Hi Jeanette, I Want Ask You Wich Was Your First Employment? Have A Good Day
Hi Jeanette, I want ask you wich was your first employment? Have a good day
I was 14 years old, and I worked at United Way doing data entry. They were going from the card files to all digital, and I could only work in the summer.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
A Beginner’s Guide to Advanced Air Mobility

Soaring over traffic in an air taxi, receiving packages faster, and participating in a sustainable, safer mode of transportation: all could be possible with a revolutionary new type of air transportation system in development called Advanced Air Mobility (AAM).
AAM could include new aircraft developed by industry, called electric vertical takeoff and landing vehicles, or eVTOLs, for use in passenger, package, or cargo delivery. It may also include new places for these aircraft to take off and land called vertiports.
Our work in Advanced Air Mobility will transform the way people and goods will move through the skies. This includes using Advanced Air Mobility for public good missions such as disaster, medical, and wildfire response.
What is Advanced Air Mobility?
Our vision for Advanced Air Mobility is to map out a safe, accessible, and affordable new air transportation system alongside industry, community partners, and the Federal Aviation Administration.

Once developed, passengers and cargo will travel on-demand in innovative, automated aircraft called eVTOLs, across town, between neighboring cities, or to other locations typically accessed today by car.
What are the benefits of Advanced Air Mobility?
The addition of Advanced Air Mobility will benefit the public in several ways: easier access for travelers between rural, suburban, and urban communities; rapid package delivery; reduced commute times; disaster response, and new solutions for medical transport of passengers and supplies.

What are the challenges associated with Advanced Air Mobility?
Various NASA simulation and flight testing efforts will study noise, automation, safety, vertiports, airspace development and operations, infrastructure, and ride quality, along with other focus areas like community integration.
These areas all need to be further researched before Advanced Air Mobility could be integrated into our skies. We’re helping emerging aviation markets navigate the creation of this new transportation system.
When will Advanced Air Mobility take off?
We provide various test results to the FAA to help with new policy and standards creation. We aim to give industry and the FAA recommendations for requirements to build a scalable Advanced Air Mobility system to help enable the industry to flourish by 2030.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Record Number of Americans Apply to #BeAnAstronaut

On Dec. 14, 2015, we announced that astronaut applications were open on USAJOBS. The window for applications closed on Feb. 18. We’re happy to announce that we have received more than 18,300 applications from excited individuals from around the country, all hoping to join the 2017 astronaut class. This surpasses the more than 6,100 received in 2012 for the most recent astronaut class, and the previous record - 8,000 applicants in 1978.

So you applied to be an astronaut...now what?
Since the applications closed on Feb. 18, many people are curious to know…what’s next? Let us help you navigate the selection process:

Now that we have received all the applications, we will review them to determine the “Highly Qualified” applicants. This process will take place through summer 2016.
What is a “Highly Qualified” Applicant?
The diversity of experiences is what separates the highly qualified from qualified. Experience that demonstrates good leadership, fellowship and decision making are beneficial.
Between fall 2016 and spring 2017, interviewees will be brought to Johnson Space Center for evaluation. This process will help us determine the finalists, which takes place in spring 2017.
Finally, in summer 2017, the Astronaut Candidate Class of 2017 is announced! These candidates will report to Johnson Space Center starting in August 2017.
To view the full astronaut candidate selection process timeline, visit: http://astronauts.nasa.gov/content/timeline.htm
*Note that the high volume of applications received, dates in the timeline could be adjusted.
Why do we need more astronauts?

We are continuing human spaceflight on the International Space Station, which has a continuous crew of six people on board. The Boeing and SpaceX commercial crew spacecraft that will travel to the station both have seats for four astronauts (the current Soyuz spacecraft, on which astronauts travel, only has three). This will add a seventh astronaut to the orbiting laboratory, and enable us to do more science!
How many astronauts will be selected?
The exact number will be determined by mission requirements, but current analysis shows about 8 - 14 astronauts will be needed. The final number will depend on updates to program plans, budgets, etc.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
World Teacher Appreciation Day!
On #WorldTeachersDay, we are recognizing our two current astronauts who are former classroom teachers, Joe Acaba and Ricky Arnold, as well as honoring teachers everywhere. What better way to celebrate than by learning from teachers who are literally out-of-this-world!
During the past Year of Education on Station, astronauts connected with more than 175,000 students and 40,000 teachers during live Q & A sessions.
Let’s take a look at some of the questions those students asked:
The view from space is supposed to be amazing. Is it really that great and could you explain?
Taking a look at our home planet from the International Space Station is one of the most fascinating things to see! The views and vistas are unforgettable, and you want to take everyone you know to the Cupola (window) to experience this. Want to see what the view is like? Check out earthkam to learn more.
What kind of experiments do you do in space?
There are several experiments that take place on a continuous basis aboard the orbiting laboratory - anything from combustion to life sciences to horticulture. Several organizations around the world have had the opportunity to test their experiments 250 miles off the surface of the Earth.
What is the most overlooked attribute of an astronaut?
If you are a good listener and follower, you can be successful on the space station. As you work with your team, you can rely on each other’s strengths to achieve a common goal. Each astronaut needs to have expeditionary skills to be successful. Check out some of those skills here.
Are you able to grow any plants on the International Space Station?
Nothing excites Serena Auñón-Chancellor more than seeing a living, green plant on the International Space Station. She can’t wait to use some of the lettuce harvest to top her next burger! Learn more about the plants that Serena sees on station here.
What food are you growing on the ISS and which tastes the best?
While aboard the International Space Station, taste buds may not react the same way as they do on earth but the astronauts have access to a variety of snacks and meals. They have also grown 12 variants of lettuce that they have had the opportunity to taste.
Learn more about Joe Acaba, Ricky Arnold, and the Year of Education on Station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Concerning the new telescope -out of curiosity- what is the maximum distance it can view planets, galaxies, objects, anything up to -in terms of common/metric measurement, and/or years (if applicable) etc.? -Rose
Why Sequencing DNA in Space is a Big Deal
... And How You Can Talk to the Scientists Who Made It Happen

Less than one month ago, DNA had never been sequenced in space. As of today, more than one billion base pairs of DNA have been sequenced aboard the International Space Station, Earth’s only orbiting laboratory. The ability to sequence the DNA of living organisms in space opens a whole new world of scientific and medical possibilities. Scientists consider it a game changer.

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins, who has a background in genomics, conducted the sequencing on the space station as part of the Biomolecule Sequencer investigation. A small, commercial, off-the-shelf device called MinION (min-EYE-ON), manufactured by Oxford Nanopore Technologies in the UK, was used to sequence the DNA of bacteria, a virus and rodents. Human DNA was not sequenced, and there are no immediate plans to sequence human DNA in space.

(Image Credit: Oxford Nanopore Technologies)
The MinION is about the size of a candy bar, and plugs into a laptop or tablet via USB connection, which also provides power to the device. The tiny, plug and play sequencer is diminutive compared to the large microwave-sized sequencers used on Earth, and uses much less power. Unlike other terrestrial instruments whose sequencing run times can take days, this device’s data is available in near real time; analysis can begin within 10-15 minutes from the application of the sample.

Having real-time analysis capabilities aboard the space station could allow crews to identify microbes, diagnose infectious disease and collect genomic and genetic data concerning crew health, without having to wait long periods of time to return samples to Earth and await ground-based analysis.
The first DNA sequencing was conducted on Aug. 26, and on Sept. 14, Rubins and the team of scientists back at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston hit the one-billionth-base-pairs-of-DNA-sequenced mark.

Have more questions about how the Biomolecule Sequencer works, or how it could benefit Earth or further space exploration? Ask the team of scientists behind the investigation, who will be available for questions during a Reddit Ask Me Anything on /r/science on Wednesday, Sept. 28 at 2 p.m. EDT.
The participants are:
Dr. Aaron Burton, NASA Johnson Space Center, Planetary Scientist and Principal Investigator
Dr. Sarah Castro-Wallace, NASA Johnson Space Center, Microbiologist and Project Manager
Dr. David J. Smith, NASA Ames Research Center, Microbiologist
Dr. Mark Lupisella, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Systems Engineer
Dr. Jason P. Dworkin, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Astrobiologist
Dr. Christopher E. Mason, Weill Cornell Medicine Dept. of Physiology and Biophysics, Associate Professor
10 “Out of This World" Facts About the James Webb Space Telescope
Wouldn’t it be neat to see a period of the universe’s history that we’ve never seen before? That’s exactly what the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will be able to do…plus more!

Specifically, Webb will see the first objects that formed as the universe cooled down after the Big Bang. We don’t know exactly when the universe made the first stars and galaxies – or how for that matter. That is what we are building Webb to help answer.
Here are 10 awesome facts about this next generation space telescope:
1. The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s largest and next premier space observatory. It will extend the discoveries of the Hubble Space telescope and observe the birthplaces of stars, galaxies, planets and life over billions of years.

2. It is named after James Webb, NASA’s second administrator and champion of our science.

3. At 3 stories high and the size of a tennis court, it will be 100 times more powerful than Hubble!

4. It is so big that it has to fold origami-style to fit in the rocket, which is only 5.4 meters wide...And then it will unfurl, segment by segment, once in space.

5. The telescope will observe infrared light with unprecedented sensitivity. It will see the first galaxies born after the Big Bang over 13.5 billion years ago.

6. Webb's infrared cameras are so sensitive they must be shielded from light from the sun, Earth, and moon. The 5-layer sunshield is like having sunblock of SPF 1 million.

7. Webb will orbit the sun 1 million miles from Earth, where the telescope will operate at temperatures below -390 F (-235 C).

8. Webb’s mirrors are coated with a super thin layer of gold only about 1000 atoms thick to optimize their reflectivity in the infrared.

9. Webb will launch from French Guiana in 2018. It is launched near the equator because the faster spin of Earth there gives the rocket an extra push.

10. Webb is an international mission, with contributions from the European Space Agency and Canadian Space Agency. Once operational, scientists from all over the world will be able to use Webb to explore our solar system, planets outside our solar system, stars and galaxies.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
The California Wildfires from Above
As massive wildfires continue to rage in southern California, our satellites, people in space and aircraft are keeping an eye on the blazes from above.
This data and imagery not only gives us a better view of the activity, but also helps first responders plan their course of action.

A prolonged spell of dry weather primed the area for major fires. The largest of the blazes – the fast-moving Thomas fire in Ventura County – charred more than 65,000 acres.

Powerful Santa Ana winds fanned the flames and forecasters with the LA office of the National Weather Service warned that the region is in the midst of its strongest and longest Santa Ana wind event of the year.
These winds are hot, dry and ferocious. They can whip a small brush fire into a raging inferno in just hours.

Our Aqua satellite captured the above natural-color image on Dec. 5. Actively burning areas are outlined in red. Each hot spot is an area where the thermal detectors on the satellite recognized temperatures higher than the background.

On the same day, the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-2 satellite captured the data for the above false-color image of the burn scar. This image uses observations of visible, shortwave infrared and near infrared light.

From the vantage point of space, our satellites and astronauts are able to see a more comprehensive view of the activity happening on the ground.

The crew living and working 250 miles above Earth on the International Space Station passed over the fires on Dec. 6. The above view was taken by astronaut Randy Bresnik as the station passed over southern California.

During an engineering flight test of our Cloud-Aerosol Multi-Angle Lidar (CAMAL) instrument, a view from our ER-2 high-altitude research aircraft shows smoke plumes. From this vantage point at roughly 65,000 feet, the Thomas Fire was seen as it burned on Dec. 5.

Our satellites can even gather data and imagery of these wildfires at night. The above image on the right shows a nighttime view of the fires on Dec. 5.
For comparison, the image on the left shows what this region looked like the day before. Both images were taken by the Suomi NPP satellite, which saw the fires by using a special “day-night band” to detect light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses light intensification to detect dim signals.

Having the capability to see natural disasters, like these wildfires in southern California, provides first responders with valuable information that helps guide their action in the field.
For more wildfire updates, visit: nasa.gov/fires.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
In recent years of tracking weather activity and the like, have there been more 'anomolies' that have stuck out more than others? (I.E hurricanes, typhoons or cyclones that start out as small storms then become hurricane 4-5 storms in a matter of days-weeks) I think what you guys are doing is awesome and keep up the good work ~TKL
Ten Observations From Our Flying Telescope

SOFIA is a Boeing 747SP aircraft with a 100-inch telescope used to study the solar system and beyond by observing infrared light that can’t reach Earth’s surface.

What is infrared light? It’s light we cannot see with our eyes that is just beyond the red portion of visible light we see in a rainbow. It can be used to change your TV channels, which is how remote controls work, and it can tell us how hot things are.

Everything emits infrared radiation, even really cold objects like ice and newly forming stars! We use infrared light to study the life cycle of stars, the area around black holes, and to analyze the chemical fingerprints of complex molecules in space and in the atmospheres of other planets – including Pluto and Mars.

Above, is the highest-resolution image of the ring of dust and clouds around the back hole at the center of our Milky Way Galaxy. The bright Y-shaped feature is believed to be material falling from the ring into the black hole – which is located where the arms of the Y intersect.

The magnetic field in the galaxy M82 (pictured above) aligns with the dramatic flow of material driven by a burst of star formation. This is helping us learn how star formation shapes magnetic fields of an entire galaxy.

A nearby planetary system around the star Epsilon Eridani, the location of the fictional Babylon 5 space station, is similar to our own: it’s the closest known planetary system around a star like our sun and it also has an asteroid belt adjacent to the orbit of its largest, Jupiter-sized planet.

Observations of a supernova that exploded 10,000 years ago, that revealed it contains enough dust to make 7,000 Earth-sized planets!

Measurements of Pluto’s upper atmosphere, made just two weeks before our New Horizons spacecraft’s Pluto flyby. Combining these observations with those from the spacecraft are helping us understand the dwarf planet’s atmosphere.

A gluttonous star that has eaten the equivalent of 18 Jupiters in the last 80 years, which may change the theory of how stars and planets form.

Molecules like those in your burnt breakfast toast may offer clues to the building blocks of life. Scientists hypothesize that the growth of complex organic molecules like these is one of the steps leading to the emergence of life.

This map of carbon molecules in Orion’s Horsehead nebula (overlaid on an image of the nebula from the Palomar Sky Survey) is helping us understand how the earliest generations of stars formed. Our instruments on SOFIA use 14 detectors simultaneously, letting us make this map faster than ever before!
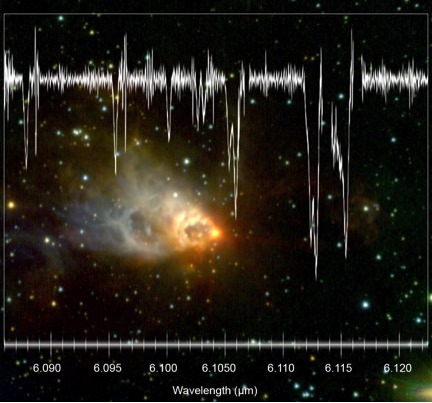
Pinpointing the location of water vapor in a newly forming star with groundbreaking precision. This is expanding our understanding of the distribution of water in the universe and its eventual incorporation into planets. The water vapor data from SOFIA is shown above laid over an image from the Gemini Observatory.

We captured the chemical fingerprints that revealed celestial clouds collapsing to form young stars like our sun. It’s very rare to directly observe this collapse in motion because it happens so quickly. One of the places where the collapse was observed is shown in this image from The Two Micron All Sky Survey.
Learn more by following SOFIA on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Be Glad You Don’t Have to Dust in Space!
Throw open the windows and break out the feather duster, because spring is here and it’s time to do a little cleaning! Fortunately, no one has to tidy up the dust in space — because there’s a lot of it — around 100 tons rain down on Earth alone every day! And there’s even more swirling around the solar system, our Milky Way galaxy, other galaxies and the spaces in between.

By studying the contents of the dust in your house — which can include skin cells, pet fur, furniture fibers, pollen, concrete particles and more — scientists learn a lot about your environment. In the same way, scientists can learn a lot by looking at space dust. Also called cosmic dust, a fleck of space dust is usually smaller than a grain of sand and is made of rock, ice, minerals or organic compounds. Scientists can study cosmic dust to learn about how it formed and how the universe recycles material.

“We are made of star-stuff,” Carl Sagan famously said. And it’s true! When a star dies, it sheds clouds of gas in strong stellar winds or in an explosion called a supernova. As the gas cools, minerals condense. Recent observations by our SOFIA mission suggest that in the wake of a supernova shockwave, dust may form more rapidly than scientists previously thought. These clouds of gas and dust created by the deaths of stars can sprawl across light-years and form new stars — like the Horsehead Nebula pictured above. Disks of dust and gas form around new stars and produce planets, moons, asteroids and comets. Here on Earth, some of that space dust eventually became included in living organisms — like us! Billions of years from now, our Sun will die too. The gas and dust it sheds will be recycled into new stars and planets and so on and so forth, in perpetuity!

Astronomers originally thought dust was a nuisance that got in the way of seeing the objects it surrounded. Dust scatters and absorbs light from stars and emits heat as infrared light. Once we started using infrared telescopes, we began to understand just how important dust is in the universe and how beautiful it can be. The picture of the Andromeda galaxy above was taken in the infrared by our Spitzer Space Telescope and reveals detailed spirals of dust that we can’t see in an optical image.

We also see plenty of dust right here in our solar system. Saturn’s rings are made of mostly ice particles and some dust, but scientists think that dust from meteorites may be darkening the rings over time. Jupiter also has faint dusty rings, although they’re hard to see — Voyager 1 only discovered them when it saw them backlit by the Sun. Astronomers think the rings formed when meteorite impacts on Jupiter’s moons released dust into orbit. The Juno spacecraft took the above picture in 2016 from inside the rings, looking out at the bright star Betelgeuse.

Copyright Josh Calcino, used with permission
And some space dust you can see from right here on Earth! In spring or autumn, right before sunrise or after sunset, you may be able to catch a glimpse of a hazy cone of light above the horizon created when the Sun’s rays are scattered by dust in the inner solar system. You can see an example in the image above, extending from above the tree on the horizon toward a spectacular view of the Milky Way. This phenomenon is called zodiacal light — and the dust that’s reflecting the sunlight probably comes from icy comets. Those comets were created by the same dusty disk that that formed our planets and eventually you and the dust under your couch!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 john-erby liked this · 3 years ago
john-erby liked this · 3 years ago -
 2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago
2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago -
 miniatureillustrationforanime liked this · 4 years ago
miniatureillustrationforanime liked this · 4 years ago -
 cosmofrog liked this · 5 years ago
cosmofrog liked this · 5 years ago -
 mwisteraizwnnkun liked this · 6 years ago
mwisteraizwnnkun liked this · 6 years ago -
 prislydawn liked this · 7 years ago
prislydawn liked this · 7 years ago -
 policebox5issherlocked liked this · 7 years ago
policebox5issherlocked liked this · 7 years ago -
 fridakahloblvd liked this · 7 years ago
fridakahloblvd liked this · 7 years ago -
 timediva liked this · 7 years ago
timediva liked this · 7 years ago -
 neginegiiyahoi liked this · 7 years ago
neginegiiyahoi liked this · 7 years ago -
 bookish-quotes-and-stuff liked this · 7 years ago
bookish-quotes-and-stuff liked this · 7 years ago -
 dirtycreekwater liked this · 7 years ago
dirtycreekwater liked this · 7 years ago -
 iambluetheraptor liked this · 7 years ago
iambluetheraptor liked this · 7 years ago -
 luludii liked this · 7 years ago
luludii liked this · 7 years ago -
 pumpkinsnuffle liked this · 8 years ago
pumpkinsnuffle liked this · 8 years ago -
 charleshdv-blog liked this · 8 years ago
charleshdv-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 punkpistashio-blog liked this · 8 years ago
punkpistashio-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 samurljackson liked this · 8 years ago
samurljackson liked this · 8 years ago -
 galaxystew liked this · 8 years ago
galaxystew liked this · 8 years ago -
 justanoldfashiontumblog liked this · 8 years ago
justanoldfashiontumblog liked this · 8 years ago -
 mega-otaku liked this · 8 years ago
mega-otaku liked this · 8 years ago -
 wandering-mech-engineer liked this · 8 years ago
wandering-mech-engineer liked this · 8 years ago -
 fvillha liked this · 8 years ago
fvillha liked this · 8 years ago -
 babamjan liked this · 8 years ago
babamjan liked this · 8 years ago -
 creamysins liked this · 8 years ago
creamysins liked this · 8 years ago -
 perfectlywiseobservation liked this · 8 years ago
perfectlywiseobservation liked this · 8 years ago -
 heiabel-blog liked this · 8 years ago
heiabel-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 i-need-some-space-man-blog liked this · 8 years ago
i-need-some-space-man-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 sciencenerd4-blog liked this · 8 years ago
sciencenerd4-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 onyxwolf liked this · 8 years ago
onyxwolf liked this · 8 years ago -
 lilytardis12 liked this · 8 years ago
lilytardis12 liked this · 8 years ago -
 humanalienhybrid liked this · 8 years ago
humanalienhybrid liked this · 8 years ago -
 derpy543 liked this · 8 years ago
derpy543 liked this · 8 years ago -
 i-likecoinsandstuff liked this · 8 years ago
i-likecoinsandstuff liked this · 8 years ago -
 thewolfbroughtindoors liked this · 8 years ago
thewolfbroughtindoors liked this · 8 years ago -
 page-vacat liked this · 8 years ago
page-vacat liked this · 8 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts