We Like Big Rockets And We Cannot Lie: Saturn V Vs. SLS
We Like Big Rockets and We Cannot Lie: Saturn V vs. SLS
On this day 50 years ago, human beings embarked on a journey to set foot on another world for the very first time.

At 9:32 a.m. EDT, millions watched as Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins lifted off from Launch Pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, flying high on the most powerful rocket ever built: the mighty Saturn V.

As we prepare to return humans to the lunar surface with our Artemis program, we’re planning to make history again with a similarly unprecedented rocket, the Space Launch System (SLS). The SLS will be our first exploration-class vehicle since the Saturn V took American astronauts to the Moon a decade ago. With its superior lift capability, the SLS will expand our reach into the solar system, allowing astronauts aboard our Orion spacecraft to explore multiple, deep-space destinations including near-Earth asteroids, the Moon and ultimately Mars.

So, how does the Saturn V measure up half a century later? Let’s take a look.
Mission Profiles: From Apollo to Artemis
Saturn V

Every human who has ever stepped foot on the Moon made it there on a Saturn V rocket. The Saturn rockets were the driving force behind our Apollo program that was designed to land humans on the Moon and return them safely back to Earth.

Developed at our Marshall Space Flight Center in the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket (V for the Roman numeral “5”) launched for the first time uncrewed during the Apollo 4 mission on November 9, 1967. One year later, it lifted off for its first crewed mission during Apollo 8. On this mission, astronauts orbited the Moon but did not land. Then, on July 16, 1969, the Apollo 11 mission was the first Saturn V flight to land astronauts on the Moon. In total, this powerful rocket completed 13 successful missions, landing humans on the lunar surface six times before lifting off for the last time in 1973.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Just as the Saturn V was the rocket of the Apollo generation, the Space Launch System will be the driving force behind a new era of spaceflight: the Artemis generation.

During our Artemis missions, SLS will take humanity farther than ever before. It is the vehicle that will return our astronauts to the Moon by 2024, transporting the first woman and the next man to a destination never before explored – the lunar South Pole. Over time, the rocket will evolve into increasingly more powerful configurations to provide the foundation for human exploration beyond Earth’s orbit to deep space destinations, including Mars.
SLS will take flight for the first time during Artemis 1 where it will travel 280,000 miles from Earth – farther into deep space than any spacecraft built for humans has ever ventured.
Size: From Big to BIGGER
Saturn V

The Saturn V was big.
In fact, the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center is one of the largest buildings in the world by volume and was built specifically for assembling the massive rocket. At a height of 363 feet, the Saturn V rocket was about the size of a 36-story building and 60 feet taller than the Statue of Liberty!
Space Launch System (SLS)

Measured at just 41 feet shy of the Saturn V, the initial SLS rocket will stand at a height of 322 feet. Because this rocket will evolve into heavier lift capacities to facilitate crew and cargo missions beyond Earth’s orbit, its size will evolve as well. When the SLS reaches its maximum lift capability, it will stand at a height of 384 feet, making it the tallest rocket in the world.
Power: Turning Up the Heat
Saturn V
For the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket was a beast – to say the least.
Fully fueled for liftoff, the Saturn V weighed 6.2 million pounds and generated 7.6 million pounds of thrust at launch. That is more power than 85 Hoover Dams! This thrust came from five F-1 engines that made up the rocket’s first stage. With this lift capability, the Saturn V had the ability to send 130 tons (about 10 school buses) into low-Earth orbit and about 50 tons (about 4 school buses) to the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Photo of SLS rocket booster test
Unlike the Saturn V, our SLS rocket will evolve over time into increasingly more powerful versions of itself to accommodate missions to the Moon and then beyond to Mars.
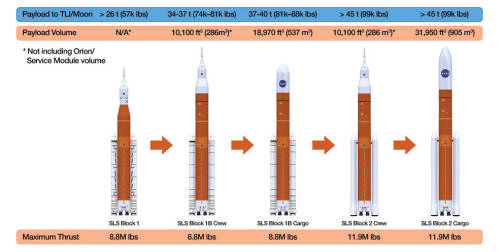
The first SLS vehicle, called Block 1, will weigh 5.75 million pounds and produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust at time of launch. That’s 15 percent more than the Saturn V produced during liftoff! It will also send more than 26 tons beyond the Moon. Powered by a pair of five-segment boosters and four RS-25 engines, the rocket will reach the period of greatest atmospheric force within 90 seconds!

Following Block 1, the SLS will evolve five more times to reach its final stage, Block 2 Cargo. At this stage, the rocket will provide 11.9 million pounds of thrust and will be the workhorse vehicle for sending cargo to the Moon, Mars and other deep space destinations. SLS Block 2 will be designed to lift more than 45 tons to deep space. With its unprecedented power and capabilities, SLS is the only rocket that can send our Orion spacecraft, astronauts and large cargo to the Moon on a single mission.
Build: How the Rockets Stack Up
Saturn V

The Saturn V was designed as a multi-stage system rocket, with three core stages. When one system ran out of fuel, it separated from the spacecraft and the next stage took over. The first stage, which was the most powerful, lifted the rocket off of Earth’s surface to an altitude of 68 kilometers (42 miles). This took only 2 minutes and 47 seconds! The first stage separated, allowing the second stage to fire and carry the rest of the stack almost into orbit. The third stage placed the Apollo spacecraft and service module into Earth orbit and pushed it toward the Moon. After the first two stages separated, they fell into the ocean for recovery. The third stage either stayed in space or crashed into the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)
Much like the Saturn V, our Space Launch System is also a multi-stage rocket. Its three stages (the solid rocket boosters, core stage and upper stage) will each take turns thrusting the spacecraft on its trajectory and separating after each individual stage has exhausted its fuel. In later, more powerful versions of the SLS, the third stage will carry both the Orion crew module and a deep space habitat module.
A New Era of Space Exploration
Just as the Saturn V and Apollo era signified a new age of exploration and technological advancements, the Space Launch System and Artemis missions will bring the United States into a new age of space travel and scientific discovery.
Join us in celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 Moon landing and hear about our future plans to go forward to the Moon and on to Mars by tuning in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Solar System: 10 Things to Know This Week
Need some space?
Here are 10 perspective-building images for your computer desktop and mobile device wallpaper.
These are all real images, sent very recently by our planetary missions throughout the solar system.
1. Our Sun

Warm up with this view from our Solar Dynamics Observatory showing active regions on the Sun in October 2017. They were observed in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light that reveals plasma heated to over a million degrees.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
2. Jupiter Up-Close

This series of enhanced-color images shows Jupiter up close and personal, as our Juno spacecraft performed its eighth flyby of the gas giant planet on Sept. 1, 2017.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
3. Saturn’s and Its Rings

With this mosaic from Oct. 28, 2016, our Cassini spacecraft captured one of its last looks at Saturn and its main rings from a distance.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
4. Gale Crater on Mars

This look from our Curiosity Mars rover includes several geological layers in Gale crater to be examined by the mission, as well as the higher reaches of Mount Sharp beyond. The redder rocks of the foreground are part of the Murray formation. Pale gray rocks in the middle distance of the right half of the image are in the Clay Unit. A band between those terrains is "Vera Rubin Ridge," where the rover is working currently. The view combines six images taken with the rover's Mast Camera (Mastcam) on Jan. 24, 2017.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
5. Sliver of Saturn

Cassini peers toward a sliver of Saturn's sunlit atmosphere while the icy rings stretch across the foreground as a dark band on March 31, 2017. This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 7 degrees below the ring plane.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
6. Dwarf Planet Ceres

This image of the limb of dwarf planet Ceres shows a section of the northern hemisphere, as seen by our Dawn mission. Prominently featured is Occator Crater, home of Ceres' intriguing "bright spots." The latest research suggests that the bright material in this crater is comprised of salts left behind after a briny liquid emerged from below.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
7. Martian Crater

This image from our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows a crater in the region with the most impressive known gully activity in Mars' northern hemisphere. Gullies are active in the winter due to carbon dioxide frost, but northern winters are shorter and warmer than southern winters, so there is less frost and less gully activity.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
8. Dynamic Storm on Jupiter

A dynamic storm at the southern edge of Jupiter's northern polar region dominates this Jovian cloudscape, courtesy of Juno. This storm is a long-lived anticyclonic oval named North North Temperate Little Red Spot 1. Citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran processed this image using data from the JunoCam imager.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
9. Rings Beyond Saturn’s Sunlit Horizon

This false-color view from the Cassini spacecraft gazes toward the rings beyond Saturn's sunlit horizon. Along the limb (the planet's edge) at left can be seen a thin, detached haze.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
10. Saturn’s Ocean-Bearing Moon Enceladus

Saturn's active, ocean-bearing moon Enceladus sinks behind the giant planet in a farewell portrait from Cassini. This view of Enceladus was taken by NASA's Cassini spacecraft on Sept. 13, 2017. It is among the last images Cassini sent back before its mission came to an end on Sept. 15, after nearly 20 years in space.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
Applying Wallpaper: 1. Click on the screen resolution you would like to use. 2. Right-click on the image (control-click on a Mac) and select the option 'Set the Background' or 'Set as Wallpaper' (or similar).
Places to look for more of our pictures include solarsystem.nasa.gov/galleries, images.nasa.gov and www.jpl.nasa.gov/spaceimages.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Rare Full Moon on Christmas Day
Not since 1977 has a full moon dawned in the skies on Christmas. But this year, a bright full moon will be an added gift for the holidays.

This full moon, the last of the year, is called the Full Cold Moon because it occurs during the beginning of winter.
Make sure you get outside to check out this rare event because it won’t happen again until 2034!

Here are a few fun facts about the event and our moon:
The moon’s peak this year will occur at 6:11 a.m. EST
As you gaze up at the Christmas moon, take note that we have a spacecraft currently orbiting Earth’s moon. Our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) mission has been investigating the lunar surface since 2009
More than 100 spacecraft have been launched to explore the moon
Our moon is the only celestial body beyond Earth that has been visited by human beings..so far!
Twelve human beings have walked on the surface of the moon
The moon makes a complete orbit around Earth in 27 Earth days and rotates or spins at the same rate. This causes the moon to keep the same side, or face, towards Earth during the course of its orbit
The moon is the brightest and largest feature in the night sky. Venus is second
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
People of OSIRIS-REx
As OSIRIS-REx closes in on its target destination—asteroid Bennu—anticipation is building for the first-ever, close-up glimpse of this small world. It took thousands of people to come this far. Get to know a few members of the team:

1. Carl Hergenrother, Astronomy Working Group Lead & Strategic and Tactical Scientist
Job Location: University of Arizona, Tucson Expertise: Asteroids & Comets Time on mission: Since before there was a mission Age: 45 Hometown: Oakland, New Jersey
“When you’re observing Bennu with a telescope, you see it as a dot. … So when it actually becomes its own little world, it’s really exciting—and almost a little sad. Up until that point, it can be anything. And now, there it is and that’s it.”

2. Heather Roper, Graphic Designer
Job Location: University of Arizona, Tucson Job Title: Graphic Designer Expertise: Visual Communications Time on mission: 5 years Age: 25 Hometown: Tucson, Arizona
“I really like the challenge of visually depicting the science of the mission and getting to show people things that we can’t see.”

3. Jason Dworkin, Project Scientist
Job Location: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland Expertise: Origin-of-life Chemistry Time on mission: Since before there was a mission Age: 49 Hometown: Houston, Texas
"In 10th grade, I had to do a science fair project for biology class. … I wanted to expand on chemistry experiments from old journal papers; but that could have been dangerous. I got in touch with … a pioneering scientist in origin-of-life research and asked for advice. He was worried that I would accidentally injure myself, so he invited me into his lab . . . that helped set my career.”

4. Sara Balram Knutson, Science Operations Lead Engineer
Job Location: University of Arizona, Tucson Expertise: Aerospace Engineering Time on mission: 6 years Age: 31 Hometown: Vacaville, California
“My dad was in the Air Force, so I grew up being a bit of an airplane nerd. When I was in high school, I really liked math, science, and anything having to do with flight. I looked for a field where I could combine all those interests and I found aerospace engineering.”

5. Nancy Neal Jones, Public Affairs Lead
Job Location: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland Expertise: Science Communications Time on mission: 7 years Age: 51 Hometown: New York, New York
“We’re going to a pristine asteroid to take a sample to bring to Earth. This means that my children and grandchildren, if they decide to go into the sciences, may have an opportunity analyze the Bennu samples.”

6. Javier Cerna, Communications System Engineer
Job Location: Lockheed Martin Corporation, Littleton, Colorado Expertise: Electrical Engineering Time on mission: Since before there was a mission Age: 37 Hometown: Born in Mexico City, and raised in Los Angeles, and Las Cruces, New Mexico
“One thing we do is evaluate how strong the signal from the spacecraft is—kind of like checking the strength of the WiFi connection. Basically, we’re ensuring that the link from the spacecraft to the ground, and vice versa, stays strong.”

7. Jamie Moore, Contamination Control Engineer
Job Location: Lockheed Martin Corporation, Littleton, Colorado Expertise: Chemistry Time on mission: 5 years Age: 32 Hometown: Apple Valley, Minnesota & Orlando, Florida
“I was there for just about every deployment of the sampling hardware to make sure it was kept clean and to evaluate the tools engineers were using. I even went to Florida with the spacecraft to make sure it stayed clean until launch.”

8. Mike Moreau, Flight Dynamics System Manager
Job Location: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland; Littleton, Colorado Expertise: Mechanical and aerospace engineering Time on mission: 5 years Age: 47 Hometown: Swanton, Vermont
“I grew up on a dairy farm in Vermont, which is a world away from working for NASA. But I can trace a lot of my success as an engineer and a leader back to things that I learned on my dad’s farm.”

9. Johnna L. McDaniel, Contamination Control Specialist
Job Location: NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, Florida Expertise: Anti-Contamination Cleaning Time on Mission: 4 months Age: 53 Hometown: Cocoa, Florida
“The clothing requirements depend on the payload. With OSIRIS-Rex, we could not wear any items made with nylon. This was because they have amino acid-based polymers in them and would have contaminated the spacecraft. I even had a special bucket for mopping.”

10. Annie Hasten, Senior Financial Analyst
Job Location: Lockheed Martin Corporation, Steamboat Springs, Colorado Expertise: Business Time on Mission: 1.5 years Age: 30 Hometown: Littleton, Colorado
“I think it’s a pleasure to work with people who are so intensely passionate about their jobs. These engineers are doing their dream jobs, so you feed off of that positive energy.”
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Small Tissue Chips in Space a Big Leap Forward for Research
Tissue chips, thumb-drive sized devices that contain human cells in a 3D matrix, represent a giant leap in science.
They can test cells’ response to:
•stresses
•drugs
•genetic changes

The Tissue Chips in Space initiative seeks to better understand the role of microgravity on human health and disease and to translate that understanding to improved human health on Earth.
This series of investigations to test tissue chips in microgravity aboard the International Space Station is planned through a collaboration between the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) at the National Institutes for Health (NIH) and the National Laboratory in partnership with NASA.

Many of the changes in the human body caused by microgravity resemble the onset and progression of diseases associated with aging on Earth, but in space, changes occur much faster. Scientists may be able to use tissue chips in space to model changes that take months or years to happen on Earth.
A tissue chip needs three properties, according to Lucie Low, scientific program manager at NCATS. “It has to be 3D,” she explained. “It must have multiple different types of cells, and it must have microfluidic channels. Essentially, you get a functional unit of what human tissues are like, outside of the body,” said Low.

As accurate models of the structure and function of human organs, tissue chips provide a model for predicting whether a drug, vaccine or biologic agent is safe in humans more quickly and effectively than current methods.

This first phase of Tissue Chips in Space includes five investigations. An investigation of immune system aging is planned for launch on the SpaceX CRS-16 flight, scheduled for mid-November. The other four, scheduled to launch on subsequent flights, include lung host defense, the blood-brain barrier, musculoskeletal disease and kidney function. This phase tests the effects of microgravity on the tissue chips and demonstrates the capability of the automated system.
All five investigations make a second flight about 18 months later to confirm use of the model, such as testing potential drugs on the particular organs. Four more projects are scheduled for launch in summer 2020, including two on engineered heart tissue to understand cardiovascular health, one on muscle wasting and another on gut inflammation.
Ultimately, the technology could allow astronauts going into space to take along personalized chips that could be used to monitor changes in their bodies and to test possible countermeasures and therapies. That would be a major leap forward in keeping astronauts healthy on missions to deep space!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Why Isn’t Every Year the Warmest Year on Record?
This just in: 2022 effectively tied for the fifth warmest year since 1880, when our record starts. Here at NASA, we work with our partners at NOAA to track temperatures across Earth’s entire surface, to keep a global record of how our planet is changing.
Overall, Earth is getting hotter.

The warming comes directly from human activities – specifically, the release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels. We started burning fossil fuels in earnest during the Industrial Revolution. Activities like driving cars and operating factories continue to release greenhouse gases into our atmosphere, where they trap heat in the atmosphere.

So…if we’re causing Earth to warm, why isn’t every year the hottest year on record?
As 2022 shows, the current global warming isn’t uniform. Every single year isn’t necessarily warmer than every previous year, but it is generally warmer than most of the preceding years. There’s a warming trend.
Earth is a really complex system, with various climate patterns, solar activity, and events like volcanic eruptions that can tip things slightly warmer or cooler.
Climate Patterns
While 2021 and 2022 continued a global trend of warming, they were both a little cooler than 2020, largely because of a natural phenomenon known as La Niña.
La Niña is one third of a climate phenomenon called El Niño Southern Oscillation, also known as ENSO, which can have significant effects around the globe. During La Niña years, ocean temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean cool off slightly. La Niña’s twin, El Niño brings warmer temperatures to the central and eastern Pacific. Neutral years bring ocean temperatures in the region closer to the average.

El Niño and La Niña affect more than ocean temperatures – they can bring changes to rainfall patterns, hurricane frequency, and global average temperature.
We’ve been in a La Niña mode the last three, which has slightly cooled global temperatures. That’s one big reason 2021 and 2022 were cooler than 2020 – which was an El Niño year.
Overall warming is still happening. Current El Niño years are warmer than previous El Niño years, and the same goes for La Niña years. In fact, enough overall warming has occurred that most current La Niña years are warmer than most previous El Niño years. This year was the warmest La Niña year on record.

Solar Activity
Our Sun cycles through periods of more and less activity, on a schedule of about every 11 years. Here on Earth, we might receive slightly less energy — heat — from the Sun during quieter periods and slightly more during active periods.

At NASA, we work with NOAA to track the solar cycle. We kicked off a new one – Solar Cycle 25 – after solar minimum in December 2019. Since then, solar activity has been slightly ramping up.
Because we closely track solar activity, we know that over the past several decades, solar activity hasn't been on the rise, while greenhouse gases have. More importantly, the "fingerprints" we see on the climate, including temperature changes in the upper atmosphere, don't fit the what we'd expect from solar-caused warming. Rather they look like what we expect from increased greenhouse warming, verifying a prediction made decades ago by NASA.
Volcanic Eruptions
Throughout history, volcanoes have driven major shifts in Earth’s climate. Large eruptions can release water vapor — a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide — which traps additional warmth within our atmosphere.
On the flip side, eruptions that loft lots of ash and soot into the atmosphere can temporarily cool the climate slightly, by reflecting some sunlight back into space.
Like solar activity, we can monitor volcanic eruptions and tease out their effect on variations in our global temperature.

At the End of the Day, It’s Us
Our satellites, airborne missions, and measurements from the ground give us a comprehensive picture of what’s happening on Earth every day. We also have computer models that can skillfully recreate Earth’s climate.
By combining the two, we can see what would happen to global temperature if all the changes were caused by natural forces, like volcanic eruptions or ENSO. By looking at the fingerprints each of these climate drivers leave in our models, it’s perfectly clear: The current global warming we’re experiencing is caused by humans.
For more information about climate change, visit climate.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
The International Space Station: Apex of International Collaboration
It's National Space Day! To mark the occasion, we're reflecting on the International Space Station, which has been continuously occupied since Nov. 2, 2000. As our orbiting laboratory that enables us to conduct important science off our home planet, the ISS allows researchers from all over the world to put their talents to work on innovative experiments in the microgravity environment. An international partnership of space agencies provides and operates the elements of the ISS. The principals are the space agencies of the United States, Russia, Europe, Japan and Canada. Although each space station partner has distinct agency goals for station research, each partner shares a unified goal to extend the resulting knowledge for the betterment of humanity! Here are 5 fun facts about our about our out-of-this world floating laboratory:
1. The ISS is a unique scientific platform that has enabled more than 3,600 researchers in 106 countries and areas to conduct more than 2,500 experiments in microgravity through February 2018—and the research continues.
2. Astronauts and cosmonauts have conducted more than 205 spacewalks (and counting!) for space station construction, maintenance and repair since December 1998.

3. The station’s orbital path takes it over 90 percent of the Earth’s population, with astronauts taking millions of images of the planet below.
4. Six spaceships can be connected to the space station at once.

5. An international crew of at most six people live and work while traveling at a speed of five miles per second, orbiting Earth about every 90 minutes.
Currently, six humans are living and working on the International Space Station, which orbits 250 miles above our planet at 17,500mph.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
15 Ways the International Space Station is Benefiting Earth
With astronauts living and working aboard the International Space Station, we’re learning a great deal about creating and testing critical systems, maintaining efficient communications and protecting the human body during a deep space mission. While these are critical to our journey to Mars, it is important to also note all the ways in which research conducted and technology tested aboard the orbiting laboratory help us here on Earth.
Here are 15 ways the space station is benefiting life on Earth:
1. Commercializing Low-Earth Orbit

An exciting new commercial pathway is revolutionizing and opening access to space, fostering America’s new space economy in low-Earth orbit. For the first time, the market is expressing what research can and should be done aboard the microgravity laboratory without direct government funding. Our move to purchase commercial cargo resupply and crew transportation to the space station enables U.S. businesses to develop a competitive capability they also can sell as a service to others while freeing our resources for deep space exploration. Private sector participation provides a new model for moving forward in partnership with the government.
2. Supporting Water Purification Efforts Worldwide

Whether in the confines of the International Space Station or a tiny hut village in sub-Saharan Africa, drinkable water is vital for human survival. Unfortunately, many people around the world lack access to clean water. Using technology developed for the space station, at-risk areas can gain access to advanced water filtration and purification systems, making a life-saving difference in these communities. The Water Security Corporation, in collaboration with other organizations, has deployed systems using NASA water-processing technology around the world.
3. Growing High-Quality Protein Crystals

There are more than 100,000 proteins in the human body and as many as 10 billion in nature. Every structure is different, and each protein holds important information related to our health and to the global environment. The perfect environment in which to study these structures is space. Microgravity allows for optimal growth of the unique and complicated crystal structures of proteins leading to the development of medical treatments. An example of a protein that was successfully crystallized in space is hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase (H-PGDS), which may hold the key to developing useful drugs for treating muscular dystrophy. This particular experiment is an example of how understanding a protein’s structure can lead to better drug designs. Further research is ongoing.
4. Bringing Space Station Ultrasound to the Ends of the Earth

Fast, efficient and readily available medical attention is key to survival in a health emergency. For those without medical facilities within easy reach, it can mean the difference between life and death. For astronauts in orbit about 250 miles above Earth aboard the International Space Station, that problem was addressed through the Advanced Diagnostic Ultrasound in Microgravity (ADUM) investigation. Medical care has become more accessible in remote regions by use of small ultrasound units, tele-medicine, and remote guidance techniques, just like those used for people living aboard the space station.
5. Improving Eye Surgery with Space Hardware

Laser surgery to correct eyesight is a common practice, and technology developed for use in space is now commonly used on Earth to track a patient’s eye and precisely direct the laser scalpel. The Eye Tracking Device experiment gave researchers insight into how humans’ frames of reference, balance and the overall control of eye movement are affected by weightlessness. In parallel with its use on the space station, the engineers realized the device had potential for applications on Earth. Tracking the eye’s position without interfering with the surgeon’s work is essential in laser surgery. The space technology proved ideal, and the Eye Tracking Device equipment is now being used in a large proportion of corrective laser surgeries throughout the world.
6. Making Inoperable Tumors Operable with a Robotic Arm

The delicate touch that successfully removed an egg-shaped tumor from Paige Nickason’s brain got a helping hand from a world-renowned arm—a robotic arm, that is. The technology that went into developing neuroArm, the world’s first robot capable of performing surgery inside magnetic resonance machines, was born of the Canadarm (developed in collaboration with engineers at MacDonald, Dettwiler, and Associates, Ltd. [MDA] for the U.S. Space Shuttle Program) as well as Canadarm2 and Dextre, the Canadian Space Agency’s family of space robots performing the heavy lifting and maintenance aboard the International Space Station. Since Nickason’s surgery in 2008, neuroArm has been used in initial clinical experience with 35 patients who were otherwise inoperable.
7. Preventing Bone Loss Through Diet and Exercise

In the early days of the space station, astronauts were losing about one-and-a-half percent of their total bone mass density per month. Researchers discovered an opportunity to identify the mechanisms that control bones at a cellular level. These scientists discovered that high-intensity resistive exercise, dietary supplementation for vitamin D and specific caloric intake can remedy loss of bone mass in space. The research also is applicable to vulnerable populations on Earth, like older adults, and is important for continuous crew member residency aboard the space station and for deep space exploration to an asteroid placed in lunar orbit and on the journey to Mars.
8. Understanding the Mechanisms of Osteoporosis

While most people will never experience life in space, the benefits of studying bone and muscle loss aboard the station has the potential to touch lives here on the ground. Model organisms are non-human species with characteristics that allow them easily to be reproduced and studied in a laboratory. Scientists conducted a study of mice in orbit to understand mechanisms of osteoporosis. This research led to availability of a pharmaceutical on Earth called Prolia® to treat people with osteoporosis, a direct benefit of pharmaceutical companies using the spaceflight opportunity available via the national lab to improve health on Earth.
9. Developing Improved Vaccines

Ground research indicated that certain bacteria, in particular Salmonella, might become more pathogenic (more able to cause disease) during spaceflight. Salmonella infections result in thousands of hospitalizations and hundreds of deaths annually in the United States. While studying them in space, scientists found a pathway for bacterial pathogens to become virulent. Researchers identified the genetic pathway activating in Salmonella bacteria, allowing the increased likelihood to spread in microgravity. This research on the space station led to new studies of microbial vaccine development.
10. Providing Students Opportunities to Conduct Their Own Science in Space

From the YouTube Space Lab competition, the Student Spaceflight Experiments Program, and SPHERES Zero Robotics, space station educational activities inspire more than 43 million students across the globe. These tyFrom the YouTube Space Lab competition, the Student Spaceflight Experiments Program, and SPHERES Zero Robotics, space station educational activities inspire more than 43 million students across the globe. These types of inquiry-based projects allow students to be involved in human space exploration with the goal of stimulating their studies of science, technology, engineering and mathematics. It is understood that when students test a hypothesis on their own or compare work in a lab to what’s going on aboard the space station, they are more motivated towards math and science.
11. Breast Cancer Detection and Treatment Technology

A surgical instrument inspired by the Canadian Space Agency’s heavy-lifting and maneuvering robotic arms on the space station is in clinical trials for use in patients with breast cancer. The Image-Guided Autonomous Robot (IGAR) works inside an MRI machine to help accurately identify the size and location of a tumor. Using IGAR, surgeons also will be able to perform highly dexterous, precise movements during biopsies.
12. Monitoring Water Quality from Space

Though it completed its mission in 2015, the Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean (HICO) was an imaging sensor that helped detect water quality parameters such as water clarity, phytoplankton concentrations, light absorption and the distribution of cyanobacteria. HICO was first designed and built by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory for the Office of Naval Research to assess water quality in the coastal ocean. Researchers at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) took the data from HICO and developed a smartphone application to help determine hazardous concentrations of contaminants in water. With the space station’s regular addition of new instruments to provide a continuous platform for Earth observation, researchers will continue to build proactive environmental protection applications that benefit all life on Earth.
13. Monitoring Natural Disasters from Space

An imaging system aboard the station, ISS SERVIR Environmental Research and Visualization System (ISERV), captured photographs of Earth from space for use in developing countries affected by natural disasters. A broader joint endeavor by NASA and the U.S. Agency for International Development, known as SERVIR, works with developing nations around the world to use satellites for environmental decision-making. Images from orbit can help with rapid response efforts to floods, fires, volcanic eruptions, deforestation, harmful algal blooms and other types of natural events. Since the station passes over more than 90 percent of the Earth’s populated areas every 24 hours, the ISERV system was available to provide imagery to developing nations quickly, collecting up to 1,000 images per day. Though ISERV successfully completed its mission, the space station continues to prove to be a valuable platform for Earth observation during times of disaster.
14. Describing the Behavior of Fluids to Improve Medical Devices

Capillary Flow Experiments (CFE) aboard the space station study the movement of a liquid along surfaces, similar to the way fluid wicks along a paper towel. These investigations produce space-based models that describe fluid behavior in microgravity, which has led to a new medical testing device on Earth. This new device could improve diagnosis of HIV/AIDS in remote areas, thanks in part to knowledge gained from the experiments.
15. Improving Indoor Air Quality

Solutions for growing crops in space now translates to solutions for mold prevention in wine cellars, homes and medical facilities, as well as other industries around the world. NASA is studying crop growth aboard the space station to develop the capability for astronauts to grow their own food as part of the agency’s journey to Mars. Scientists working on this investigation noticed that a buildup of a naturally-occurring plant hormone called ethylene was destroying plants within the confined plant growth chambers. Researchers developed and successfully tested an ethylene removal system in space, called Advanced Astroculture (ADVASC). It helped to keep the plants alive by removing viruses, bacteria and mold from the plant growth chamber. Scientists adapted the ADVASC system for use in air purification. Now this technology is used to prolong the shelf-life of fruits and vegetables in the grocery store, and winemakers are using it in their storage cellars.
For more information on the International Space Station, and regular updates, follow @Space_Station on Twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space:http://nasa.tumblr.com

Today we celebrate the mission that piqued our curiosities, and drove NASA’s perseverance to pursue further exploration of the Red Planet. The Sojourner rover landed on July 4, 1997, after hitching a ride aboard the Mars Pathfinder mission. Its innovative design became the template for future missions. The rover, named after civil rights pioneer Sojourner Truth, outlived its design life 12 times. This panoramic view of Pathfinder's Ares Vallis landing site shows Sojourner rover is the distance. Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
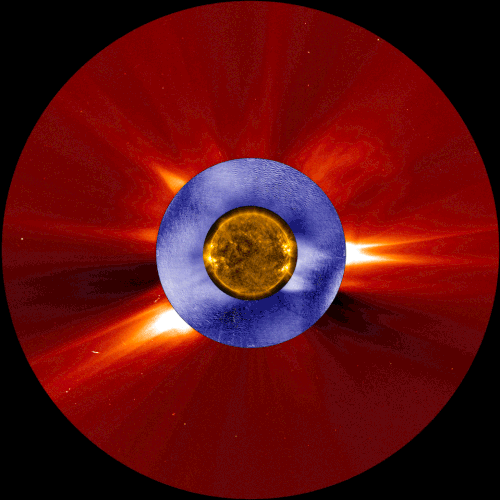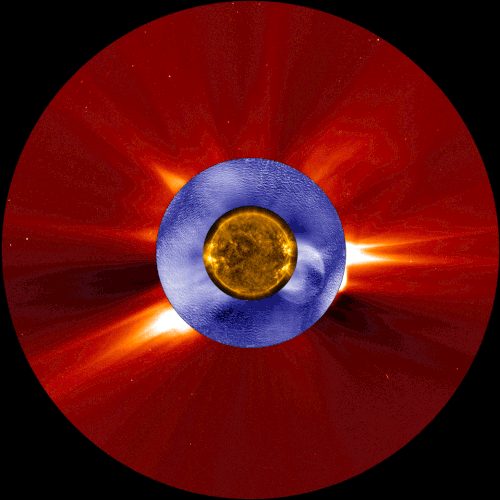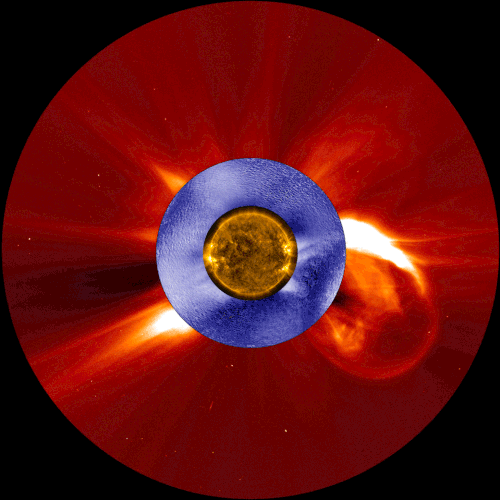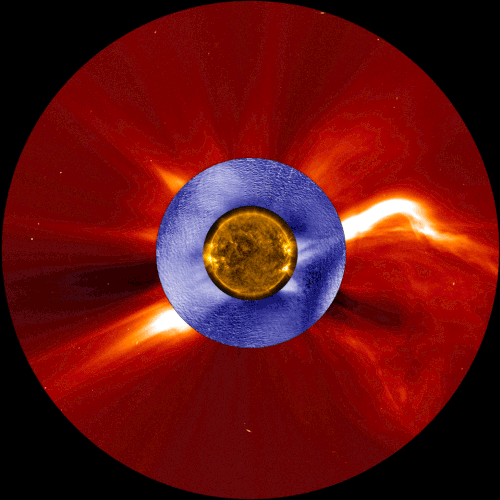
This composite image shows a coronal mass ejection, a type of space weather linked to solar energetic particles, as seen from two space-based solar observatories and one ground-based instrument. The image in gold is from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, the image in blue is from the Manua Loa Solar Observatory’s K-Cor coronagraph, and the image in red is from ESA and NASA’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory.
Our constantly-changing sun sometimes erupts with bursts of light, solar material, or ultra-fast energized particles — collectively, these events contribute to space weather. A new study shows that the warning signs of one type of space weather event can be detected tens of minutes earlier than with current forecasting techniques – critical extra time that could help protect astronauts in space.
Credits: NASA/ESA/SOHO/SDO/Joy Ng and MLSO/K-Cor
-
 temis01 liked this · 1 year ago
temis01 liked this · 1 year ago -
 rocketshipheroes reblogged this · 1 year ago
rocketshipheroes reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 srheault2001 liked this · 1 year ago
srheault2001 liked this · 1 year ago -
 neptuneblueeee liked this · 2 years ago
neptuneblueeee liked this · 2 years ago -
 northernlite liked this · 2 years ago
northernlite liked this · 2 years ago -
 zimiras-wasteland liked this · 2 years ago
zimiras-wasteland liked this · 2 years ago -
 aerospaz reblogged this · 3 years ago
aerospaz reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 aerospaz reblogged this · 3 years ago
aerospaz reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 roboticowboy liked this · 3 years ago
roboticowboy liked this · 3 years ago -
 artemis2021-blog liked this · 3 years ago
artemis2021-blog liked this · 3 years ago -
 highclassassmel liked this · 4 years ago
highclassassmel liked this · 4 years ago -
 lolagonnamakeit liked this · 4 years ago
lolagonnamakeit liked this · 4 years ago -
 vessel-of-horror reblogged this · 4 years ago
vessel-of-horror reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 michaeltoke liked this · 4 years ago
michaeltoke liked this · 4 years ago -
 carrion-aac reblogged this · 4 years ago
carrion-aac reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 carrion-aac liked this · 4 years ago
carrion-aac liked this · 4 years ago -
 olivesnotebook liked this · 4 years ago
olivesnotebook liked this · 4 years ago -
 rolexdpracer liked this · 4 years ago
rolexdpracer liked this · 4 years ago -
 definitelynotacuttlefish liked this · 4 years ago
definitelynotacuttlefish liked this · 4 years ago -
 belles--rose liked this · 4 years ago
belles--rose liked this · 4 years ago -
 dudelthefirst liked this · 4 years ago
dudelthefirst liked this · 4 years ago -
 titania-harbinger liked this · 4 years ago
titania-harbinger liked this · 4 years ago -
 spurdo-sparde-gondola liked this · 4 years ago
spurdo-sparde-gondola liked this · 4 years ago -
 i-have-a-permit liked this · 4 years ago
i-have-a-permit liked this · 4 years ago -
 1dvsbstd74 liked this · 4 years ago
1dvsbstd74 liked this · 4 years ago -
 slytherinqueenatheart liked this · 4 years ago
slytherinqueenatheart liked this · 4 years ago -
 solitudep liked this · 4 years ago
solitudep liked this · 4 years ago -
 greatbear2121 liked this · 4 years ago
greatbear2121 liked this · 4 years ago -
 motherfuckingspaceresearch reblogged this · 5 years ago
motherfuckingspaceresearch reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 motherfuckingspaceresearch reblogged this · 5 years ago
motherfuckingspaceresearch reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 janewilson-rdo liked this · 5 years ago
janewilson-rdo liked this · 5 years ago -
 imagin-trees liked this · 5 years ago
imagin-trees liked this · 5 years ago -
 caffeinatedvampireslayer liked this · 5 years ago
caffeinatedvampireslayer liked this · 5 years ago -
 nailets reblogged this · 5 years ago
nailets reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 zephyr-of-the-south liked this · 5 years ago
zephyr-of-the-south liked this · 5 years ago -
 passkale reblogged this · 5 years ago
passkale reblogged this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts