrna with movie star Julia Roberts!
3. Shane had an accomplished military career

A retired Army colonel, Shane graduated from West Point, after which he became an Army aviator. He later became a jumpmaster and has had a long and distinguished military career.
Read his bio.
4. He loves sports. All sports!

He LOVES playing, coaching and watching sports. Watching college football is one of the things he’ll miss while he’s on the station.
5. Leading the future

His passion for teaching is one that he finds “most rewarding.”
Follow Shane on the station at @astro_kimbrough.
Learn more about missions to the International Space Station HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Rare & Record-Breaking Black Holes
While even the most “normal” black hole seems exotic compared to the tranquil objects in our solar system, there are some record-breaking oddballs. Tag along as we look at the biggest, closest, farthest, and even “spinniest” black holes discovered in the universe … that we know of right now!

Located 700 million light-years away in the galaxy Holmberg 15A, astronomers found a black hole that is a whopping 40 billion times the mass of the Sun — setting the record for the biggest black hole found so far. On the other hand, the smallest known black hole isn’t quite so easy to pinpoint. There are several black holes with masses around five times that of our Sun. There’s even one candidate with just two and a half times the Sun’s mass, but scientists aren’t sure whether it’s the smallest known black hole or actually the heaviest known neutron star!

You may need to take a seat for this one. The black hole GRS 1915+105 will make you dizzier than an afternoon at an amusement park, as it spins over 1,000 times per second! Maybe even more bizarre than how fast this black hole is spinning is what it means for a black hole to spin at all! What we're actually measuring is how strongly the black hole drags the space-time right outside its event horizon — the point where nothing can escape. Yikes!

If you’re from Earth, the closest black hole that we know of right now, Mon X-1 in the constellation Monoceros, is about 3,000 light-years away. But never fear — that’s still really far away! The farthest known black hole is J0313-1806. The light from its surroundings took a whopping 13 billion years to get to us! And with the universe constantly expanding, that distance continues to grow.

So, we know about large (supermassive, hundreds of thousands to billions of times the Sun's mass) and small (stellar-mass, five to dozens of times the Sun's mass) black holes, but what about other sizes? Though rare, astronomers have found a couple that seem to fit in between and call them intermediate-mass black holes. As for tiny ones, primordial black holes, there is a possibility that they were around when the universe got its start — but there’s not enough evidence so far to prove that they exist!

One thing that’s on astronomers’ wishlist is to see two supermassive black holes crashing into one another. Unfortunately, that event hasn’t been detected — yet! It could be only a matter of time before one reveals itself.

Though these are the records now, in early 2021 … records are meant to be broken, so who knows what we’ll find next!
Add some of these records and rare finds to your black hole-watch list, grab your handy-dandy black hole field guide to learn even more about them — and get to searching!
Keep up with NASA Universe on Facebook and Twitter where we post regularly about black holes.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What are CubeSats?
CubeSats are a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. They provide low-cost opportunities for small satellite payloads to fly on rockets planned for upcoming launches. Small satellites, including CubeSats, are playing an increasingly larger role in exploration, technology demonstration, scientific research and educational investigations here at NASA.

Fourteen miniature satellites were deployed from the International Space Station earlier this week. Two of the CubeSats were Danish and have communication and ship signal tracking capabilities. The remaining are Dove satellites from Planet Labs and will take images of Earth from space.
On Thursday, Oct. 8, thirteen CubeSats are scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 8:49 a.m. EDT. Watch live on NASA TV starting at 8:29 a.m. http://www.nasa.gov/nasatv
To learn more about tomorrow’s launch, watch NASA Television today, Oct. 7 at 1 p.m. and 2 p.m. EDT. The briefings will highlight the growing importance of CubeSats in space exploration.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 souless6 liked this · 3 years ago
souless6 liked this · 3 years ago -
 wanderinginthecosmos liked this · 3 years ago
wanderinginthecosmos liked this · 3 years ago -
 qualityinternetphilosopher liked this · 3 years ago
qualityinternetphilosopher liked this · 3 years ago -
 aleeutr liked this · 3 years ago
aleeutr liked this · 3 years ago -
 vinniepoooh liked this · 3 years ago
vinniepoooh liked this · 3 years ago -
 nlockett reblogged this · 4 years ago
nlockett reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 nlockett liked this · 4 years ago
nlockett liked this · 4 years ago -
 thistrashisreadytobash liked this · 4 years ago
thistrashisreadytobash liked this · 4 years ago -
 way-too-indecisive liked this · 4 years ago
way-too-indecisive liked this · 4 years ago -
 selfc0ntr0ls liked this · 4 years ago
selfc0ntr0ls liked this · 4 years ago -
 heythereokaybye liked this · 4 years ago
heythereokaybye liked this · 4 years ago -
 absinthiion liked this · 4 years ago
absinthiion liked this · 4 years ago -
 emotsuki liked this · 4 years ago
emotsuki liked this · 4 years ago -
 whatshehassaid liked this · 4 years ago
whatshehassaid liked this · 4 years ago -
 starlightmeissa-main liked this · 5 years ago
starlightmeissa-main liked this · 5 years ago -
 cinnabunsprincess liked this · 5 years ago
cinnabunsprincess liked this · 5 years ago -
 neptunic-loser liked this · 5 years ago
neptunic-loser liked this · 5 years ago -
 visionazul reblogged this · 5 years ago
visionazul reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 caffeinatedvampireslayer liked this · 5 years ago
caffeinatedvampireslayer liked this · 5 years ago -
 moon-icarus liked this · 5 years ago
moon-icarus liked this · 5 years ago -
 unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago
unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago -
 catyuy reblogged this · 5 years ago
catyuy reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 elysiabot reblogged this · 5 years ago
elysiabot reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mmamadi liked this · 5 years ago
mmamadi liked this · 5 years ago -
 yeseriquita reblogged this · 5 years ago
yeseriquita reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 b4byghoull-blog liked this · 5 years ago
b4byghoull-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 xwxterfxll liked this · 5 years ago
xwxterfxll liked this · 5 years ago -
 chopinspre reblogged this · 5 years ago
chopinspre reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 bstormhands reblogged this · 5 years ago
bstormhands reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 stickoflicorice reblogged this · 5 years ago
stickoflicorice reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 imalesca liked this · 5 years ago
imalesca liked this · 5 years ago -
 zympz liked this · 5 years ago
zympz liked this · 5 years ago -
 thedankmemeconnoisseur liked this · 5 years ago
thedankmemeconnoisseur liked this · 5 years ago -
 yourbestdream liked this · 5 years ago
yourbestdream liked this · 5 years ago -
 lynfantasy liked this · 5 years ago
lynfantasy liked this · 5 years ago -
 shinygoku liked this · 5 years ago
shinygoku liked this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts