What's Your Favorite Part Of The Job?
What's your favorite part of the job?
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Behold—the space station of the future! (…from 1973)

This artist’s concept gives a cutaway view of the Skylab orbital workshop, which launched 50 years ago on May 14, 1973. Established in 1970, the Skylab Program's goals were to enrich our scientific knowledge of Earth, the sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials in the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth-resource observations.
Three crews visited Skylab and carried out 270 scientific and technical investigations in the fields of physics, astronomy, and biological sciences. They also proved that humans could live and work in outer space for extended periods of time, laying the groundwork for the International Space Station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
As an astronaut who has been on a spacewalk before, what does the all-woman spacewalk mean to you?
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
There’s even more to Mars.

1. Batten Down the Hatches
Good news for future astronauts: scientists are closer to being able to predict when global dust storms will strike the Red Planet. The winds there don't carry nearly the same force that was shown in the movie "The Martian," but the dust lofted by storms can still wreak havoc on people and machines, as well as reduce available solar energy. Recent studies indicate a big storm may be brewing during the next few months.
+ Get the full forecast

2. Where No Rover Has Gone Before
Our Opportunity Mars rover will drive down an ancient gully that may have been carved by liquid water. Several spacecraft at Mars have observed such channels from a distance, but this will be the first up-close exploration. Opportunity will also, for the first time, enter the interior of Endeavour Crater, where it has worked for the last five years. All this is part of a two-year extended mission that began Oct. 1, the latest in a series of extensions going back to the end of Opportunity's prime mission in April 2004. Opportunity landed on Mars in January of that year, on a mission planned to last 90 Martian days (92.4 Earth days). More than 12 Earth years later, it's still rolling.
+ Follow along + See other recent pictures from Endeavour Crater

3. An Uphill Climb
Opportunity isn't the only NASA Mars rover getting a mission extension. On the other side of the planet, the Curiosity rover is driving and collecting samples amid some of the most scenic landscapes ever visited on Mars. Curiosity's two-year mission extension also began Oct. 1. It's driving toward uphill destinations, including a ridge capped with material rich in the iron-oxide mineral hematite, about a mile-and-a-half (two-and-a-half kilometers) ahead. Beyond that, there's an exposure of clay-rich bedrock. These are key exploration sites on lower Mount Sharp, which is a layered, Mount-Rainier-size mound where Curiosity is investigating evidence of ancient, water-rich environments that contrast with the harsh, dry conditions on the surface of Mars today.
+ Learn more

4. Keep a Sharp Lookout
Meanwhile, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter continues its watch on the Red Planet from above. The mission team has just released a massive new collection of super-high-resolution images of the Martian surface.
+ Take a look

5. 20/20 Vision for the 2020 Rover
In the year 2020, Opportunity and Curiosity will be joined by a new mobile laboratory on Mars. In the past week, we tested new "eyes" for that mission. The Mars 2020 rover's Lander Vision System helped guide the rocket to a precise landing at a predesignated target. The system can direct the craft toward a safe landing at its primary target site or divert touchdown toward better terrain if there are hazards in the approaching target area.
+ Get details
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
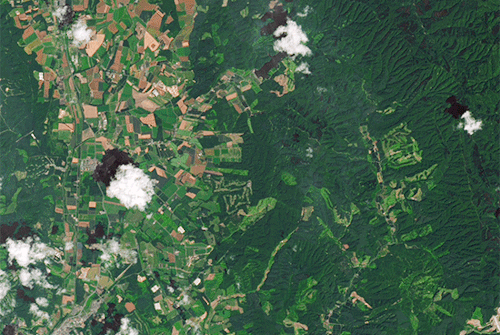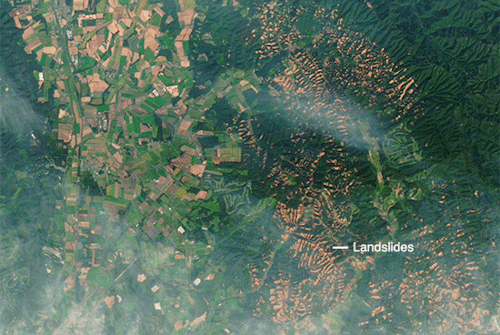
Landslides in Japan
On Sept. 6, 2018, shortly after the remnants of Typhoon Jebi drenched southern Hokkaido, a powerful earthquake rattled the Japanese island. The 6.6-magnitude quake shook the surface enough to unleash hundreds of landslides.
The Landsat 8 satellite acquired imagery of the widespread damage. An image acquired on Sept. 15, 2018, shows mud and debris in a hilly area east of Abira. For comparison, the previous image shows the same area on July 26, 2017.
Read more about this
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Small Businesses with Big Plans for the Moon and Mars
Today is Small Business Saturday, which the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) recognizes as a day to celebrate and support small businesses and all they do for their communities.

Source: Techshot
We are proud to partner with small businesses across the country through NASA’s Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) and Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) programs, which have funded the research, development and demonstration of innovative space technologies since 1982. This year, we’ve awarded 571 SBIR/STTR contracts totaling nearly $180 million to companies who will support our future exploration:
Techshot, Inc. was selected to bioprint micro-organs in a zero-gravity environment for research and testing of organs-on-chip devices, which simulate the physiological functions of body organs at a miniature scale for health research without the need for expensive tests or live subjects.
CertainTech, Inc., with the George Washington University, will demonstrate an improved water recovery system for restoring nontoxic water from wastewater using nanotechnology.
Electrochem, Inc. was contracted to create a compact and lightweight regenerative fuel cell system that can store energy from an electrolyzer during the lunar day to be used for operations during the lunar night.

Source: Electrochem
Small businesses are also developing technologies for the Artemis missions to the Moon and for human and robotic exploration of Mars. As we prepare to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024, these are just a few of the small businesses working with us to make it happen.
Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Services
Masten Space Systems, Astrobotic and Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems are three NASA SBIR/STTR alumni now eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts. Other small businesses selected as CLPS providers include Ceres Robotics, Deep Space Systems, Intuitive Machines, Moon Express, and Orbit Beyond. Under the Artemis program, these companies could land robotic missions on the Moon to perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help the human exploration that will follow. The first delivery could be as early as July 2021.

A Pathfinder CubeSat
One cornerstone of our return to the Moon is a small spaceship called Gateway that will orbit our nearest neighbor to provide more access to the lunar surface. SBIR/STTR alum Advanced Space Systems will develop a CubeSat that will test out the lunar orbit planned for Gateway, demonstrating how to enter into and operate in the unique orbit. The Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) could launch as early as December 2020.

Tipping Point for Moon to Mars
We selected 14 companies as part of our Tipping Point solicitation, which fosters the development of critical, industry-led space capabilities for our future missions. These small businesses all proposed unique technologies that could benefit the Artemis program.
Many of these small businesses are also NASA SBIR/STTR alumni whose Tipping Point awards are related to their SBIR or STTR awards. For example, Infinity Fuel Cell and Hydrogen, Inc. (Infinity Fuel) will develop a power and energy product that could be used for lunar rovers, surface equipment, and habitats. This technology stems from a new type of fuel cell that Infinity Fuel developed with the help of NASA SBIR/STTR awards.
CU Aerospace and Astrobotic are also small businesses whose Tipping Point award can be traced back to technology developed through the NASA SBIR/STTR program. CU Aerospace will build a CubeSat with two different propulsion systems, which will offer high performance at a low cost, and Astrobotic will develop small rover “scouts” that can host payloads and interface with landers on the lunar surface.

Small Businesses, Big Impact
This is just a handful of the small businesses supporting our journey back to the Moon and on to Mars, and just a taste of how they impact the economy and American innovation. We are grateful for the contributions that small businesses make—though they be but “small,” they are fierce.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

As Neil Armstrong became the first human to step foot onto another world on July 20, 1969, lunar dust collected on the boots of his spacesuit. He peered through the gold coating of his visor and looked out across the surface of the Moon, an entirely different landscape than he was used to.
Now, just in time for the 50th anniversary of the Moon landing, you can experience the boots that stepped in Moon dust and the visor that saw the moonscape up close. Neil Armstrong’s spacesuit from the historic Apollo 11 Moon landing is on display for the first time in 13 years in its new display case in the Wright Brothers & the Invention of the Aerial Age Gallery of the National Air and Space Museum.
This week, you can also watch us salute our Apollo 50th heroes and look forward to our next giant leap for future missions to the Moon and Mars. Tune in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn all about the end of the Rosetta Mission and more about the weather on Mars, the Moon’s colorful palette.
1. Rosetta’s Last Dance

The Rosetta mission was one of firsts: the first to orbit a comet and the first to dispatch a lander to a comet's surface. Rosetta transformed our understanding of these ancient wanderers, and this week, mission controllers will command the spacecraft to execute a series of maneuvers to bring it out of orbit around Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Watch live on Sept. 30 from 6:15-8 a.m. EDT, the Rosetta mission's 12-year odyssey in space reaches its conclusion. Rosetta will descend to make a planned impact on the comet’s surface with its instruments recording science data during descent.
+Watch live as Rosetta crash lands on NASA TV, recording data along the way
+More on the mission’s final descent
+Mission highlights
2. Hubble Spots Possible Water Plumes Erupting on Jupiter's Moon Europa

On Monday, Sept. 26, our scientists announced what may be water vapor plumes erupting off the surface of Jupiter's moon Europa, based on data from the Hubble Space Telescope. This finding bolsters other Hubble observations suggesting the icy moon erupts with high altitude water vapor plumes.
+Learn the latest on Europa
3. Not So Impossible After All

Scientists have found an "impossible" ice cloud on Saturn's moon Titan. The puzzling appearance of an ice cloud prompted our researchers to suggest that a different process than previously thought could be forming clouds on Titan. The process may be similar to one seen over Earth's poles. Today, the Cassini spacecraft will perform a targeted Titan flyby, skimming just 1,079 miles (1,736 kilometers) above its hazy surface. Several of Cassini's instruments will be watching for clouds and other phenomena in the atmosphere, as well as taking measurements of the surface.
+Learn more about Titan’s clouds
4. Lunar Intrigue

Earth's moon is a colorless world of grays and whites, right? Not really. As seen in these images from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, some landscapes on the moon reveal a whole range of color. One such place is the mountainous complex of ancient lava flows known as the Lassell Massif, one of the moon's so-called "red spots."
+Take a look
5. Weather Report: Mars

A camera aboard our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter monitors global weather patterns daily. The most recent report includes the remains of a large dust storm in the Noachis region, and smaller tempests spotted along the edge of the south polar ice cap and water-ice clouds over the volcano Arsia Mons.
+ Learn more and see Mars weather videos
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
10 Technologies That Are Changing the Game
Earlier this year, we hosted a Game Changing Technology Industry Day for the aerospace industry, and in October our engineers and technologists visited Capitol Hill showcasing some of these exciting innovations. Check out these technology developments that could soon be making waves on Earth and in space.
1. Wearable technology

With smartwatches, glasses, and headsets already captivating users around the world, it’s no surprise that the next evolution of wearable technology could be used by first responders at the scene of an accident or by soldiers on a battlefield. The Integrated Display and Environmental Awareness System (IDEAS) is an interactive optical computer that works for smart glasses.

It has a transparent display, so users have an unobstructed view even during video conferences or while visualizing environmental data.

And while the IDEAS prototype is an innovative solution to the challenges of in-space missions, it won’t just benefit astronauts -- this technology can be applied to countless fields here on Earth.
2. Every breath they take: life support technologies
Before astronauts can venture to Mars and beyond, we need to significantly upgrade our life support systems. The Next Generation Life Support project is developing technologies to allow astronauts to safely carry out longer duration missions beyond low-Earth orbit.

The Variable Oxygen Regulator will improve the control of space suit pressure, with features for preventing decompression sickness. The Rapid Cycle Amine technology will remove carbon dioxide and humidity and greatly improve upon today’s current complex system.

3. 3-D printing (for more than just pizza)
New Advanced Manufacturing Technologies (AMT), such as 3-D printing, can help us build rocket parts more quickly and aid in building habitats on other planets.

These manufacturing initiatives will result in innovative, cost-efficient solutions to many of our planetary missions. Back in 2014, the International Space Station’s 3-D printer manufactured the first 3-D printed object in space, paving the way to future long-term space expeditions.

The object, a printhead faceplate, is engraved with names of the organizations that collaborated on this space station technology demonstration: NASA and Made In Space, Inc., the space manufacturing company that worked with us to design, build and test the 3-D printer.

4. Spacecraft landing gear
Large spacecraft entering the atmosphere of Mars will be traveling over five times the speed of sound, exposing the craft to extreme heat and drag forces. The Hypersonic Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator (HIAD) is designed to protect spacecraft from this environment with an inflatable structure that helps slow a craft for landing.

To get astronauts and other heavy loads to the surface safely, these components must be very strong. The inflatable consists of a material 15 times stronger than steel, while the thermal protection system can withstand temperatures over 1600°C.
5. From heat shield technology to firefighter shelters

For the Convective Heating Improvement for Emergency Fire Shelters (CHIEFS) project, we partnered with the U.S. Forest Service to develop safer, more effective emergency fire shelters for wild land firefighters.

Using existing technology for flexible spacecraft heat shields like HIAD, we are building and testing new fire shelters composed of stacks of durable, insulated materials that could help protect the lives of firefighters.

6. Robots and rovers
Real life is looking a bit more like science fiction as Human Robotics Systems are becoming highly complex. They are amplifying human productivity and reducing mission risk by improving the effectiveness of human-robot teams.

Our humanoid assistant Robonaut is currently aboard the International Space Station helping astronauts perform tasks.

A fleet of robotic spacecraft and rovers already on and around Mars is dramatically increasing our knowledge and paving the way for future human explorers. The Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover measured radiation on the way to Mars and is sending back data from the surface.

This data will help us plan how to protect the astronauts who will explore Mars.

Future missions like the Mars 2020 rover, seeking signs of past life, will demonstrate new technologies that could help astronauts survive on the Red Planet.

7. Robotic repairs
Currently, a satellite that is even partially damaged cannot be fixed in orbit. Instead, it must be disposed of, which is a lot of potential science lost.

Satellite Servicing technologies would make it possible to repair, upgrade, and even assemble spacecraft in orbit using robotics.

This can extend the lifespan of a mission, and also enable deeper space exploration.

Restore-L, set to launch in 2020, is a mission that will demonstrate the ability to grab and refuel a satellite.
8. Low-cost spacecraft avionics controllers
Small satellites, or smallsats, are quickly becoming useful tools for both scientists and industry. However, the high cost of spacecraft avionics—the systems that guide and control the craft—often limits how and when smallsats can be sent into orbit by tagging along as payloads on larger launches.

Using Affordable Vehicle Avionics (AVA) technology, we could launch many more small satellites using an inexpensive avionics controller. This device is smaller than a stack of six CD cases and weighs less than two pounds!
9. Making glass from metal
After a JPL research team of modern-day alchemists set about mixing their own alloys, they discovered that a glass made of metal had the wear resistance of a ceramic, was twice as strong as titanium, and could withstand the extreme cold of planetary surfaces, with temperatures below -150 degrees Fahrenheit.

Bulk Metallic Glass (BMG) gears would enable mechanisms to function without wasting energy on heaters. Most machines need to maintain a warmer temperature to run smoothly, which expends precious fuel and decreases the mission’s science return.

By developing gearboxes made of BMG alloys, we can extend the life of a spacecraft and learn more about the far reaches of our solar system than ever before. Plus, given their extremely high melting points, metallic glasses can be cheaply manufactured into parts by injection molding, just like plastics.
10. Lighter, cheaper, safer spacecraft fuel tanks
Cryogenic propellant tanks are essential for holding fuel for launch vehicles like our Space Launch System—the world’s most powerful rocket. But the current method for building these tanks is costly and time-consuming, involving almost a mile of welded parts.

Advanced Near Net Shape Technology, part of our Advanced Manufacturing Technologies, is an innovative manufacturing process for constructing cryotanks, using cylinders that only have welds in one area.

This makes the tank lighter, cheaper, and safer for astronauts, as there are fewer potentially defective welds.
Follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
5 Myths About Becoming a Flight Director
Have you ever wondered if you have what it takes to become a NASA Flight Director?
They are historically well known for making difficult calls and guiding the crew through "Houston, we've had a problem" situations, but in all spaceflight operations, they are ultimately responsible for the success of the mission.
We're looking for a new class of Flight Directors to join our team, and there are a few things to know.
Here are a few myths about becoming a Flight Director:
MYTH: You have to have already been a flight controller in Mission Control at NASA to become a flight director.
FACT: Although many flight directors have previously been NASA flight controllers, that is not a prerequisite to apply. The necessary experience could come from the military, other spaceflight organizations or areas that operate in similar high-stakes conditions.

MYTH: You have to already have a special spaceship flying license to apply.
FACT: The only place to get certified is on the job at NASA. Once chosen, the new flight directors will receive training on flight control and vehicle systems, as well as operational leadership and risk management.

MYTH: All flight directors have advanced degrees like, a PhD.
FACT: While a Bachelor's degree in engineering, biological science, physical science, computer science or mathematics from an accredited university is necessary, an advanced degree is not required to become a flight director.

MYTH: Flight directors are required to have experience in the space industry.
FACT: While you need at least three years of related, progressively responsible professional experience to apply, it can come from a variety of industries as long as it represents time-critical decision-making experience in high-stress, high-risk environments.

MYTH: Only astronauts become flight directors and vice versa.
FACT: To date, only one astronaut, T.J. Creamer, has become a flight director, and no flight directors have become astronauts. However, members of the flight controller teams have become astronauts. The "capsule communicator," or CAPCOM, role in Mission Control is more often filled by astronauts because the CAPCOM is the one responsible for relaying the flight director's decisions to the astronauts in space.

Okay, but What are the requirements?
Basic Qualification Requirements

Applicants must meet the following minimum requirements before submitting an application:
Be a U.S. citizen.
Have a Bachelor's degree from an accredited institution in engineering, biological science, physical science, computer science or math.
Have at least three years of related, progressively responsible professional experience.
Applications for our next Flight Director class open on Dec. 3, 2021 and close Dec. 16, 2021! Visit: go.nasa.gov/FlightDirector
Learn more about what Flight Directors do with our Everything About Mission Control Houston video featuring Flight Director Mary Lawrence!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn the latest on Cassini’s Grand Finale, Pluto, Hubble Space Telescope and the Red Planet.
1. Cassini’s Grand Finale

After more than 12 years at Saturn, our Cassini mission has entered the final year of its epic voyage to the giant planet and its family of moons. But the journey isn't over. The upcoming months will be like a whole new mission, with lots of new science and a truly thrilling ride in the unexplored space near the rings. Later this year, the spacecraft will fly repeatedly just outside the rings, capturing the closest views ever. Then, it will actually orbit inside the gap between the rings and the planet's cloud tops.
Get details on Cassini’s final mission
The von Kármán Lecture Series: 2016
2. Chandra X-Rays Pluto

As the New Horizon’s mission headed to Pluto, our Chandra X-Ray Observatory made the first detection of the planet in X-rays. Chandra’s observations offer new insight into the space environment surrounding the largest and best-known object in the solar system’s outermost regions.
See Pluto’s X-Ray
3. ... And Then Pluto Painted the Town Red

When the cameras on our approaching New Horizons spacecraft first spotted the large reddish polar region on Pluto's largest moon, Charon, mission scientists knew two things: they'd never seen anything like it before, and they couldn't wait to get the story behind it. After analyzing the images and other data that New Horizons has sent back from its July 2015 flight through the Pluto system, scientists think they've solved the mystery. Charon's polar coloring comes from Pluto itself—as methane gas that escapes from Pluto's atmosphere and becomes trapped by the moon's gravity and freezes to the cold, icy surface at Charon's pole.
Get the details
4. Pretty as a Postcard

The famed red-rock deserts of the American Southwest and recent images of Mars bear a striking similarity. New color images returned by our Curiosity Mars rover reveal the layered geologic past of the Red Planet in stunning detail.
More images
5. Things Fall Apart

Our Hubble Space Telescope recently observed a comet breaking apart. In a series of images taken over a three-day span in January 2016, Hubble captured images of 25 building-size blocks made of a mixture of ice and dust drifting away from the comet. The resulting debris is now scattered along a 3,000-mile-long trail, larger than the width of the continental U.S.
Learn more
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 watch reblogged this · 1 year ago
watch reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 ninapina reblogged this · 2 years ago
ninapina reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 ninapina liked this · 2 years ago
ninapina liked this · 2 years ago -
 dawgstreetbank20trillion liked this · 3 years ago
dawgstreetbank20trillion liked this · 3 years ago -
 rockymountainlegend liked this · 3 years ago
rockymountainlegend liked this · 3 years ago -
 zhenzhein liked this · 3 years ago
zhenzhein liked this · 3 years ago -
 mdjony liked this · 3 years ago
mdjony liked this · 3 years ago -
 vap01 liked this · 4 years ago
vap01 liked this · 4 years ago -
 mawusifitnesstraining liked this · 4 years ago
mawusifitnesstraining liked this · 4 years ago -
 edsonlima17 liked this · 4 years ago
edsonlima17 liked this · 4 years ago -
 missionchessboxing liked this · 4 years ago
missionchessboxing liked this · 4 years ago -
 fhhsing-blog liked this · 4 years ago
fhhsing-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 aamerk2 liked this · 4 years ago
aamerk2 liked this · 4 years ago -
 icecreamango liked this · 4 years ago
icecreamango liked this · 4 years ago -
 bonjaaks liked this · 4 years ago
bonjaaks liked this · 4 years ago -
 child-of-addiction liked this · 4 years ago
child-of-addiction liked this · 4 years ago -
 abrokendawn liked this · 4 years ago
abrokendawn liked this · 4 years ago -
 harleythecosmonaut liked this · 4 years ago
harleythecosmonaut liked this · 4 years ago -
 shefdawg liked this · 4 years ago
shefdawg liked this · 4 years ago -
 themisanthropistnerd liked this · 4 years ago
themisanthropistnerd liked this · 4 years ago -
 johanneswelwich liked this · 4 years ago
johanneswelwich liked this · 4 years ago -
 dorklesblog liked this · 4 years ago
dorklesblog liked this · 4 years ago -
 flamesparks liked this · 4 years ago
flamesparks liked this · 4 years ago -
 butyoutoldmeiwasfunny reblogged this · 4 years ago
butyoutoldmeiwasfunny reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 narusesbby liked this · 4 years ago
narusesbby liked this · 4 years ago -
 propinquitine liked this · 4 years ago
propinquitine liked this · 4 years ago -
 zelink-nalu liked this · 4 years ago
zelink-nalu liked this · 4 years ago -
 mlu liked this · 4 years ago
mlu liked this · 4 years ago -
 virtualzonkslimepickle liked this · 4 years ago
virtualzonkslimepickle liked this · 4 years ago -
 hotbedofsin liked this · 4 years ago
hotbedofsin liked this · 4 years ago -
 bulanfan liked this · 4 years ago
bulanfan liked this · 4 years ago -
 rumbadeluxe liked this · 4 years ago
rumbadeluxe liked this · 4 years ago -
 chocolateismynemesis reblogged this · 4 years ago
chocolateismynemesis reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 pg-chan liked this · 4 years ago
pg-chan liked this · 4 years ago -
 deep-dive51 liked this · 4 years ago
deep-dive51 liked this · 4 years ago -
 cbgmo liked this · 4 years ago
cbgmo liked this · 4 years ago -
 xphro liked this · 4 years ago
xphro liked this · 4 years ago -
 actually-afrog liked this · 4 years ago
actually-afrog liked this · 4 years ago -
 sanpiano liked this · 4 years ago
sanpiano liked this · 4 years ago -
 justkerrieb liked this · 4 years ago
justkerrieb liked this · 4 years ago -
 laz3watt liked this · 4 years ago
laz3watt liked this · 4 years ago -
 piratesknife liked this · 4 years ago
piratesknife liked this · 4 years ago -
 rosaliachristian liked this · 4 years ago
rosaliachristian liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts