Leap Day…Why Does It Exist?
Leap Day…Why Does It Exist?
Once every four years, an extra calendar day is added: a leap day. But why?
The reason for adding leap days to the calendar is to align the calendar year with the actual year – which is defined by the time it takes Earth to circle the sun. It is equal to 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes and 46 seconds, or 365.24219 days.

If all calendar years contained exactly 365 days, they would drift from the actual year by about 1 day every 4 years. Eventually, July would occur during the northern hemisphere winter! Wouldn’t that be weird?
To correct (approximately), we add 1 day every 4 years...resulting in a leap year.
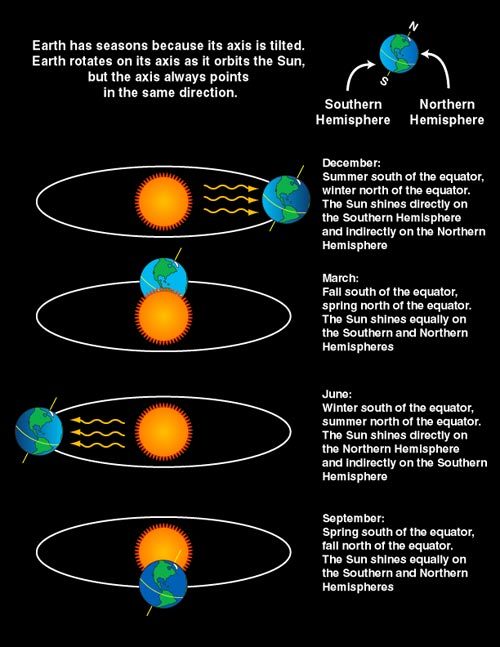
By making most years 365 days but every fourth year 366 days, the calendar year and the actual year remain more nearly in step.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others

Setting Sail to Travel Through Space: 5 Things to Know about our New Mission
Our Advanced Composite Solar Sail System will launch aboard Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand no earlier than April 23, at 6 p.m. EDT. This mission will demonstrate the use of innovative materials and structures to deploy a next-generation solar sail from a CubeSat in low Earth orbit.
Here are five things to know about this upcoming mission:
1. Sailing on Sunshine
Solar sails use the pressure of sunlight for propulsion much like sailboats harness the wind, eliminating the need for rocket fuel after the spacecraft has launched. If all goes according to plan, this technology demonstration will help us test how the solar sail shape and design work in different orbits.

2. Small Package, Big Impact
The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft is a CubeSat the size of a microwave, but when the package inside is fully unfurled, it will measure about 860 square feet (80 square meters) which is about the size of six parking spots. Once fully deployed, it will be the biggest, functional solar sail system – capable of controlled propulsion maneuvers – to be tested in space.

3. Second NASA Solar Sail in Space
If successful, the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System will be the second NASA solar sail to deploy in space, and not only will it be much larger, but this system will also test navigation capabilities to change the spacecraft’s orbit. This will help us gather data for future missions with even larger sails.

4. BOOM: Stronger, Lighter Booms
Just like a sailboat mast supports its cloth sails, a solar sail has support beams called booms that provide structure. The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System mission’s primary objective is to deploy a new type of boom. These booms are made from flexible polymer and carbon fiber materials that are stiffer and 75% lighter than previous boom designs. They can also be flattened and rolled like a tape measure. Two booms spanning the diagonal of the square (23 feet or about 7 meters in length) could be rolled up and fit into the palm of your hand!

5. It’s a bird...it’s a plane...it’s our solar sail!
About one to two months after launch, the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft will deploy its booms and unfurl its solar sail. Because of its large size and reflective material, the spacecraft may be visible from Earth with the naked eye if the lighting conditions and orientation are just right!
To learn more about this mission that will inform future space travel and expand our understanding of our Sun and solar system, visit https://www.nasa.gov/mission/acs3/.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
See history in the making on September 22! That's the day OSIRIS-REx, the first U.S. mission to carry samples from an asteroid back to Earth, will make a close approach to Earth as it uses our planet's gravity to slingshot itself toward the asteroid Bennu.

Over the course of several days, observatories and amateur astronomers will be able to spot the spacecraft. Below, 10 things to know about this incredible mission that will bring us the largest sample returned from space since the Apollo era.
1. Big Deal

OSIRIS-REx seeks answers to the questions that are central to the human experience: Where did we come from? What is our destiny? Asteroids, the leftover debris from the solar system formation process, can help us answer these questions and teach us about the history of the Sun and planets.
2. That's a Long Acronym
Yup. OSIRIS-REx stands for the Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer spacecraft. The gist: It will rendezvous with, study, and return a sample of the asteroid Bennu to Earth.
3. Lots of Instruments, Too

While all the acronyms for each instrument may be alphabet soup, each has a job/role to perform in order to complete the mission. Explore what each one will do in this interactive webpage.
4. Nice to Meet You, Bennu
Scientists chose Bennu as the mission target because of its composition, size, and proximity to Earth. Bennu is a rare B-type asteroid (primitive and carbon-rich), which is expected to have organic compounds and water-bearing minerals like clays.
5. Hard Knock Life
Bennu had a tough life in a rough neighborhood: the early solar system. It's an asteroid the size of a small mountain born from the rubble of a violent collision, hurled through space for millions of years and dismembered by the gravity of planets—but that's exactly what makes it a fascinating destination.
6. High Fives All Around
In 2018, OSIRIS-REx will approach Bennu and begin an intricate dance with the asteroid, mapping and studying Bennu in preparation for sample collection. In July 2020, the spacecraft will perform a daring maneuver in which its 11-foot arm will reach out for a five-second "high-five" to stir up surface material, collecting at least 2 ounces (60 grams) of small rocks and dust into a sample return capsule.
7. Home Sweet Home

OSIRIS-REx launched on September 8, 2016 from Cape Canaveral, Florida on an Atlas V rocket. In March 2021, the window for departure from the asteroid will open and OSIRIS-REx will begin its return journey to Earth, arriving two-and-a-half years later in September 2023.
8. Precious Cargo

The sample will head to Earth inside of a return capsule with a heat shield and parachutes that will separate from the spacecraft once it enters the Earth's atmosphere. The capsule containing the sample will be collected at the Utah Test and Training Range. Once it arrives, it will be transported to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston for examination. For two years after the sample return (from late 2023-2025) the science team will catalog the sample and conduct the analysis needed to meet the mission science goals. NASA will preserve at least 75% of the sample at NASA's Johnson Space Flight Center in Houston for further research by scientists worldwide, including future generations of scientists.
9. Knowledge Is Power

Analyzing the sample will help scientists understand the early solar system, as well as the hazards and resources of near-Earth space. Asteroids are remnants of the building blocks that formed the planets and enabled life. Those like Bennu contain natural resources such as water, organics and metals. Future space exploration and economic development may rely on asteroids for these materials.
10. Hitch a Ride
Journey with OSIRIS-REx as it launches, cruises, and arrives to Bennu in this interactive timeline.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
The Overview Effect
Observing Earth from space can alter an astronauts’ cosmic perspective, a mental shift known as the “Overview Effect.” First coined by space writer Frank White in 1987, the Overview Effect is described as a feeling of awe for our home planet and a sense of responsibility for taking care of it.
See Earth from the vantage point of our astronauts in these perspective-changing views:
Floating Free in Space

Astronaut Bruce McCandless II used his hands to control his movement above the Earth during the first-ever spacewalk that didn't use restrictive tethers and umbilicals. Fellow crew members aboard the space shuttle Challenger captured this image on Feb. 7, 1984, through windows on the flight deck.
Of his famous spacewalk, McCandless wrote in 2015: "My wife [Bernice] was at mission control, and there was quite a bit of apprehension. I wanted to say something similar to Neil [Armstrong] when he landed on the moon, so I said, 'It may have been a small step for Neil, but it’s a heck of a big leap for me.' That loosened the tension a bit."
Earth Reflections

Astronaut Tracy Caldwell Dyson looks through a window in the Cupola of the International Space Station (ISS). A blue and white part of Earth and the blackness of space are visible through the windows. The image was a self-portrait using natural light.
In a preflight interview for Expedition 23/24, Dyson said: “hands down, the best part about it is being able to look at that view every day and during the time frame we’ll be up there, hopefully, we’ll have a big bay window and much more opportunity to observe this beautiful planet.”
Taking in the View

As astronaut Nick Hague prepared to conclude his six-month stay aboard the ISS, he shared this photo saying: "Today is my last Monday living on this orbiting laboratory and I’m soaking up my final views. The @Space_Station is truly an engineering marvel. #MondayMotivation."
He and Expedition 60 and Soyuz commander Alexey Ovchinin of the Russian space agency Roscosmos completed a 203-day mission, spanning 3,248 orbits of Earth, and a journey of 80.8 million miles.
Earthrise

On Dec. 24, 1968, Apollo 8 astronauts Frank Borman, Jim Lovell and Bill Anders became the first humans to witness the Earth rising above the Moon's surface.
Anders, photographing the Moon from the right-side window, caught sight of the view, and exclaimed: “Oh my God, look at that picture over there! There’s the Earth comin’ up. Wow, is that pretty!”
The Blue Marble

Besides Earthrise, the Blue Marble is probably the most famous image of Earth that NASA has produced. Taken by the Apollo 17 crew on their way to the Moon in 1972, the Blue Marble and other NASA imagery of Earth has been credited by some with helping to fuel the environmental movement.
For more information on the Overview Effect, check out this episode of Houston We Have a Podcast.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Photograph of the Apollo 13 Spacecraft Being Returned to the Prime Recovery Ship, USS Iwo Jima, 4/17/1970
Series: Color Photograph Files, 1965 - 2002. Record Group 255: Records of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 1903 - 2006.
Apollo 13 was intended to be the third Apollo mission to land on the Moon. The craft was launched from Kennedy Space Center in Merritt Island, Florida on April 11, 1970. Two days into the flight, damaged wire insulation inside the oxygen tank in the service module ignited, causing an explosion which vented the oxygen tank into space. Without oxygen, the service module became inoperable and the lunar mission quickly turned into a mission to safely return the crew to Earth. The astronauts worked with Mission Control to shut down the command module in order to conserve the remaining oxygen, forcing all three astronauts into the lunar module. The astronauts continued to work with Mission Control to combat one technical failure after another until, on April 17, 1970, the crew landed safely in the South Pacific Ocean.
source: phillyarchives.tumblr.com
Take a deep breath. Even if the air looks clear, it is nearly certain that you will inhale millions of solid particles and liquid droplets. These ubiquitous specks of matter are known as aerosols, and they can be found in the air over oceans, deserts, mountains, forests, ice, and every ecosystem in between.
If you have ever watched smoke billowing from a wildfire, ash erupting from a volcano, or dust blowing in the wind, you have seen aerosols. Satellites like Terra, Aqua, Aura, and Suomi NPP “see” them as well, though they offer a completely different perspective from hundreds of kilometers above Earth’s surface. A version of one of our models called the Goddard Earth Observing System Forward Processing (GEOS FP) offers a similarly expansive view of the mishmash of particles that dance and swirl through the atmosphere.
The visualization above highlights GEOS FP model output for aerosols on August 23, 2018. On that day, huge plumes of smoke drifted over North America and Africa, three different tropical cyclones churned in the Pacific Ocean, and large clouds of dust blew over deserts in Africa and Asia. The storms are visible within giant swirls of sea salt aerosol(blue), which winds loft into the air as part of sea spray. Black carbon particles (red) are among the particles emitted by fires; vehicle and factory emissions are another common source. Particles the model classified as dust are shown in purple. The visualization includes a layer of night light data collected by the day-night band of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on Suomi NPP that shows the locations of towns and cities.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
NASA Science Show & Tell
This week, we’re at one of the biggest science conferences in the country, where our scientists are presenting new results from our missions and projects. It’s called the American Geophysical Union’s Fall Meeting.
Here are a few of the things we shared this week...

The Sun
A few months into its seven-year mission, Parker Solar Probe has already flown far closer to the Sun than any spacecraft has ever gone. The data from this visit to the Sun has just started to come back to Earth, and scientists are hard at work on their analysis.

Parker Solar Probe sent us this new view of the Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona. The image was taken by the mission’s WISPR instrument on Nov. 8, 2018, and shows a coronal streamer seen over the east limb of the Sun. Coronal streamers are structures of solar material within the Sun's atmosphere, the corona, that usually overlie regions of increased solar activity. The fine structure of the streamer is very clear, with at least two rays visible. Parker Solar Probe was about 16.9 million miles from the Sun's surface when this image was taken. The bright object near the center of the image is Mercury, and the dark spots are a result of background correction.
Hurricane Maria
Using a satellite view of human lights, our scientists watched the lights go out in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria. They could see the slow return of electricity to the island, and track how rural and mountainous regions took longer to regain power.

In the spring, a team of scientists flew a plane over Puerto Rico’s forests, using a laser instrument to measure how trees were damaged and how the overall structure of the forests had changed.

Earth’s Ice
Our scientists who study Antarctica saw some surprising changes to East Antarctica. Until now, most of the continent’s melting has been on the peninsula and West Antarctica, but our scientists have seen glaciers in East Antarctica lose lots of ice in the last few years.


Our ICESat-2 team showed some of their brand new data. From the changing height of Antarctic ice to lagoons off the coast of Mexico, the little satellite has spent its first few months measuring our planet in 3D. The laser pulses even see individual ocean waves, in this graph.

Scientists are using our satellite data to track Adélie penguin populations, by using an unusual proxy -- pictures of their poop! Penguins are too small to be seen by satellites, but they can see large amounts of their poop (which is pink!) and use that as a proxy for penguin populations.

Asteroid Bennu
Our OSIRIS-REx mission recently arrived at its destination, asteroid Bennu. On approach, data from the spacecraft’s spectrometers revealed chemical signatures of water trapped in clay minerals. While Bennu itself is too small to have ever hosted liquid water, the finding indicates that liquid water was present at some time on Bennu’s parent body, a much larger asteroid.
We also released a new, detailed shape model of Bennu, which is very similar to our ground-based observations of Bennu’s shape. This is a boon to ground-based radar astronomy since this is our first validation of the accuracy of the method for an asteroid! One change from the original shape model is the size of the large boulder near Bennu’s south pole, nicknamed “Benben.” The boulder is much bigger than we thought and overall, the quantity of boulders on the surface is higher than expected. Now the team will make further observations at closer ranges to more accurately assess where a sample can be taken on Bennu to later be returned to Earth.

Jupiter
The Juno mission celebrated it’s 16th science pass of #Jupiter, marking the halfway point in data collection of the prime mission. Over the second half of the prime mission — science flybys 17 through 32 — the spacecraft will split the difference, flying exactly halfway between each previous orbit. This will provide coverage of the planet every 11.25 degrees of longitude, providing a more detailed picture of what makes the whole of Jupiter tick.

Mars
The Mars 2020 team had a workshop to discuss the newly announced landing site for our next rover on the Red Planet. The landing site...Jezero Crater! The goal of Mars 2020 is to learn whether life ever existed on Mars. It's too cold and dry for life to exist on the Martian surface today. But after Jezero Crater formed billions of years ago, water filled it to form a deep lake about the same size as Lake Tahoe. Eventually, as Mars' climate changed, Lake Jezero dried up. And surface water disappeared from the planet.
Interstellar Space
Humanity now has two interstellar ambassadors. On Nov. 5, 2018, our Voyager 2 spacecraft left the heliosphere — the bubble of the Sun’s magnetic influence formed by the solar wind. It’s only the second-ever human-made object to enter interstellar space, following its twin, Voyager 1, that left the heliosphere in 2012.

Scientists are especially excited to keep receiving data from Voyager 2, because — unlike Voyager 1 — its plasma science instrument is still working. That means we’ll learn brand-new information about what fills the space between the stars.
Learn more about NASA Science at science.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Black Hole Friday Deals!

Get these deals before they are sucked into a black hole and gone forever! This “Black Hole Friday,” we have some cosmic savings that are sure to be out of this world.
Your classic black holes — the ultimate storage solution.
Galactic 5-for-1 special! Learn more about Stephan’s Quintet.
Limited-time offer game DLC! Try your hand at the Roman Space Observer Video Game, Black Hole edition, available this weekend only.
Standard candles: Exploding stars that are reliably bright. Multi-functional — can be used to measure distances in space!
Feed the black hole in your stomach. Spaghettification’s on the menu.
Act quickly before the stars in this widow system are gone!
Add some planets to your solar system! Grab our Exoplanet Bundle.
Get ready to ride this (gravitational) wave before this Black Hole Merger ends!
Be the center of attention in this stylish accretion disk skirt. Made of 100% recycled cosmic material.
Should you ever travel to a black hole? No. But if you do, here’s a free guide to make your trip as safe* as possible. *Note: black holes are never safe.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Black Marble: NASA View Illuminates Earth at Night
When the sun goes down, the lights on Earth shine bright. A new look using our satellite data captures the lights coming from our neighborhoods, vehicles, buildings, factories, fishing vessels and other human activity brightening the night.

Our scientists have just released the first new global map of Earth at night since 2012. This nighttime view of our home planet, dubbed the Black Marble, provides researchers with a unique perspective of human activities around the globe.
By studying Earth at night, researchers can investigate how and why cities expand, monitor light intensity to estimate energy use and economic activity, and aid in disaster response in near-real time.

The data on Earth at night comes from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument on the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite, jointly managed by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
VIIRS captures visible and infrared light, allowing researchers to glimpse the Earth as it looks to astronauts peering out of the International Space Station. The new map is a composite of data collected in 2016, and it took several months of processing to filter out clouds, moonlight, airglow, and other interfering features to create the global image. In the coming months our scientists will release daily nighttime lights data at even finer resolutions for the first time.

The East Coast sparkles with population hubs, suburbs circling cities and major roadways. The I-95 corridor includes the most densely populated region of the United States – the stretch from Washington, DC to Boston.
To get images like these from the satellite data, our scientists had to filter out moonlight, aerosols and other sources of extraneous light – the goal is to eventually be able to detect the lights from a single building or fishing boat.

Daytime satellite images, like this one from Landsat 8, can show us the forests, deserts, mountains, waterways and built-up cities. Add a nighttime view, and scientists can study when and how people are using these limited resources – like the lights tracing the Nile River leading to the metropolis of Cairo, Egypt.

Lights aren’t confined to land. With the global nighttime view, the ocean is dotted with fishing fleets, including boats that try to attract their catch with bright lights.

What lights illuminate your neighborhood? Download a high-resolution version of the Black Marble HERE, and find out more about our new night lights data HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Be a scientist for a day, solstice on the Red Planet, historic launches and more!

1. Scientist for a Day!
This year's Scientist for a Day essay contest was announced last week. Write an essay on one of the three images above. Essays are due in Feb. 2017. Students in grades 5-12 in U.S. schools, after-school and home-school programs, scout troops and museum programs are eligible to participate.
+ Learn more

2. Tuesday is Winter Solstice on Mars' Northern Hemisphere
Mars' orbit is much more eccentric than Earth's. The winters in the northern hemisphere are warm and short, as Mars is near perihelion—closer to the sun. This means that the winters in the southern hemisphere are long and cold.
+ Read Mars: The Other Terrestrial Planet
+ Seasons on Mars (Malin Space Science Systems)

3. Launch-iversaries!
We’re celebrating two launch anniversaries. Before Curiosity. Before Spirit and Opportunity, there was Pathfinder and the hardy Sojourner rover, launched on Dec. 4, 1996. Pathfinder was a demonstration of the technology necessary to deliver a lander and a free-ranging robotic rover to the surface of Mars in a cost-effective and efficient manner. The lander, formally named the Carl Sagan Memorial Station following its successful touchdown, and the rover, named Sojourner after American civil rights crusader Sojourner Truth, both outlived their design lives — the lander by nearly three times, and the rover by 12 times! We continued the tradition with Spirit and Opportunity. Now there is the Mars Science Laboratory (with the Curiosity rover in stowage), which was launched on Nov. 26, 2011. It landed successfully in Gale Crater at 1:31 am EDT on Aug. 6, 2012.
+ Go Back in Time
+ Video: Where Were You When Curiosity Landed on Mars?

4. Mars Ice Deposit Holds as Much Water as Lake Superior
Water ice makes up half or more of an underground layer in a large region of Mars, about halfway from the equator to the north pole. The amount of water in this deposit—assessed using a radar aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter—is about as much as in Lake Superior.
+ Read More

5. A Little Bit of History
Finally, it’s been seven years since Cassini caught one of its most stunning views of the plume on Saturn's moon Enceladus.
+ Read More
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Earth: Your Home, Our Mission
We pioneer and support an amazing range of advanced technologies and tools to help us better understand our home planet, the solar system and far beyond.
Here are 5 ways our tech improves life here on Earth...
1. Eyes in the Sky Spot Fires on the Ground

Our Earth observing satellites enable conservation groups to spot and monitor fires across vast rainforests, helping them protect our planet on Earth Day and every day.
2. Helping Tractors Drive Themselves

There has been a lot of talk about self-driving cars, but farmers have already been making good use of self-driving tractors for more than a decade - due in part to a partnership between John Deere and our Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Growing food sustainably requires smart technology - our GPS correction algorithms help self-driving tractors steer with precision, cutting down on water and fertilizer waste.
3. Turning Smartphones into Satellites

On Earth Day (and every day), we get nonstop "Earth selfies" thanks to Planet Labs' small satellites, inspired by smartphones and created by a team at our Ames Research Center. The high res imagery helps conservation efforts worldwide.
4. Early Flood Warnings

Monsoons, perhaps the least understood and most erratic weather pattern in the United States, bring rain vital to agriculture and ecosystems, but also threaten lives and property. Severe flash-flooding is common. Roads are washed out. Miles away from the cloudburst, dry gulches become raging torrents in seconds. The storms are often accompanied by driving winds, hail and barrages of lightning.
We are working to get better forecasting information to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Our satellites can track moisture in the air - helping forecasters provide an early warning of flash floods from monsoons.
5. Watching the World's Water

Around the world, agriculture is by far the biggest user of freshwater. Thanks in part to infrared imagery from Landsat, operated by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), we can now map, in real time, how much water a field is using, helping conserve that precious resource.
We use the vantage point of space to understand and explore our home planet, improve lives and safeguard our future. Our observations of Earth’s complex natural environment are critical to understanding how our planet’s natural resources and climate are changing now and could change in the future.
Join the celebration online by using #NASA4Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 jamieroxxartist reblogged this · 1 year ago
jamieroxxartist reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 squeackygee reblogged this · 1 year ago
squeackygee reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 squeackygee reblogged this · 1 year ago
squeackygee reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 squeackygee liked this · 1 year ago
squeackygee liked this · 1 year ago -
 thomasswift85 liked this · 2 years ago
thomasswift85 liked this · 2 years ago -
 datmoongamer reblogged this · 5 years ago
datmoongamer reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 datmoongamer liked this · 5 years ago
datmoongamer liked this · 5 years ago -
 iamthecutestofborg liked this · 5 years ago
iamthecutestofborg liked this · 5 years ago -
 jamieroxxartist reblogged this · 5 years ago
jamieroxxartist reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 youmightbeanidiotif liked this · 5 years ago
youmightbeanidiotif liked this · 5 years ago -
 norestforthemildlywicked reblogged this · 5 years ago
norestforthemildlywicked reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 remarkablylizzy reblogged this · 5 years ago
remarkablylizzy reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 iphleandro-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
iphleandro-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 behindxblueeyes liked this · 7 years ago
behindxblueeyes liked this · 7 years ago -
 timallenphoto liked this · 7 years ago
timallenphoto liked this · 7 years ago -
 trappist-1g reblogged this · 8 years ago
trappist-1g reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 lonamatatastudies-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
lonamatatastudies-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 oafdaaaaaaam liked this · 8 years ago
oafdaaaaaaam liked this · 8 years ago -
 closeyoureyesthereisnogravity liked this · 8 years ago
closeyoureyesthereisnogravity liked this · 8 years ago -
 aj-xii liked this · 8 years ago
aj-xii liked this · 8 years ago -
 harryhumble liked this · 8 years ago
harryhumble liked this · 8 years ago -
 march2206-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
march2206-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 pixiekitten-blog1 reblogged this · 8 years ago
pixiekitten-blog1 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 yenpham24-blog liked this · 8 years ago
yenpham24-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 wolfsheart-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
wolfsheart-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 coldtidalwavecreator reblogged this · 8 years ago
coldtidalwavecreator reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 grandcrusadenightmare reblogged this · 9 years ago
grandcrusadenightmare reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 s-castillo reblogged this · 9 years ago
s-castillo reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 safouane-reus liked this · 9 years ago
safouane-reus liked this · 9 years ago -
 jsbustaman liked this · 9 years ago
jsbustaman liked this · 9 years ago -
 rubinaambrosina reblogged this · 9 years ago
rubinaambrosina reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 rubinaambrosina liked this · 9 years ago
rubinaambrosina liked this · 9 years ago -
 callofdementia reblogged this · 9 years ago
callofdementia reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 hell-noooo liked this · 9 years ago
hell-noooo liked this · 9 years ago -
 sweet-pee reblogged this · 9 years ago
sweet-pee reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 aqu1l4-blog liked this · 9 years ago
aqu1l4-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 vbnzx liked this · 9 years ago
vbnzx liked this · 9 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts